Mechanical properties of RoadyesTM-modified loess
-
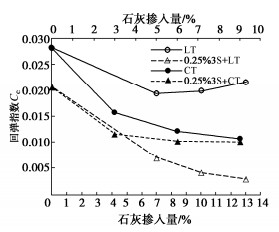
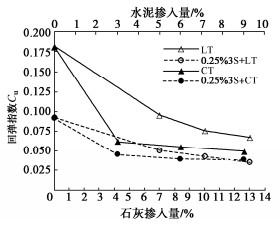
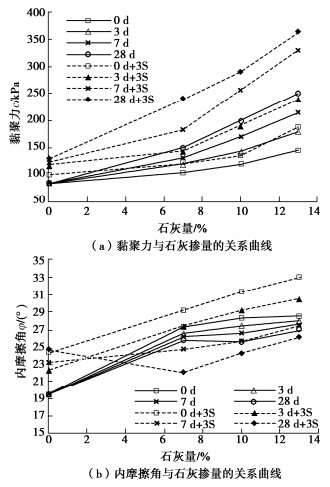
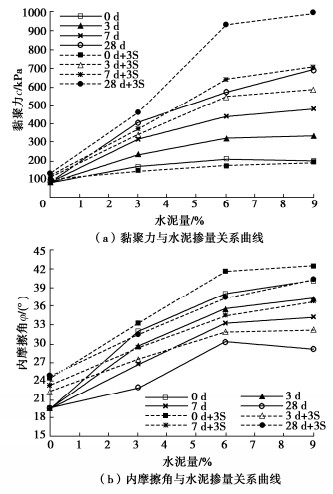
摘要: 黄土具有结构性,难以碾压密实,如何解决黄土压实问题一直是黄土场地地基处理挑战性的技术难题。选取路液(RoadyesTM)固化剂分别结合石灰和水泥对黄土进行不同组合方案下的改性处理研究。通过压缩、三轴剪切试验,研究了添加剂不同组合下改性黄土的压缩和回弹指数及抗剪强度指标差异性。研究结果表明:路液、路液分别结合石灰、水泥改性黄土,发现固化剂并非掺量越大,改性效果越好。综合对比分析后,路液掺量0.25%,并将其分别和7%石灰,3%的水泥组合使用效果最优,改性黄土抗压缩性、抗剪强度指标均远大于未改性黄土,可显著提高重塑黄土的强度指标,并随着养护期延长,改性黄土力学特性向硬脆性发展。研究成果能够为路液结合石灰或水泥改性黄土的应用提供重要的参考。Abstract: The loess is structural and difficult to compact. How to solve the problem of loess compaction has always been a challenging technical problem in treatment of loess site foundation. In this study, the RoadyesTM curing agent combined with lime or cement is used to modify loess under different combinations. Through the compression and triaxial shear tests, the differences of compression and resilience indexes and shear strength indexes of the modified loess with different additive combinations are studied. The results show that for the RoadyesTM-modified loess with lime or cement respectively, the modification effects are not better with the increasing dosage of the curing agent. Among them, the combination scheme of adding 0.25% RoadyesTM and 3% cement is better than the 3% cement-modified loess without RoadyesTM, and it can significantly improve the strength index of the remolded loess. With the extension of the curing period, the modified loess develops towards hard and brittle. The research results may provide important reference for the application of the RoadyesTM-modified loess with lime or cement.
-
Keywords:
- RoadyesTM /
- modified loess /
- compression index /
- rebound index /
- shear strength index
-
-
表 1 黄土基本物理性质指标
Table 1 Basic physical properties of loess
干密度
/(g·cm-3)含水率/
%塑限/
%液限/
%塑性
指数Ip土粒相对质量密度Gs 1.44 17.2 20.1 30.3 10.2 2.70 -
[1] YUAN Z X, WANG L M. Collapsibility and seismic settlement of loess[J]. Engineering Geology, 2010, 105(S1/2): 119-123.
[2] 邓津, 王兰民, 张振中. 黄土显微结构特征与震陷性[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2007, 29(4): 542-548. http://www.cgejournal.com/cn/article/id/12459 DENG Jin, WANG Lanmin, ZHANG Zhenzhong. Microstructure characteristics and seismic subsidence of loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2007, 29(4): 542-548. (in Chinese) http://www.cgejournal.com/cn/article/id/12459
[3] 王谦, 王兰民, 王峻, 等. 基于密度控制理论的饱和黄土地基抗液化处理指标研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(增刊2): 844-847. http://www.cgejournal.com/cn/article/id/15503 WANG Qian, WANG Lanmin, WANG Jun, et al. Indices of anti-liquefaction treatment of saturated compacted loess foundation based on theory of density control[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(S2): 844-847. (in Chinese) http://www.cgejournal.com/cn/article/id/15503
[4] 郭婷婷, 张伯平, 田志高, 等. 黄土二灰土工程特性研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2004, 26(5): 719-721. http://www.cgejournal.com/cn/article/id/11512 GUO Tingting, ZHANG Boping, TIAN Zhigao, et al. Study on engineering characteristic of lime-flyash loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2004, 26(5): 719-721. (in Chinese) http://www.cgejournal.com/cn/article/id/11512
[5] CHEN X, YU F, HONG Z M, et al. Comparative investigation on the curing behavior of GS-stabilized and cemented soils at micromechanical and microstructural scales[J]. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 2022, 50(6): 20200631. doi: 10.1520/JTE20200631
[6] YANG B H, WENG X Z, LIU J Z, et al. Strength characteristics of modified polypropylene fiber and cement-reinforced loess[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(3): 560-568. doi: 10.1007/s11771-017-3458-0
[7] SU X P. Research on the properties of collapsible loess reinforced by cement[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 3441(1015): 110-113.
[8] 王谦, 刘红玫, 马海萍, 等. 水泥改性黄土的抗液化特性与机制[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2016, 38(11): 2128-2134. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201611025 WANG Qian, LIU Hongmei, MA Haiping, et al. Liquefaction behavior and mechanism of cement-stabilized loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(11): 2128-2134. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201611025
[9] NG Qing-wei. A comparative study on shear strength of the fly ash-treated expansive soil and the expansive soil[J]. Building Science, 2011, 2(7): 50-52.
[10] 陈瑞锋, 田高源, 米栋云, 等. 赤泥改性黄土的基本工程性质研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(S1): 89-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2018S1012.htm CHEN Ruifeng, TIAN Gaoyuan, MI Dongyun, et al. Study of basic engineering properties of loess modified by red mud[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(S1): 89-97. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2018S1012.htm
[11] 刘钊钊, 王谦, 钟秀梅, 等. 木质素改良黄土的持水性和水稳性[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(12): 2582-2592. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202012019.htm LIU Zhaozhao, WANG Qian, ZHONG Xiumei, et al. Water holding capacity and water stability of lignin-modified loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(12): 2582-2592. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202012019.htm
[12] 徐菲, 蔡跃波, 钱文勋, 等. 脂肪族离子固化剂改性水泥土的机理研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(9): 1679-1687. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201909012 XU Fei, CAI Yuebo, QIAN Wenxun, et al. Mechanism of cemented soil modified by aliphatic ionic soil stabilizer[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(9): 1679-1687. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201909012
[13] 张耀, 胡再强, 陈昊, 等. 酸性溶液对黄土结构改良的试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2018, 40(4): 681-688. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201804012 ZHANG Yao, HU Zaiqiang, CHEN Hao, et al. Experimental study on evolution of loess structure using acid solutions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(4): 681-688. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201804012
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 廖洁,刘斯宏,徐思远,樊科伟,于博文. 土工袋技术在乡村公路软基加固中的应用研究. 公路. 2024(06): 52-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李钒,林国兵,王雅华,樊科伟. 面板对土工袋挡土墙工作性状影响的足尺试验研究. 水电能源科学. 2023(06): 133-136 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 关帅,孙嘉辉,刘越,王波,黄泽华. 纤维增强复合材料(FRP)锚索性能及其工程应用. 市政技术. 2023(08): 166-179 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 曹旻昊. 淤泥质袋装土挡墙技术研究和应用分析. 现代交通技术. 2023(05): 93-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 文华,杨青青,吴学宇,付文涛. 稳定固化土重力式挡土墙承载特性研究. 施工技术(中英文). 2022(20): 70-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 黄英豪,吴敏,陈永,王硕,王文翀,武亚军. 絮凝技术在疏浚淤泥脱水处治中的研究进展. 水道港口. 2022(06): 802-812 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 中国路基工程学术研究综述·2021. 中国公路学报. 2021(03): 1-49 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: