Penetration behavior of suction bucket foundations in an offshore wind farm
-
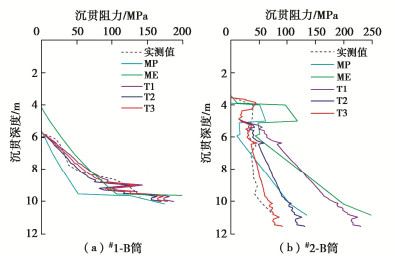
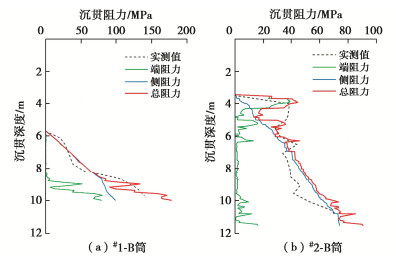
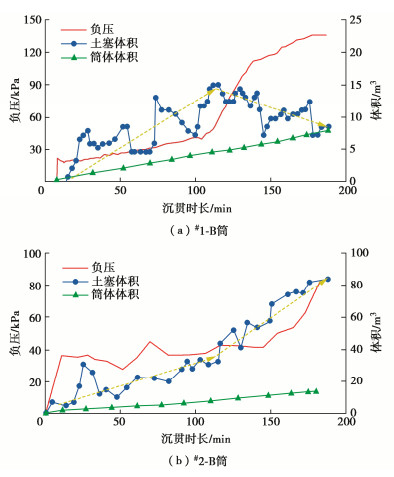
摘要: 吸力筒沉贯特性是影响其工程应用的重要因素。基于海上风电场吸力筒导管架基础筒体下沉过程的实测数据,研究真实海床地基条件下吸力筒沉贯阻力的CPT计算方法的可行性以及DNV规范推荐的土体沉贯阻力的经验系数的适用性,分析黏土层和砂土层中沉贯阻力的组成和负压下沉过程中的筒内土塞机制。研究结果表明:CPT计算方法能够较精确地计算吸力筒沉贯阻力,DNV规范推荐的经验系数高估了海床地基中淤泥质土、粉质黏土层的黏土经验系数kf(z)以及砂砾、中砂、粗砂层等砂土经验系数kp(z);负压下沉过程中,筒内土塞体积的发展规律与海床土层分布及土体物理力学性质密切相关。Abstract: The penetration behavior of suction bucket foundations has a significant effect on engineering application. Based on the measured installation data of two suction bucket jacket foundations in an offshore wind farm, the CPT-based method used for calculating the penetration resistance in seabed and the two critical empirical factors, kp(z) and kf(z), recommended by the DNV code are studied. The component of penetration resistance of suction bucket in clay soil layer and sand soil layer, respectively, and the soil plug during suction penetration process are analyzed. The results show that the penetration resistance of suction bucket can be precisely predicted by the CPT-based method. The empirical factor kf(z) for silty soil, silty clay soil and the empirical factor kp(z) for grit sand, medium-dense sand and coarse sand are overestimated by the DNV code. During suction penetration process, the soil plug of suction bucket foundations relies on the seabed soil layers and mechanical properties of soils.
-
Keywords:
- offshore wind power /
- suction bucket foundation /
- penetration behavior /
- soil plug
-
-
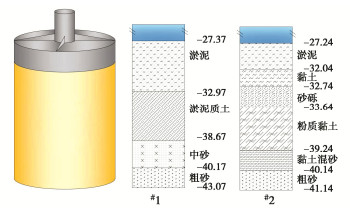
表 1 吸力筒设计参数
Table 1 Parameters of suction buckets
设计参数 筒体外径/m 筒体长度/m 沉贯深度/m 预留间隙/m 筒体壁厚/mm 筒体数量/个 筒体间距/m 筒体重量/t 筒体承受荷载/kN #1 13 10.6 10.1 0.5 45 3 30 241.6 2029.58 #2 12.3 11.3 10.8 0.5 40 3 30 218.7 2052.12 表 2 CPT方法经验系数
Table 2 Empirical factors for CPT method factors
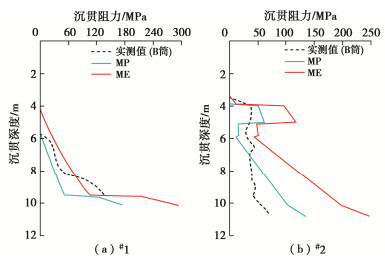
表 3 自重入泥深度预测值
Table 3 Predicted values of self-weight penetration depth
吸力筒 下沉深度/m MP ME #1 6.03 4.63 #2 5.89 5.18 表 4 负压沉贯阻力预测值
Table 4 Predicted values of penetration resistance
吸力筒 沉贯阻力(负压)/kPa MP ME #1 48 99 #2 78 155 表 5 吸力筒实测沉贯结果
Table 5 Measured results of penetration process of suction buckets
吸力筒 自重下沉深度/m 沉贯总深度/m 最大负压值/kPa #1 B筒 5.7 9.67 140 #2 B筒 3.5 10.8 70 表 6 #1机位点土体经验系数取值
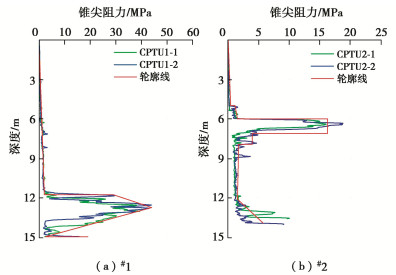
Table 6 Empirical factors of kp(z) and kf(z) for location #1
土层 顶高 底高 T1 T2 T3 m n m n m n 淤泥质土 -5.7 -8.77 1 1 1 0.8 1 0.9 中砂 -8.77 -11.0 0.5 1 0.5 1 0.5 1 表 7 #2机位点土体经验系数取值
Table 7 Empirical factors of kp(z) and kf(z) for location #2
土层 顶高 底高 T1 T2 T3 m n m n m n 砂砾 -3.5 -4.9 0.6 1.5 0.6 1.5 0.6 1.5 粉质黏土 -4.9 -10.9 1 1 1 0.5 1 0.3 粗砂 -10.9 -11.5 0.6 1.5 0.6 1.5 0.6 1.5 -
[1] LIU B, ZHANG Y H, MA Z, ANDERSEN K H, et al. Design considerations of suction caisson foundations for offshore wind turbines in Southern China[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2020, 104: 102358. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2020.102358
[2] HOULSBY G T, BYRNE B W. Design procedures for installation of suction caissons in clay and other materials[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers- Geotechnical Engineering, 2005, 158(2): 75-82. doi: 10.1680/geng.2005.158.2.75
[3] HOULSBY G T, BYRNE B W. Design procedures for installation of suction caissons in sand[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Geotechnical Engineering, 2005, 158(3): 135-144. doi: 10.1680/geng.2005.158.3.135
[4] DNVGL-RP-E303. Geotechnical Design and Installation of Suction Anchors in Clay[S]. 2017.
[5] ANDERSEN K H, JOSTAD H P, DYVIK R. Penetration resistance of offshore skirted foundations and anchors in dense sand[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2008, 134(1): 106-116. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2008)134:1(106)
[6] SENDERS M, RANDOLPH M F. CPT-based method for the installation of suction caissons in sand[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2009, 135(1): 14-25. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2009)135:1(14)
[7] 李大勇, 张雨坤, 高玉峰, 等. 中粗砂中吸力锚的负压沉贯模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2012, 34(12): 2277-2283. http://cge.nhri.cn/cn/article/id/14955 LI Dayong, ZHANG Yukun, GAO Yufeng, et al. Model tests on penetration of suction anchors in medium-coarse sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(12): 2277-2283. (in Chinese) http://cge.nhri.cn/cn/article/id/14955
[8] 李大勇, 吴宇旗, 张雨坤, 等. 砂土中桶形基础吸力值的设定范围[J]. 岩土力学, 2017, 38(4): 985-992, 1002. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201704010.htm LI Dayong, WU Yuqi, ZHANG Yukun, et al. Determination of suction range for penetration of suction caissons in sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(4): 985-992, 1002. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201704010.htm
[9] 李大勇, 侯新宇, 张雨坤, 等. 相对密实度对沉贯中吸力基础桶壁-砂土界面力学特性的影响[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(9): 1598-1607. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202209004 LI Dayong, HOU Xinyu, ZHANG Yukun, et al. Effects of relative densities on mechanical characteristics of interface between sand and suction caisson during penetration[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(9): 1598-1607. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202209004
[10] ZHANG Y, LI D, BAI Y. Experimental studies on suction-assisted installation of the modified suction caisson in dense sand[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2022, 124: 103221. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2022.103221
[11] SENPERE D, AUVERGNE G A. Suction anchor piles-a proven alternative to driving or drilling[C]// Offshore Technology Conference. OnePetro, 1982.
[12] TJELTA T I. Suction piles: their position and application today[C]// The Eleventh International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference. OnePetro, 2001.
[13] API-RP-2SK. Recommended Practice for Design and Analysis of Stationkeeping Systems for Floating Structures[S]. American Petroleum Institute, 2015.
[14] ANDERSEN K H, JEANJEAN P, LUGER D, et al. Centrifuge tests on installation of suction anchors in soft clay[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2005, 32: 845-863. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2004.10.005
[15] ZHOU H, RANDOLPH M F. Large deformation analysis of suction caisson installation in clay[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2006, 43(12): 1344-1357. doi: 10.1139/t06-087
[16] CHEN W, ZHOU H, RANDOLPH M F. Effect of installation method on external shaft friction of caissons in soft clay[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2009, 135(5): 605-615. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000033
[17] 丁红岩, 刘振勇, 陈星. 吸力锚土塞在粉质黏土中形成的模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2001, 23(4): 441-444. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2001.04.012 DING Hongyan, LIU Zhenyong, CHEN Xing. Model tests on soil plug formation in suction anchor for silty clay[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2001, 23(4): 441-444. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2001.04.012
[18] 闫澍旺, 霍知亮, 楚剑, 等. 黏土中桶形基础负压下沉阻力及土塞发展试验[J]. 天津大学学报, 2016, 49(10): 1027-1033. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDX201610004.htm YAN Shuwang, HUO Zhiliang, CHU Jian, et al. Experiment on penetration resistance and soil plug development during suction caisson penetration in soft clay[J]. Journal of Tianjin University, 2016, 49(10): 1027-1033. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDX201610004.htm
[19] DNVGL-RP-C212. Offshore Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering[S]. 2017.
[20] CHEN F, LIAN J J, WANG H J, et al. Large-scale experimental investigation of the installation of suction caissons in silt sand[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2016, 60: 109-120. doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2016.09.004
[21] 王胤, 朱兴运, 杨庆. 考虑砂土渗透性变化的吸力锚沉贯及土塞特性研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(1): 184-190. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201901021 WANG Yin, ZHU Xingyun, YANG Qing. Installation of suction caissons and formation of soil plug considering variation of permeability of sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(1): 184-190. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201901021
-
其他相关附件




 下载:
下载: