System reliability analysis of slopes based on weighted uniform simulation method
-
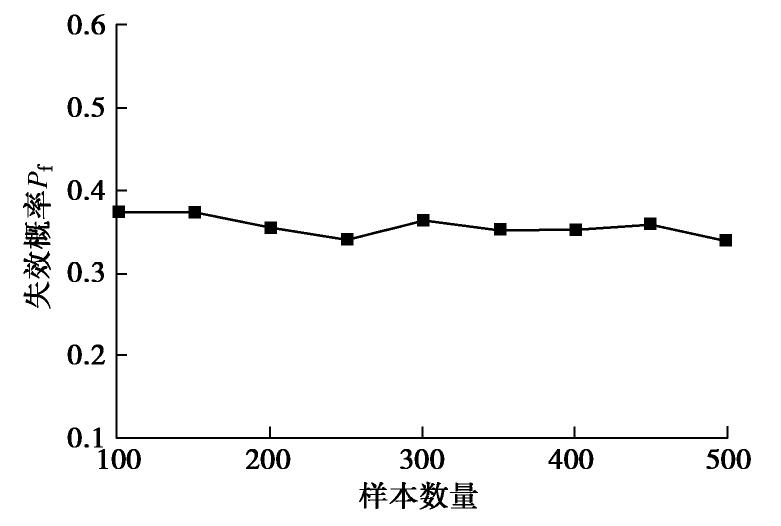
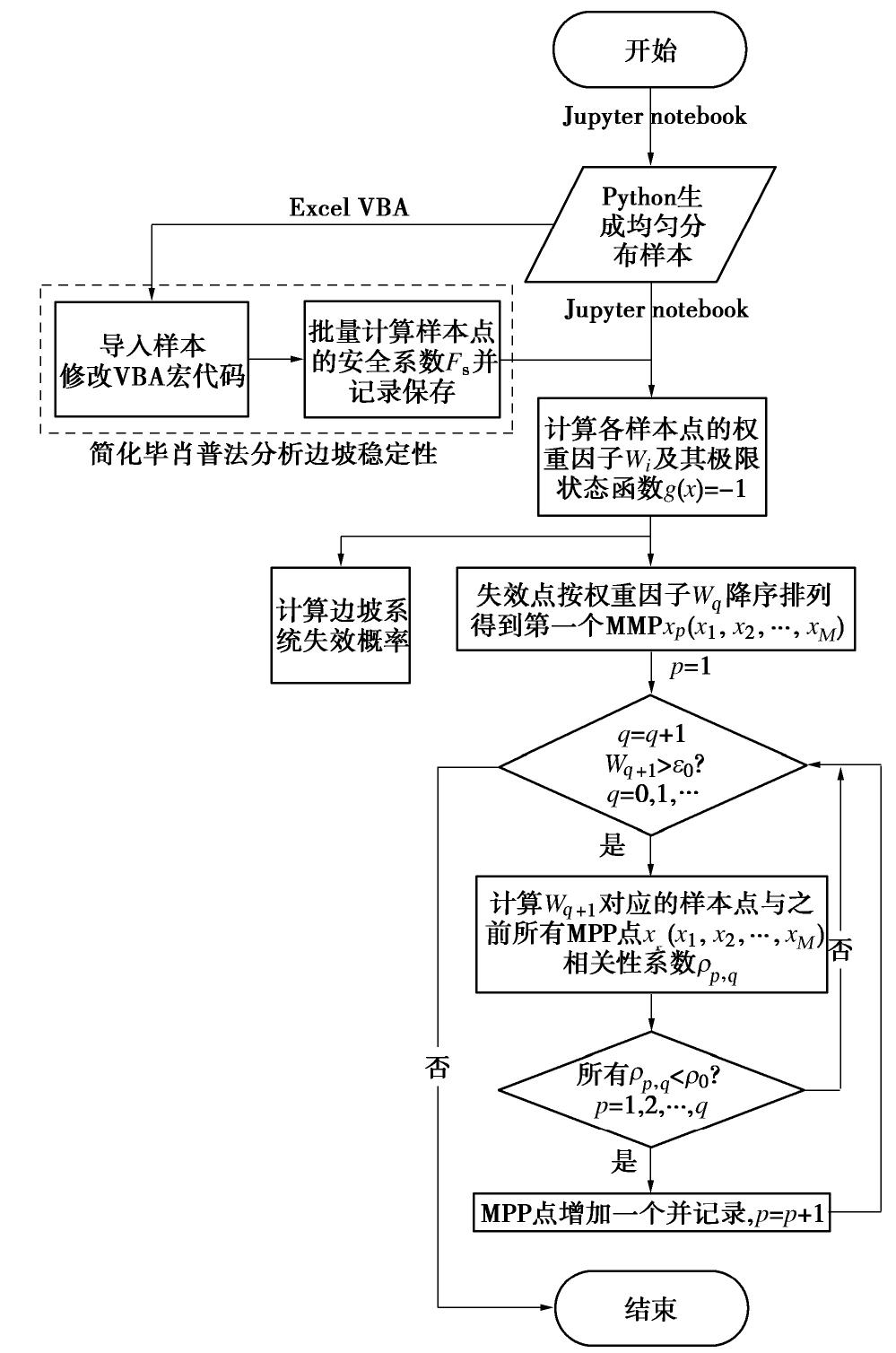
摘要: 复杂边坡工程中由于边坡土体分层或土体参数的不确定性等因素,边坡失稳往往会发生在多个潜在失稳滑面,因此,采用单一临界确定性滑面或临界概率滑面对边坡系统可靠度进行分析会极大低估其失效概率。运用WUS(Weighted Uniform Simulation)方法对边坡系统可靠度进行了概率分析,运用4个多层边坡算例演示WUS对于边坡系统可靠度分析的良好适用性。分析结果表明,该方法对高维、隐式极限状态方程下的多层土边坡问题分析精度较高的同时,可极大减少边坡模型计算样本数,例如,对于边坡可靠度分析MCS通常需要104以上的样本量,而WUS仅需500组左右即可满足精度要求。通过对原始WUS算法的修正,在样本量足够的情况下,修正WUS法能更加高效计算得到复杂边坡系统失效概率,并且可以自动摒弃冗余失效模式而得到较为准确的多失效模式所对应的多组可靠度参数设计点,即MPP(Most Probable Failure Point),进而高效识别出多层土复杂边坡的代表性滑动面,为边坡安全及失稳灾害防治提供重要的参考价值。Abstract: In practical engineering, due to the slope stratification or the spatial variability of soil properties, the slope will often fail along multiple potential sliding surfaces. Considering that using a single critical deterministic sliding surface or a critical probability sliding surface to analyze slope reliability will greatly underestimate the probability of failure, this study uses the weighted uniform simulation (WUS) method to analyze the system reliability of slopes. Four multi-layer slope cases are used to prove that the WUS has good applicability for system reliability analysis of slopes. High accuracy is obtained for multi-layer slope problems under high-dimensional and implicit limit state equations by this method, while the sample size is greatly reduced from 104 samples required by the direct Monte Carlo simulation to only about 500 samples under the same accuracy requirements. By modifying the original WUS algorithm, when the sample size is sufficient, the modified WUS can efficiently obtain the system failure probability and effectively abandon redundant failure modes to obtain accurate most probable failure points corresponding to multiple failure modes. Furthermore, the representative sliding surfaces of the multi-layer slope can be effectively and automatically identified, which provides important reference value for the later maintenance and failure prevention of slopes.
-
-
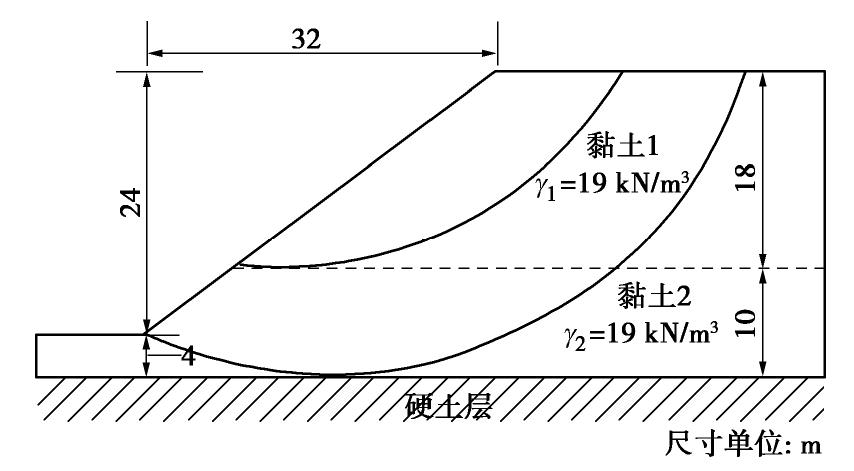
表 1 土体不确定性强度参数(算例1)
Table 1 Uncertain strength properties of soil (Case 1)
随机变量 分布类型 均值/kPa 变异系数 黏土1 cu 对数正态分布 120 0.3 黏土2 cu 对数正态分布 160 0.3 表 2 MPP点随样本数量变化情况(算例1)
Table 2 Change of MPPs with sample size (Case 1)
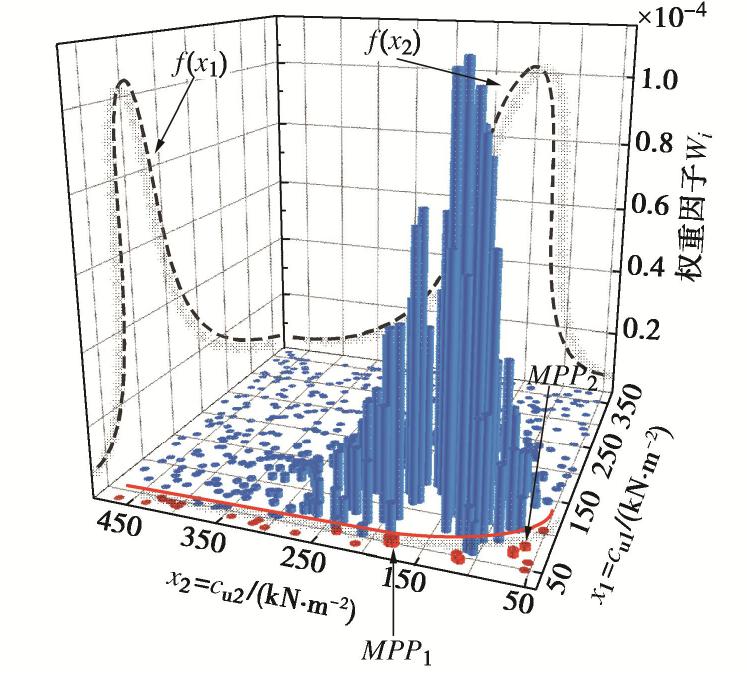
样本数量 可靠度指标β MPP (cu1/cu2) 100 2.25 (47.24, 251.34) (76.39, 71.19) 200 2.69 (44.58, 160.79) (102.70, 49.77) 300 2.59 (50.34, 125.51) (72.45, 52.79) 400 2.66 (48.96, 119.39) (77.43, 57.43) 500 2.68 (47.95, 177.87) (75.67, 61.73) 表 3 不同方法边坡的系统可靠度结果比较(算例1)
Table 3 Comparison of different system reliability analysis results of slopes (Case 1)
表 4 土体不确定性强度参数(算例2)
Table 4 Uncertain strength properties of soil (Case 2)
随机变量 分布类型 均值/kPa 变异系数 cu1 正态分布 55 0.37 cu2 正态分布 43 0.19 cu3 正态分布 56 0.24 表 5 MPP点随样本数量变化情况(算例2)
Table 5 Change of MPPs with sample size (Case 2)
样本数量 可靠度指标β MPP (cu1/cu2 /cu3) 100 0.32 (43.33, 36.05, 48.72) (110.10, 47.72, 24.05) (38.60, 44.87, 39.79) 200 0.37 (63.01, 34.28, 37.86) (40.18, 41.04, 39.92) (34.67, 36.44, 53.61) 300 0.35 (58.15, 31.30, 44.63) (46.62, 52.08, 36.64) (29.65, 35.54, 70.51) 400 0.38 (49.28, 36.93, 41.30) (34.53, 46.96, 35.31) (39.55, 37.42, 71.50) 500 0.34 (42.38, 36.90, 49.77) (39.05, 44.96, 34.13) (14.86, 49.61, 48.61) 表 6 不同方法边坡的系统可靠度结果比较(算例2)
Table 6 Comparison of different system reliability analysis results of slopes (Case 2)
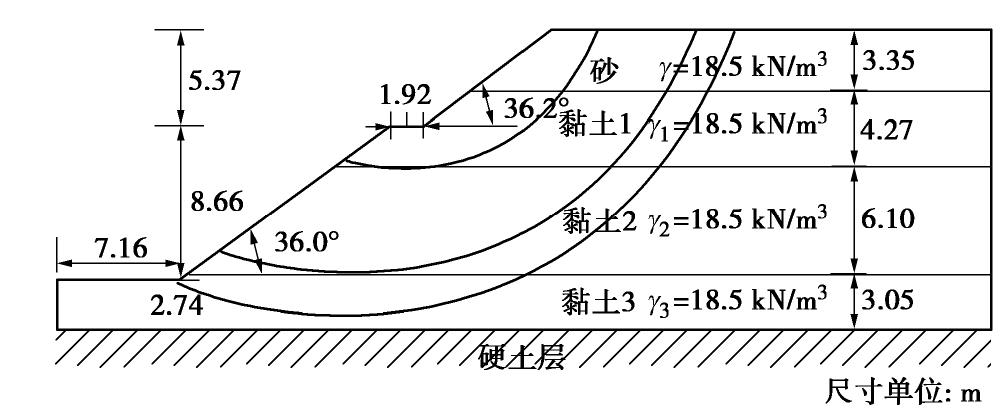
表 7 土体不确定性强度参数(算例3)
Table 7 Uncertain strength properties of soil (Case 3)
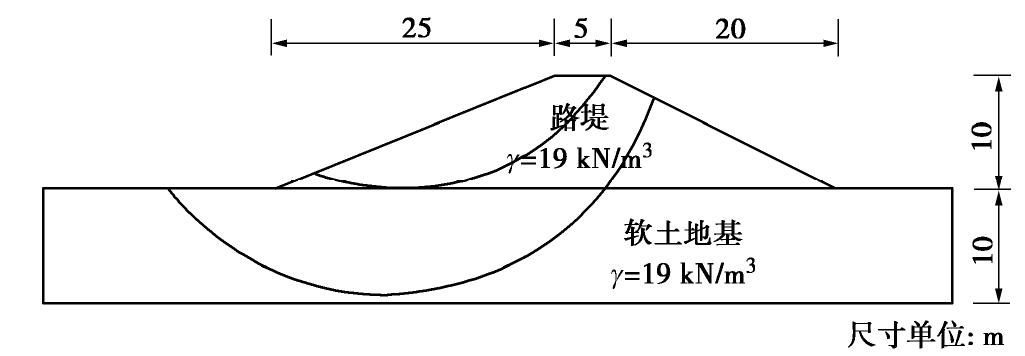
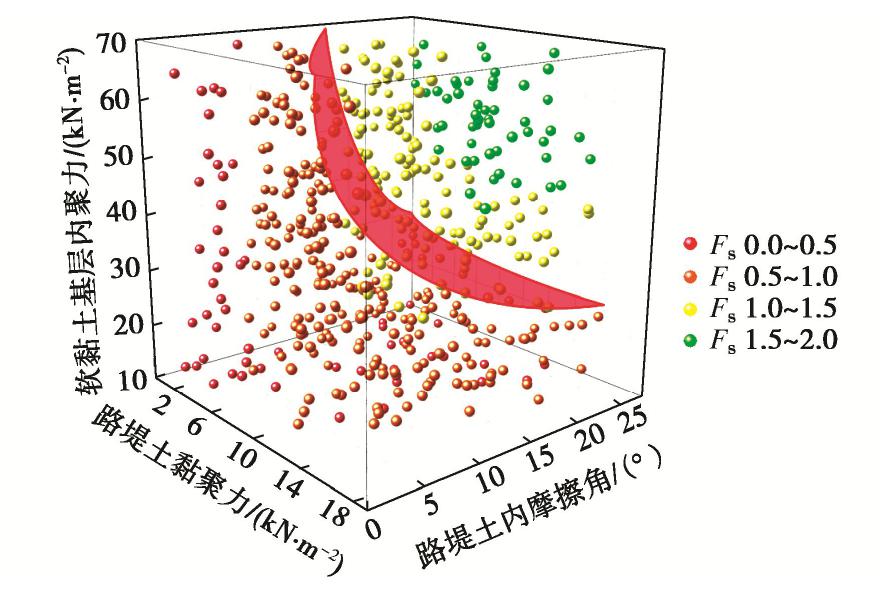
随机变量 位置 分布类型 均值 变异系数 内聚力c/kPa 路堤 正态分布 10 0.20 软黏土基层 正态分布 40 0.20 摩擦角φ/(°) 路堤 正态分布 12 0.25 表 8 MPP点随样本数量变化情况(算例3)
Table 8 Change of MPPs with sample size (Case 3)
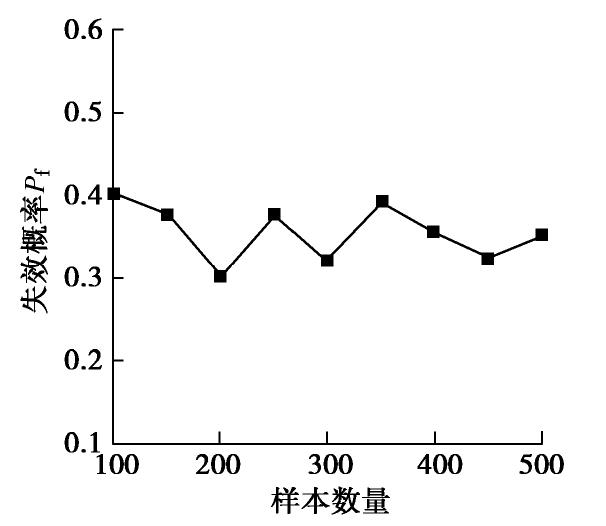
样本数量 可靠度指标β 最可能失效点MPP (c路堤/φ路堤/c基层) 100 0.24 (8.58,11.88, 31.60), (11.42,16.04, 10.80) 200 0.52 (10.86,10.45,29.99), (11.57, 15.35, 9.98) 300 0.46 (9.68, 8.07, 36.63) (10.10, 15.90,13.09) 400 0.37 (9.68, 8.19, 44.93) (10.68,15.03, 10.97) 500 0.35 (9.29, 8.53, 41.68) (10.04,18.34, 13.65) 表 9 不同方法边坡的系统可靠度结果比较(算例3)
Table 9 Comparison of different system reliability analysis results of slopes (Case 3)
表 10 土体不确定性强度参数(算例4)
Table 10 Uncertain strength properties of soil (Case 4)
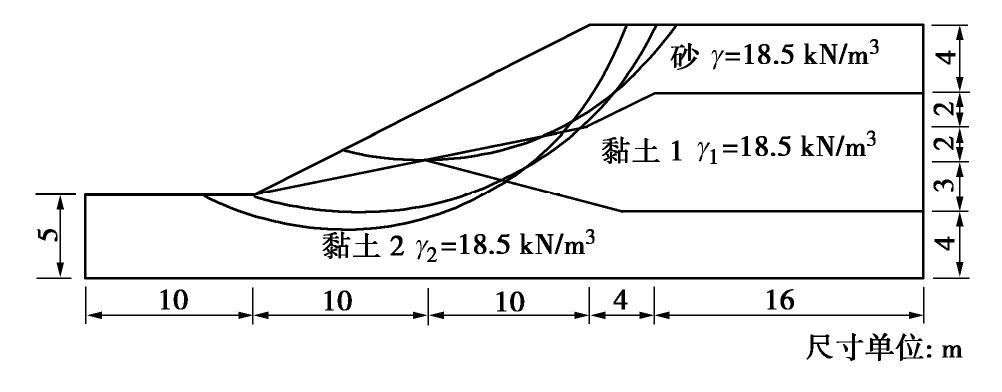
随机变量 分布类型 均值 变异系数 黏聚力c/kPa 黏土1 正态分布 5.3 0.3 黏土2 正态分布 7.2 0.3 摩擦角φ/(°) 黏土1 正态分布 23 0.2 黏土2 正态分布 20 0.2 表 11 MPP点随样本数量变化情况(算例4)
Table 11 Change of MPPs with sample size (Case 4)
样本数量 可靠度指标β 最可能失效点MPP (c1 /φ1 / c2 /φ2 ) 100 2.14 (14.27, 3.49, 12.33, 4.84) (8.56, 5.74, 10.68, 14.30) (8.65, 10.73, 8.77, 9.04) 200 2.12 (21.40, 5.47, 12.84, 2.27) (4.34, 4.32, 14.77, 7.80) (5.39, 10.53, 5.12, 4.37) 300 2.16 (20.50, 4.60, 11.40, 4.62) (6.58, 5.26, 23.17, 5.83) (6.14, 6.02, 4.33, 7.55) 400 2.12 (21.56, 7.20, 11.27, 4.95) (5.22, 4.58, 18.31, 4.46) (12.23, 5.54, 6.04, 13.98) 500 2.17 (17.73, 4.93, 10.58, 7.91) (6.54, 2.21, 28.87, 5.85) (9.38, 6.92, 9.56, 12.29) 表 12 不同方法边坡的系统可靠度结果比较(算例4)
Table 12 Comparison of different system reliability analysis results of slopes (Case 4)
-
[1] 蒋水华, 刘贤, 黄发明, 等. 考虑多参数空间变异性的降雨入渗边坡失稳机理及可靠度分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2020, 42(5): 900-907. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202005017.htm JIANG Shui-hua, LIU Xian, HUANG Fa-ming, et al. Failure mechanism and reliability analysis of soil slopes under rainfall infiltration considering spatial variability of multiple soil parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(5): 900-907. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202005017.htm
[2] LOW B K. Reliability analysis of rock slopes involving correlated nonnormals[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2007, 44(6): 922-935. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2007.02.008
[3] 蒋辽, 喻兴, 刘林洁, 等. 基于蒙特卡罗模拟的填方边坡可靠度分析[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2017, 13(增刊2): 693-697. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE2017S2031.htm JIANG Liao, YU Xing, LIU Lin-jie, et al. Reliability analysis on filled slope based on Monte Carlo simulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2017, 13(S2): 693-697. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE2017S2031.htm
[4] JI J, KODIKARA J K. Efficient reliability method for implicit limit state surface with correlated non-Gaussian variables[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2015, 39(17): 1898-1911. doi: 10.1002/nag.2380
[5] OKA Y, WU T H. System reliability of slope stability[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1990, 116(8): 1185-1189. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1990)116:8(1185)
[6] HASSAN A M, WOLFF T F. Search algorithm for minimum reliability index of earth slopes[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 1999, 125(4): 301-308. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1999)125:4(301)
[7] CHOWDHURY R N, XU D W. Geotechnical system reliability of slopes[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 1995, 47(3): 141-151.
[8] JI J, LOW B K. Stratified response surfaces for system probabilistic evaluation of slopes[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2012, 138(11): 1398-1406. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000711
[9] LOW B K, ZHANG J, TANG W H. Efficient system reliability analysis illustrated for a retaining wall and a soil slope[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2011, 38(2): 196-204. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2010.11.005
[10] CHO S E. First-order reliability analysis of slope considering multiple failure modes[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, 154: 98-105. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.12.014
[11] XIAO N C, YUAN K, ZHOU C N. Adaptive kriging-based efficient reliability method for structural systems with multiple failure modes and mixed variables[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 359: 112649. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2019.112649
[12] 曾鹏, 陈语, 李天斌. 基于拟牛顿近似二阶法的岩土工程系统可靠性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(3): 726-733. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201803021.htm ZENG Peng, CHEN Yu, LI Tian-bin. System reliability of geotechnical problems using quasi-Newton approximation-based sorm[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(3): 726-733. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201803021.htm
[13] 杨智勇, 李典庆, 曹子君, 等. 基于广义子集模拟的土坡系统可靠度分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(3): 957-966, 984. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201803024.htm YANG Zhi-yong, LI Dian-qing, CAO Zi-jun, et al. System reliability of soil slope using generalized subset simulation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(3): 957-966, 984. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201803024.htm
[14] 李静萍, 程勇刚, 李典庆, 等. 基于多重响应面法的空间变异土坡系统可靠度分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(1): 147-155, 165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201601019.htm LI Jing-ping, CHENG Yong-gang, LI Dian-qing, et al. System reliability analysis of spatially variable soil slopes using the multiple response surfaces method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(1): 147-155, 165. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201601019.htm
[15] 陈松坤, 王德禹. 基于神经网络的蒙特卡罗可靠性分析方法[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2018, 52(6): 687-692. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJT201806011.htm CHEN Song-kun, WANG De-yu. An improved Monte Carlo reliability analysis method based on neural network[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2018, 52(6): 687-692. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJT201806011.htm
[16] CHING J, PHOON K-K, HU Y-G. Efficient Evaluation of reliability for slopes with circular slip surfaces using importance sampling[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, American Society of Civil Engineers, 2009, 135(6): 768-777.
[17] 吴振君, 王水林, 葛修润. LHS方法在边坡可靠度分析中的应用[J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(4): 1047-1054. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201004009.htm WU Zhen-jun, WANG Shui-lin, GE Xiu-run, et al. Application of Latin hypercube sampling technique to slope reliability analysis[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(4): 1047-1054. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201004009.htm
[18] ECHARD B, GAYTON N, LEMAIRE M. AK-MCS: an active learning reliability method combining Kriging and Monte Carlo Simulation[J]. Structural Safety, 2011, 33(2): 145-154.
[19] BICHON B J, MCFARLAND J M, MAHADEVAN S. Efficient surrogate models for reliability analysis of systems with multiple failure modes[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2011, 96(10): 1386-1395.
[20] FAURIAT W, GAYTON N. AK-SYS: An adaptation of the AK-MCS method for system reliability[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2014, 123: 137-144.
[21] 蒋水华, 祁小辉, 曹子君, 等. 基于随机响应面法的边坡系统可靠度分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(3): 809-818. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201503032.htm JIANG Shui-hua, QI Xiao-hui, CAO Zi-jun, et al. System reliability analysis of slope with stochastic response surface method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(3): 809-818. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201503032.htm
[22] 张天龙, 曾鹏, 李天斌, 等. 基于主动学习径向基函数的边坡系统可靠度分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2020, 41(9): 3098-3108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202009028.htm ZHANG Tian-long, ZENG Peng, LI Tian-bin, et al. System reliability analyses of slopes based on active-learning radial basis function[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(9): 3098-3108. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202009028.htm
[23] RASHKI M, MIRI M, AZHDARY MOGHADDAM M. A new efficient simulation method to approximate the probability of failure and most probable point[J]. Structural Safety, 2012, 39: 22-29.
[24] GHOHANI ARAB H, GHASEMI M R, MIRI M. Enhancing weighted uniform simulation for structural reliability analysis[J]. Iran University of Science & Technology, 2013, 3(4): 635-651.
[25] RASHKI M, MIRI M, MOGHADDAM M A. Closure to “a new efficient simulation method to approximate the probability of failure and most probable point” (Struct. Safety 2012:39:22-9)[J]. Structural Safety, 2014, 46: 15-16.
[26] IBRAHIM Y. Observations on applications of importance sampling in structural reliability analysis[J]. Structural Safety, 1991, 9(4): 269-281.
[27] 祁小辉, 李典庆, 周创兵, 等. 考虑土体空间变异性的边坡最危险滑动面随机分析方法[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(4): 745-753. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201304022.htm QI Xiao-hui, LI Dian-qing, ZHOU Chuang-bing, et al. Stochastic analysis method of critical slip surfaces in soil slopes considering spatial variability[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(4): 745-753. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201304022.htm
[28] LI L, WANG Y, CAO Z. Probabilistic slope stability analysis by risk aggregation[J]. Engineering Geology, 2014, 176: 57-65.
[29] ZHANG J, HUANG H W, JUANG C H, et al. Extension of Hassan and Wolff method for system reliability analysis of soil slopes[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, 160: 81-88.
[30] ZHU B, PEI H, YANG Q. An intelligent response surface method for analyzing slope reliability based on Gaussian process regression[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2019, 43(15): 2431-2448.
[31] TUN Y W, LLANO-SERNA M A, PEDROSO D M, et al. Multimodal reliability analysis of 3D slopes with a genetic algorithm[J]. Acta Geotechnica, Springer, 2019, 14(1): 207-223.
[32] 任斌斌, 苏立君, 张崇磊, 等. 基于Python语言和Abaqus平台的边坡可靠度计算自动化算法开发[J]. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文), 2019, 41(5): 67-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JIAN201905009.htm REN Bin-bin, SU Li-jun, ZHANG Chong-lei, et al. A slope reliability automated algorithm based on python language and Abaqus platform[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2019, 41(5): 67-72. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JIAN201905009.htm



 下载:
下载: