Tests and analysis of ground motion signals of ice-rock avanlanches
-
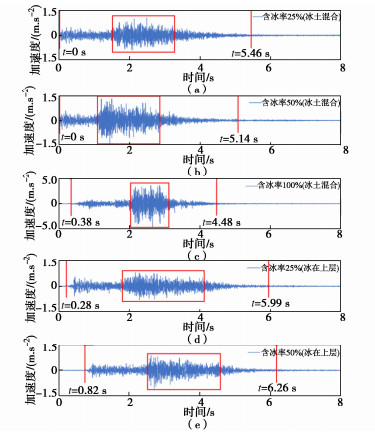
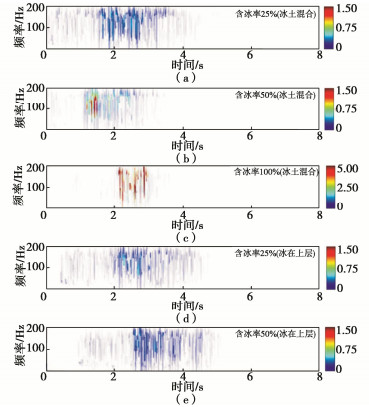
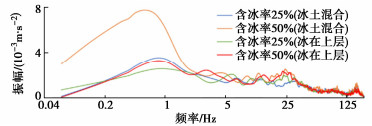
摘要: 随着西部大开发的战略部署及全球气温的持续升高,冰-岩碎屑流滑坡因其超强的运动性和破坏力而引起了业内学者的广泛关注。通过开展大型斜槽试验来模拟高寒山区特有的冰-岩碎屑流崩滑,利用现场布设的高精度传感器获取冰-岩碎屑流激发出的地震动信号,并基于Hilbert-Huang变换方法对比分析了5种工况下信号的时频特征,探究了含冰率和冰所处位置两个相关变量与冰-岩碎屑流的冲击力间的相关性。根据分析结果:冰-岩碎屑流中含冰率越大、冰与滑脱面的接触面越大,其激发的地震动信号振幅越大、时间越短、峰值更集中;信号频率主要分布在0.06~45 Hz范围内,以低频振动为主,高频信号集中出现在冰-岩碎屑流与缓坡段及河道两岸发生强烈冲击碰撞时期。Abstract: With the strategic deployment of western development and the continuous rise of global temperature, the ice-rock avalanches have attracted the wide attention of scholars in the industry because of their high mobility and destructive power. The large-scale flume tests are carried out to simulate the ice-rock avalanches. The seismic signals generated by the ice-rock avalanches are obtained by using the high-precision sensors in the field, and the time-frequency characteristics of signals under 5 working conditions are compared and analyzed based on the Hilbert-Huang transform method. The correlation between ice content and ice location and the impact force of ice-rock avalanches are investigated. According to the analysis results, the larger the ice content and the larger the contact surface between the ice and the detachment surface, the larger the amplitude, the shorter the time and the more concentrated the peak value of the induced seismic signals. The frequency of signals is mainly distributed in the range of 0.06~45 Hz. The low-frequency vibration is dominant, while the high-frequency ones are concentrated in the period of strong impact and collision between the ice-rock avalanches and the gentle slope section and the river banks.
-
Keywords:
- ice-rock avalanches /
- flume test /
- HHT method /
- seismic signal
-
-
表 1 物料组成
Table 1 Material compositions
物质 冰 砾粒 砂粒 黏土 状态 粒径/mm 10~20 10~20 5~10 2~5 1~2 — 百分比/% / 54 49 32 9 10 质量/kg 1 25 40.35 16.92 11.19 3.00 3.54 混合 2 50 26.90 11.28 7.46 2.00 2.36 3 100 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 4 25 40.35 16.92 11.19 3.00 3.54 冰在上 5 50 26.90 11.28 7.46 2.00 2.36 -
[1] EVANS S G, CLAGUE J J. Catastrophic rock avalanches in glacial environment, landslides[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Landslides. Lausanne, 1988.
[2] 刘伟. 西藏易贡巨型超高速远程滑坡地质灾害链特征研析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2002, 13(3): 9-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200203001.htm LIU Wei. Study on the characteristics of huge scale-super highspeed-long distance landslide cain in Yigong, Tibet[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2002, 13(3): 9-18. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200203001.htm
[3] 邢爱国, 徐娜娜, 宋新远. 易贡滑坡堰塞湖溃坝洪水分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2010, 18(1): 78-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201001014.htm XING Aiguo, XU Nana, SONG Xinyuan. Numerical simulation of lake water down-stream flooding due to sudden breakage of yigong landslide dam in Tibet[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(1): 78-83. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201001014.htm
[4] 刘传正, 吕杰堂, 童立强, 等. 雅鲁藏布江色东普沟崩滑-碎屑流堵江灾害初步研究[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(2): 219-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201902002.htm LIU Chuanzheng, LÜ Jietang, TONG Liqiang, et al. Research on glacial/rock fall-landslide-debris flows in Sedongpu Basin along Yarlung Zangbo River in Tibet[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(2): 219-234. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201902002.htm
[5] 杨情情, 苏志满, 陈锣增, 等. 冰屑对冰-岩碎屑流运动特性影响作用的初步分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2015, 23(6): 1117-1126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201506013.htm YANG Qingqing, SU Zhiman, CHEN Luozeng, et al. Flume tests on influence of ice to mobility of rock-ice avalanches[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2015, 23(6): 1117-1126. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201506013.htm
[6] 杨情情, 郑欣玉, 苏志满, 等. 高速远程冰-岩碎屑流研究进展[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(3): 935-949. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202203014.htm YANG Qingqing, ZHENG Xinyu, SU Zhiman, et al. Review on rock-ice avalanches[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(3): 935-949. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202203014.htm
[7] 李昆仲, 张明哲, 邢爱国. 雅鲁藏布江色东普沟崩滑-碎屑流过程模拟及运动特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2021, 32(1): 18-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202101003.htm LI Kunzhong, ZHANG Mingzhe, XING Aiguo. Numerical runout modeling and dynamic analysis of the ice avalanche-debris flow in Sedongpu Basin along Yarlung Zangbo River in Tibet[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(1): 18-27. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH202101003.htm
[8] 师璐璐, 陈剑, 陈瑞琛, 等. 丽江干河坝冰-岩碎屑流地貌、沉积特征与成因机制分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2022, 44(4): 1382-1394. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT202204023.htm SHI Lulu, CHEN Jian, CHEN Ruichen, et al. Geomorphological characteristics and failure mechanism of Ganheba rock-ice avalanche in Lijiang[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2022, 44(4): 1382-1394. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT202204023.htm
[9] HUANG N E, SHEN Z, LONG S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995.
[10] HUANG N E, SHEN Z, LONG S R. A new view of nonlinear water waves: the Hilbert spectrum[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1999, 31: 417-457.
[11] HUANG N E, SHEN S S P. Hilbert-Huang Transform and Its Applications[M]. Singapore: World Scientfic, 2005.
[12] FAN G, ZHANG L M, ZHANG J J, et al. Energy-based analysis of mechanisms of earthquake-induced landslide using Hilbert-Huang transform and marginal spectrum[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2017, 50(9): 2425-2441.
[13] FAN G, ZHANG L M, ZHANG J J, et al. Analysis of seismic stability of an obsequent rock slope using time-frequency method[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019, 52(10): 3809-3823.




 下载:
下载: