Bulging deformation mechanism of asphalt pavement in sulfate saline soil areas of Xinjiang
-
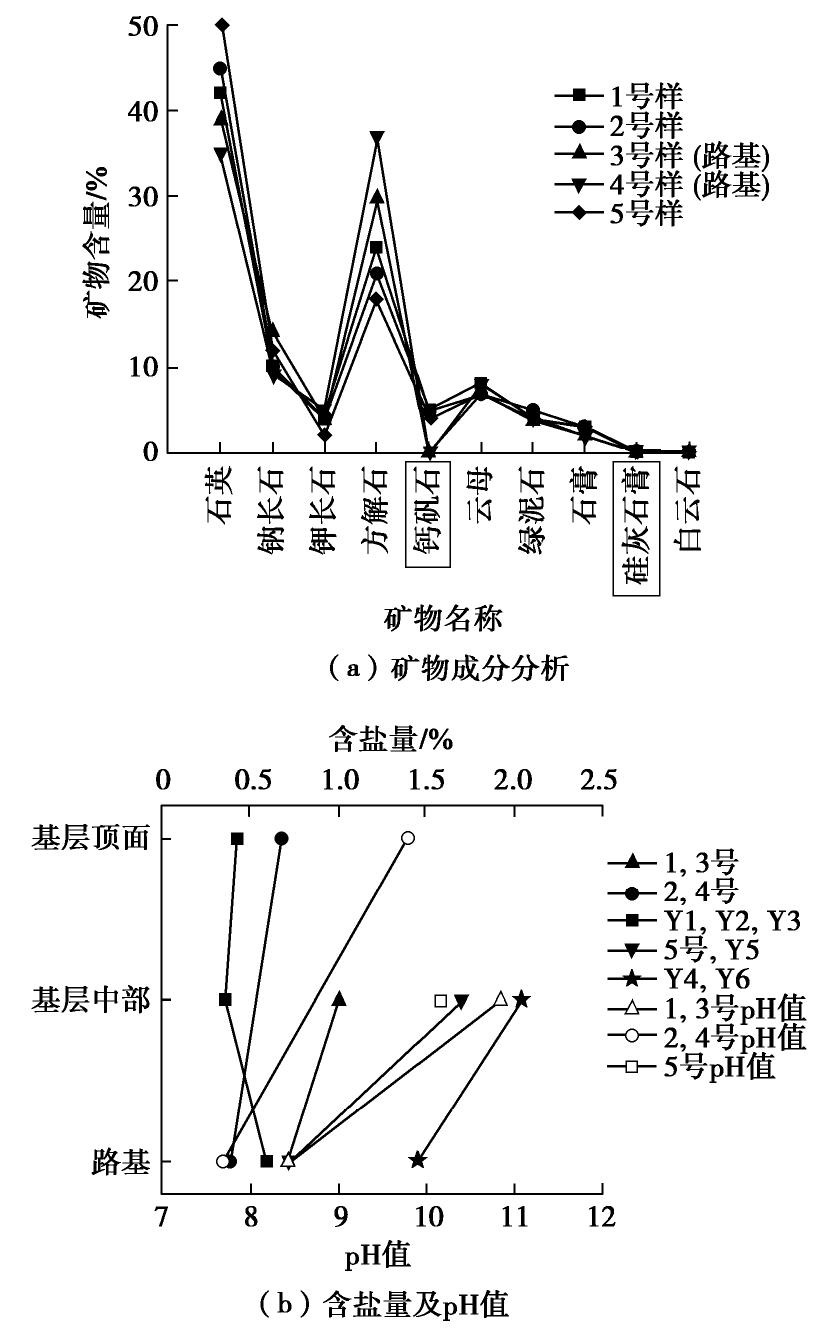
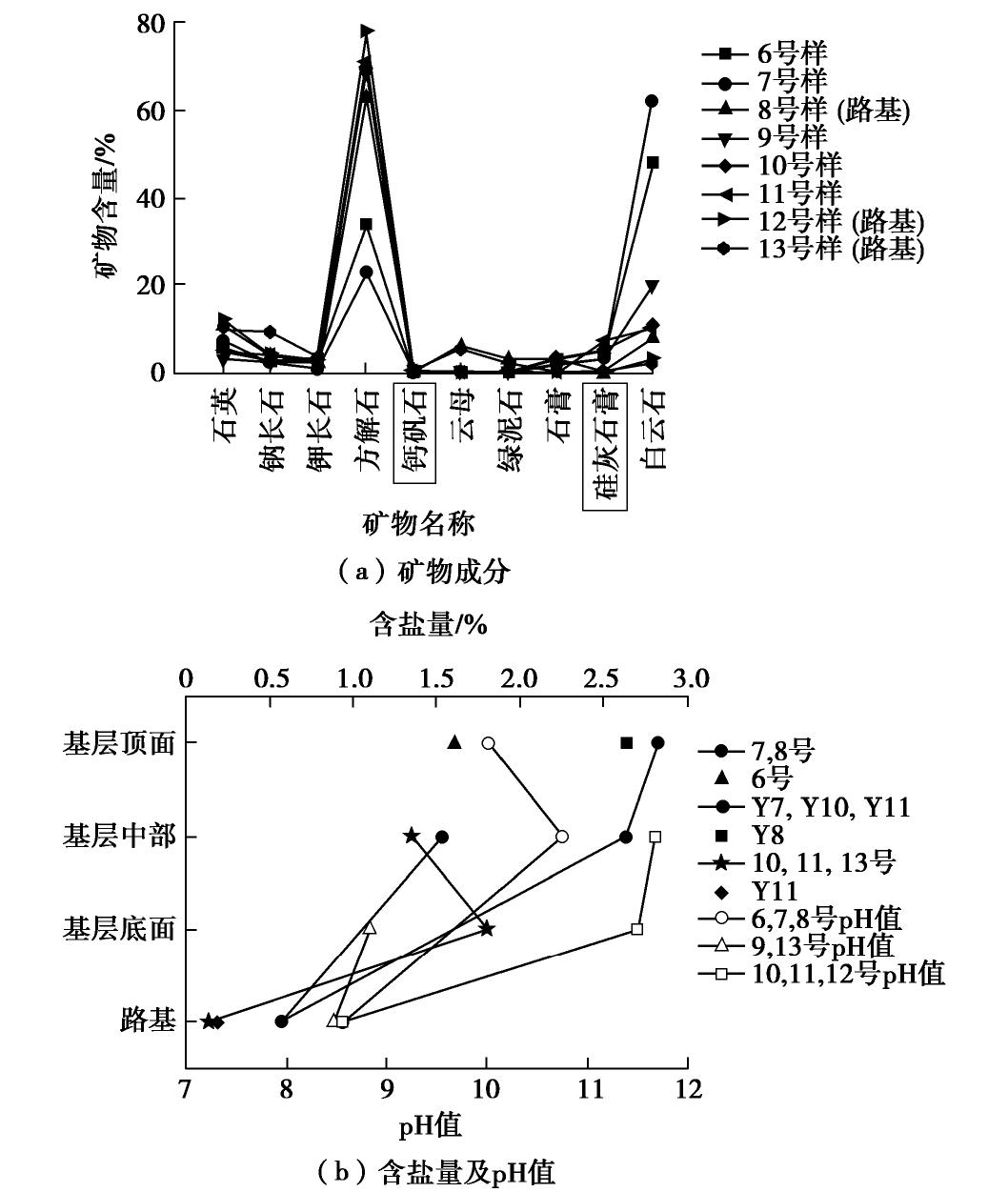
摘要: 依托新疆阿克苏地区的两条公路,在进行公路路面鼓胀病害调查的基础上,选择4个典型病害部位开挖试坑,观察了路面结构层中损坏的情况,同时取样测试了基层及路基填料的含盐量、矿物成分、pH值等,分析了两条公路路面鼓胀病害的产生机理。研究结果表明:公路A(省道)路面基层中的离子以
SO2−4 、Ca2+ 为主,因此发生了钙矾石型硫酸盐侵蚀。公路B(国道)路面基层中Ca2+ 含量较高,同时含有一定量SO2−4 和CO2−3 ,因此发生了硅灰石膏型硫酸盐侵蚀。此外,夏季高温条件、水泥中碱含量超标等都加剧了两种硫酸盐侵蚀的发生。最后,根据两条公路病害产生机理,提出了硫酸盐渍土地区路面鼓胀病害的预防措施。Abstract: Based on two highways in Aksu prefecture of Xinjiang, four typical diseased sections are selected to excavate test pits on the basis of investigating bulging diseases of highways, the damage of structure layer pavement is observed, the salt content, mineral composition and pH value of base and subgrade fill are sampled and tested, and the mechanism of pavement diseases of the two highways is analyzed. The results show that the ions in the base course of Highway A (Provincial Highway) are mainlySO2−4 andCa2+ , so a chemical reaction takes place and Ettringite is formed. The content ofCa2+ in the base course of Highway B (National Highway) is high, and it also contains a certain amount ofSO2−4 andCO2−3 , so a chemical reaction takes place and Wollastonite gypsum is formed. In addition, the high temperature in summer and the alkali content in cement exceed the standard, accelerate the occurrence of two kinds of sulfate erosion. Finally, according to the mechanism of the two highway diseases, the preventive measures for bulging diseases of highways in the sulfate saline soil areas are put forward.-
Keywords:
- sulphate saline soil /
- asphalt pavement /
- semi-rigid base /
- bulging deformation /
- sulfate attack
-
-
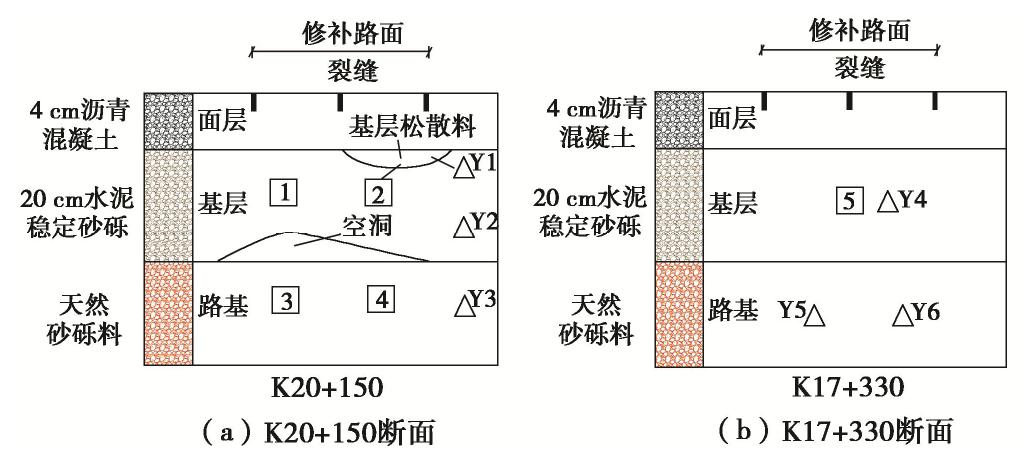
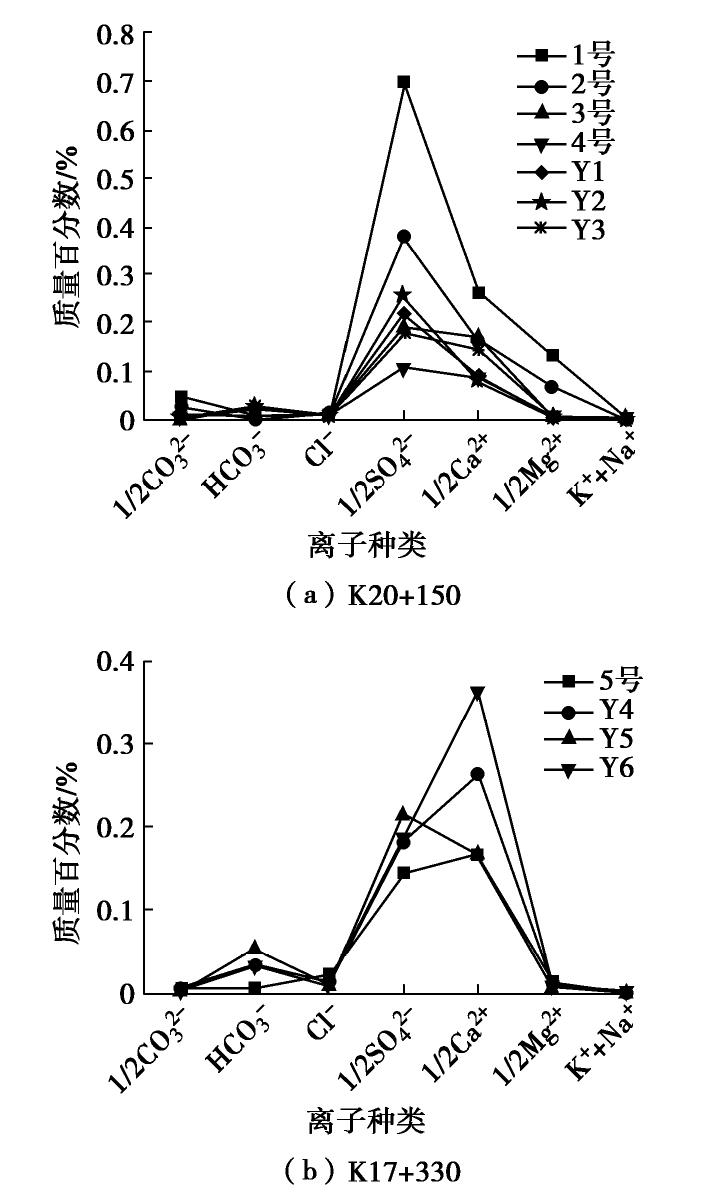
表 1 公路A病害部位含盐量测试结果
Table 1 Test results of salt content in diseased parts of Highway A
取样位置 试样编号 Cl− /SO2−4 含盐量/% 盐渍土名称 K20+150 1 0.018 1.002 硫酸盐中盐渍土 2 0.038 0.677 硫酸盐中盐渍土 3 0.048 0.709 硫酸盐中盐渍土 4 0.103 0.383 硫酸盐中盐渍土 Y1 0.090 0.428 硫酸盐中盐渍土 Y2 0.035 0.355 硫酸盐中盐渍土 Y3 0.061 0.588 硫酸盐中盐渍土 K17+330 5 0.201 1.705 硫酸盐中盐渍土 Y4 0.101 2.041 硫酸盐强盐渍土 Y5 0.067 0.717 硫酸盐中盐渍土 Y6 0.068 1.447 硫酸盐中盐渍土 表 2 公路B病害部位含盐量测试结果
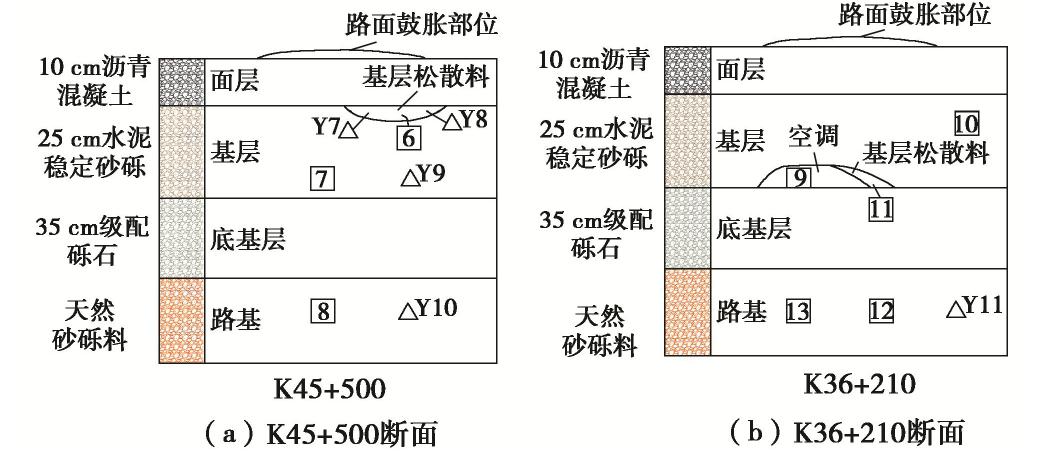
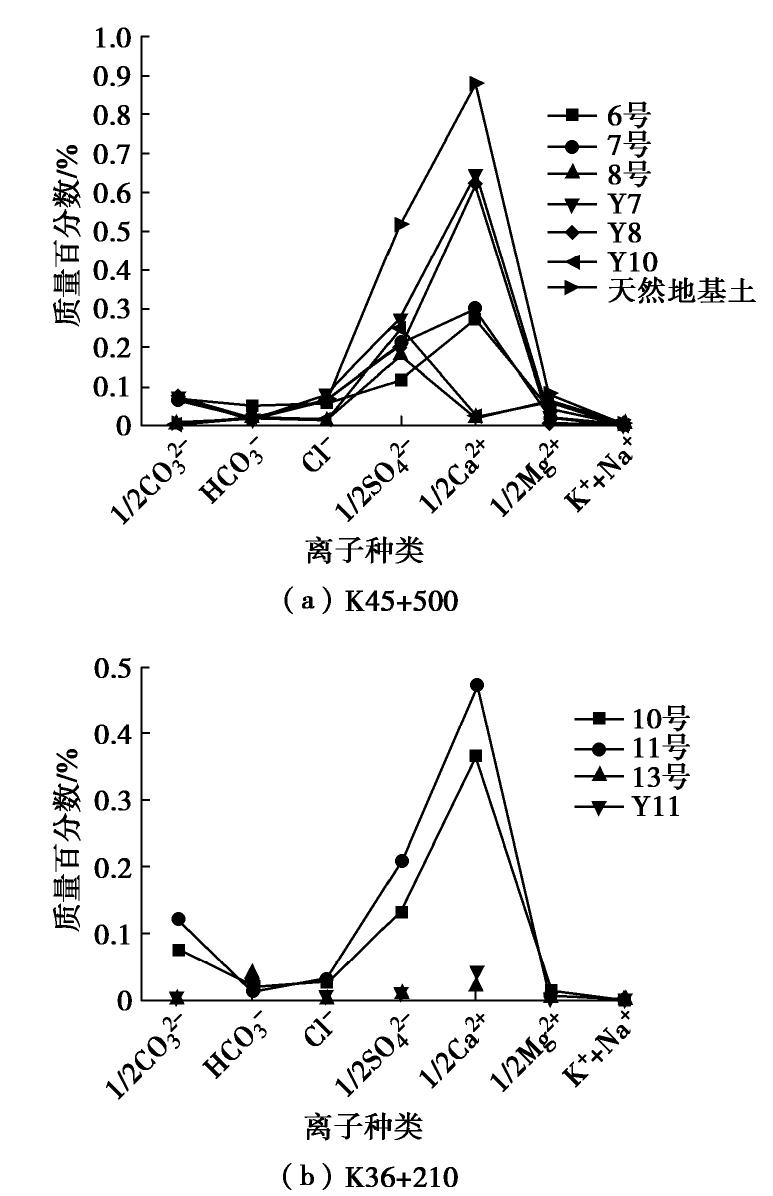
Table 2 Test results of salt content in diseased parts of Highway B
取样位置 试样编号 Cl− /SO2−4 含盐量/% 盐渍土名称 K45+500 6 0.670 1.614 亚硫酸盐中盐渍土 7 0.407 1.533 亚硫酸盐中盐渍土 8 0.111 0.570 硫酸盐中盐渍土 Y7 0.416 2.827 亚硫酸盐强盐渍土 Y8 0.444 2.635 亚硫酸盐强盐渍土 Y9 11.417 2.637 氯盐中盐渍土 Y10 0.095 0.568 硫酸盐中盐渍土 坡脚外原状土 0.181 7.838 硫酸盐过盐渍土 K36+210 10 0.262 1.352 硫酸盐中盐渍土 11 0.209 1.806 硫酸盐中盐渍土 13 0.518 0.135 亚硫酸盐非盐渍土 Y11 0.475 0.184 亚硫酸盐非盐渍土 -
[1] 王军伟. 水泥稳定碎石基层沥青路面拱起开裂研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2017. WANG Jun-wei. Research on Expansion Cracking of Asphalt Pavement by Cement Stabilized Macadam Base[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2017. (in Chinese)
[2] 张海龙. 沙漠区沥青混凝土路面横向隆起成因及力学分析[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2018. ZHANG Hai-long. The Cause and Mechanical Analysis on the Transverse Uplift of Asphalt Concrete Pavement in Desert Area[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2018. (in Chinese)
[3] ROLLINGS R S, BURKES J P, ROLLINGS M P. Sulfate attack on cement-stabilized sand[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2000, 125(5): 364-372.
[4] CHEN D H, HARRIS P, SCULLION T, et al. Forensic investigation of a sulfate-heaved project in Texas[J]. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 2005, 19(4): 324-330. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0887-3828(2005)19:4(324)
[5] DURAN D R. Case study: heave potential associated with ettringite formation in lime treated materials for an Aurora, Colorado, roadway[C]//Biennial Geotechnical Seminar, 2010, Denver.
[6] AMANDA G A, ONDRA M D, WASSIM T, et al. Sulfate induced heave in Oklahoma soils due to lime stabilization[C]//Characterization, Monitoring, and, Modeling of Geosystems, 2008, Geocongress New Orleans.
[7] MCCARTHY M J, CSETENYI L J, SACHDEVA A, et al. Fly ash influences on sulfate heave in lime-stabilised soils[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers, 2012, 165(3): 147-158.
[8] 许刚. 硫酸盐环境下水稳基层的病害分析及防治措施[J]. 山西建筑, 2017, 43(1): 162-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2017.01.085 XU Gang. On disease analysis of moisture base under sulfate environment and its prevention measures[J]. Shanxi Architecture, 2017, 43(1): 162-164. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2017.01.085
[9] 蒲翠玲. 盐渍化半刚性基层材料强度与变形规律研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2008. PU Cui-ling. Study on the Intensity and Law Out of Shape of the Semi-Rigid Matearial Intensity at the Basic Level of Salty Soil[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2008. (in Chinese)
[10] 高江平, 蒲翠玲, 赵永祥, 等. 含硫酸盐的半刚性基层材料干缩性能试验研究[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 42(3): 323-328. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7930.2010.03.004 GAO Jiang-ping, PU Cui-ling, ZHAO Yong-xiang, et al. Experimental study on the dry shrinking performance of the semi-rigid material intensity at the basic level of sulfate salty soil[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology (Nature Science Edition), 2010, 42(3): 323-328. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7930.2010.03.004
[11] 沙爱民, 许永明, 刘文锁, 等. 掺有硫酸钠石灰类稳定土的强度与体积变化[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1998, 20(1): 34-38. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1998.01.009 SHA Ai-min, XU Yong-ming, LIU Wen-suo, et al. Strength and volume change of lime-stabilized soils with sodium sulphate[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1998, 20(1): 34-38. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1998.01.009
[12] 高艳龙, 黄莘, 刘峰. 高含硫粉煤灰对二灰基层膨胀开裂的影响与分析[J]. 重庆交通学院学报, 2005, 24(5): 53-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0696.2005.05.013 GAO Yan-long, HUANG Xin, LIU Feng. The influence and analyse of fly ash with high sulphur content on expansion cracks of lime-fly ash base[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2005, 24(5): 53-55. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0696.2005.05.013
[13] 胡江洋, 毛君, 张浩, 等. 环保脱硫型粉煤灰对水泥粉煤灰稳定基层膨胀开裂的破坏机理研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2016, 13(1): 69-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2016.01.011 HU Jiang-yang, MAO Jun, ZHANG Hao, et al. Environmental protection desulfurization fly ash on the destruction mechanism of expansion crack on the base of the cement fly-ash stabilized[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2016, 13(1): 69-73. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7029.2016.01.011
[14] 宋亮, 王选仓. 新疆盐渍土地区水泥稳定基层盐胀变形规律及机理[J]. 公路交通科技, 2019, 36(7): 20-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK201907003.htm SONG Liang, WANG Xuan-chang. Salt heaving deformation rule and mechanism of cement stabilized base of saline areas in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2019, 36(7): 20-28. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GLJK201907003.htm
[15] 尧俊凯, 叶阳升, 王鹏程, 等. 硫酸盐侵蚀水泥改良路基段上拱研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(4): 782-788. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201904029.htm YAO Jun-kai, YE Yang-sheng, WANG Peng-cheng, et al. Subgrade heave of sulfate attacking on cement-stabilized filler[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(4): 782-788. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201904029.htm
[16] 应赛, 周凤玺, 文桃, 等. 盐渍土冻结过程中的特征温度研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 41(1): 53-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202101009.htm YING Sai, ZHOU Feng-xi, WEN Tao, et al. Characteristic temperatures of saline soil during freezing[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 41(1): 53-61. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202101009.htm
[17] 田林杰. 盐渍土地区水泥基材抗硫酸盐侵蚀宏观性能及微观结构研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学, 2017. TIAN Lin-jie. Study on Macroscopic Properties and Microstructure of Cement-Based Materials of Sulfate Corrosion Resistance in Saline Soil Area[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2017. (in Chinese)
[18] 孙彬, 王景贤, 周燕, 等. 冻融循环、硫酸盐侵蚀和碱骨料反应的混凝土损伤鉴别方法[J]. 建筑科学, 2011, 27(增刊1): 29-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZKX2011S1009.htm SUN Bin, WANG Jing-xian, ZHOU Yan, et al. Identification method for damages due to freeze-thaw sulfate attack and alkali-aggregate reaction[J]. Building Science, 2011, 27(S1): 29-36. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JZKX2011S1009.htm
[19] 殷强. 混凝土碱—骨料反应检测方法和碱活性的预防措施[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2006. YIN Qiang. The Testing Method and Suppressing Measure of Alkali Aggregate Reaction[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2006. (in Chinese)
[20] Kumar MEHTA P. Sulfate attack on concrete separating myths from reality[J]. Concrete International, 2000, 22(8): 57-59.
[21] 公路路面基层施工技术细则:JTG F20—2015[S]. 2015. Technical Guidelines for Construction of Highway Roadbases: JTG F20—2015[S]. 2015. (in Chinese)




 下载:
下载: