Deformation characteristics and shakedown behaviors of frozen silty clay under complex cyclic stress paths
-
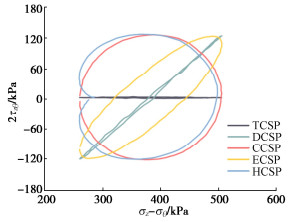
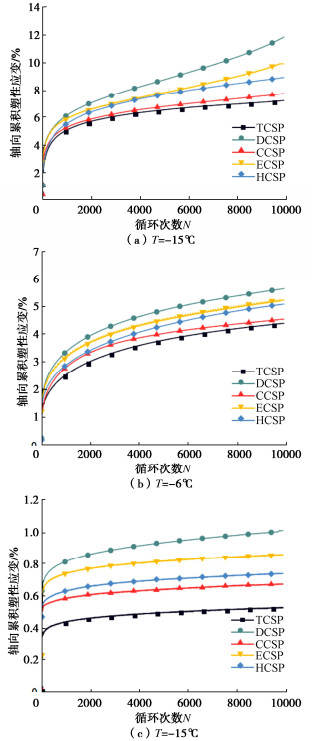
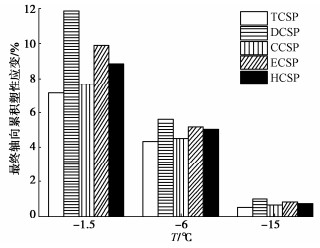
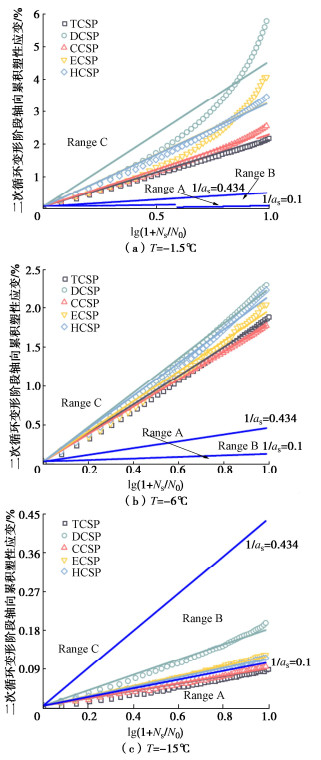
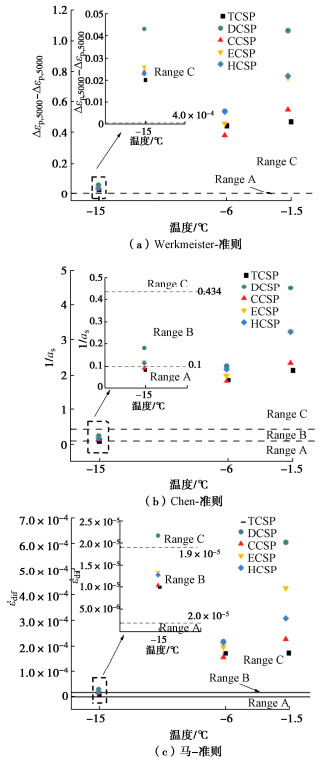
摘要: 复杂循环应力路径下冻土的变形特性与安定性行为研究对寒区工程的长期稳定性具有重要作用。为分析不同复杂循环应力路径对冻土变形特性与安定性行为的影响,设计不同温度同一水平下的5种循环应力路径,即三轴循环应力路径(TCSP)、定向循环应力路径(DCSP)、圆形循环应力路径(CCSP)、椭圆循环应力路径(ECSP)和心形循环应力路径(HCSP),分析了粉质黏土的轴向累积塑性应变,同时利用3种安定性评价准则对结果进行评估。研究结果表明:不同温度5种循环应力路径下的轴向累积塑性应变满足DCSP > ECSP > HCSP > CCSP > TCSP。安定性评价结果表明,定向循环应力路径对土体的安定性行为影响最大,在3种准则下都属于增量破坏。在-15℃时,心形循环应力路径与椭圆循环应力路径试验结果在Chen-准则评估下也属于增量破坏。Abstract: The deformation characteristics and stability behaviors of frozen soil under complex cyclic stress paths play an important role in the long-term stability of cold region engineering. To analyze the influences of different complex cyclic stress paths on the deformation characteristics and shakedown behaviors of frozen soil, five cyclic stress paths are designed at the same level, namely triaxial cyclic stress path (TCSP), directional cyclic stress path (DCSP), circular cyclic stress path (CCSP), elliptical cyclic stress path (ECSP) and heart-shaped cyclic stress path (HCSP). The axial cumulative plastic strains of the samples are analyzed, and the results are evaluated by three shakedown evaluation criteria. The axial cumulative plastic strains under five cyclic stress paths at different temperatures satisfy the following: DCSP > ECSP > HCSP > CCSP > TCSP. The directional cyclic stress path has the greatest influences on the shakedown behaviors of the soil, and the failure belongs to the incremental one under the three criteria. At the temperature of -15℃, the results of the HCSP and ECSP tests also belong to the incremental failure under the evaluation of Chen criterion.
-
-
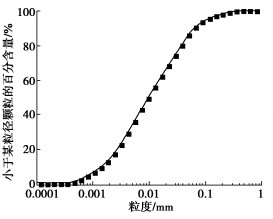
表 1 试验土体基本物理性质
Table 1 Physical properties of test soil
最大干密度ρdmax/(g·cm-3) 最优含水率wopt/% 饱和含水率wsat/% 液限wL/% 塑限wP/% 塑性指数IP 1.84 17.51 20.12 31.17 17.20 13.97 表 2 试验方案
Table 2 Test schemes
试样编号 温度/℃ CSR 应力路径 TN1~5 -1.5 0.875 TCSP, DCSP, CCSP, ECSP, HCSP TN6~10 -6 1.750 TCSP, DCSP, CCSP, ECSP, HCSP TN11~15 -15 1.750 TCSP, DCSP, CCSP, ECSP, HCSP -
[1] NIE R S, LI Y F, LENG W M, et al. Deformation characteristics of fine-grained soil under cyclic loading with intermittence[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2020, 15(11): 3041-3054. doi: 10.1007/s11440-020-00955-3
[2] LIN T S, ISHIKAWA T, MARUYAMA K, et al. Pavement design method in Japan with consideration of climate effect and principal stress axis rotation[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2021, 28: 100552. doi: 10.1016/j.trgeo.2021.100552
[3] WU T Y, JIN H X, GUO L, et al. Predicting method on settlement of soft subgrade soil caused by traffic loading involving principal stress rotation and loading frequency[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2022, 152: 107023. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2021.107023
[4] 董彤, 郑颖人, 孔亮, 等. 考虑主应力轴方向的砂土各向异性强度准则与滑动面研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2018, 40(4): 736-742. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201804024.htm DONG Tong, ZHENG Yingren, KONG Liang, et al. Strength criteria and slipping planes of anisotropic sand considering direction of major principal stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(4): 736-742. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201804024.htm
[5] 陈敦, 马巍, 王大雁, 等. 定向剪切应力路径下冻结黏土变形特性试验[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(7): 2483-2490. CHEN Dun, MA Wei, WANG Dayan, et al. Experimental study of deformation characteristics of frozen clay under directional shear stress path[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(7): 2483-2490. (in Chinese)
[6] 张斌龙, 王大雁, 马巍, 等. 主应力轴旋转条件下冻结黏土累积塑性应变与临界动应力特性研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2023, 45(3): 551-560. doi: 10.11779/CJGE20211149 ZHANG Binlong, WANG Dayan, MA Wei, et al. Characteristics of cumulative plastic strain and critical dynamic stress of frozen clay under principal stress rotation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 45(3): 551-560. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE20211149
[7] QIAN J G, WANG Y G, YIN Z Y, et al. Experimental identification of plastic shakedown behavior of saturated clay subjected to traffic loading with principal stress rotation[J]. Engineering Geology, 2016, 214: 29-42. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.09.012
[8] ZHOU Z W, MA W, LI G Y, et al. A novel evaluation method for accumulative plastic deformation of granular materials subjected to cyclic loading: taking frozen subgrade soil as an example[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2020, 179: 103152. doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions.2020.103152
[9] 王庆志, 周志伟, 张淑娟. 青藏铁路路基粗颗粒填料动力特性和安定性行为研究[J]. 冰川冻土, 2022, 44(2): 566-582. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT202202020.htm WANG Qingzhi, ZHOU Zhiwei, ZHANG Shujuan. Study on dynamic properties and shakedown behaviors of coarse-grained fillers in Qinghai-Tibet Railway subgrade[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2022, 44(2): 566-582. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT202202020.htm
[10] CHEN D, WANG D Y, MA W, et al. A strength criterion for frozen clay considering the influence of stress Lode angle[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2019, 56(11): 1557-1572. doi: 10.1139/cgj-2018-0054
[11] GU F, ZHANG Y Q, LUO X, et al. Characterization and prediction of permanent deformation properties of unbound granular materials for Pavement ME Design[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 155: 584-592. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.08.116
[12] WERKMEISTER S, DAWSON A R, WELLNER F. Pavement design model for unbound granular materials[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2004, 130(5): 665-674. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(2004)130:5(665)
[13] CHEN W B, FENG W Q, YIN J H, et al. Characterization of permanent axial strain of granular materials subjected to cyclic loading based on shakedown theory[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 198: 751-761. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.12.012



 下载:
下载: