Shear mechanical properties of limestone structural plane under hydrodynamic force-dissolution
-
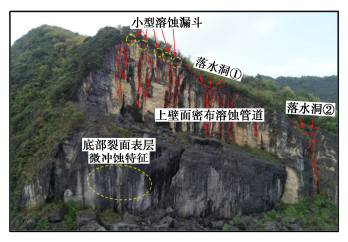
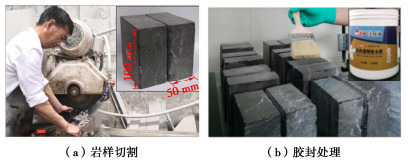
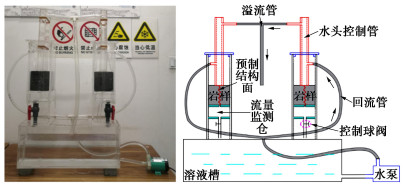
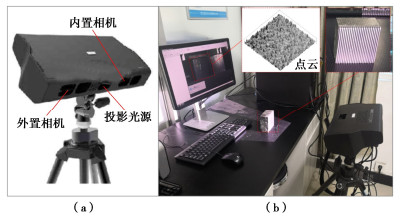
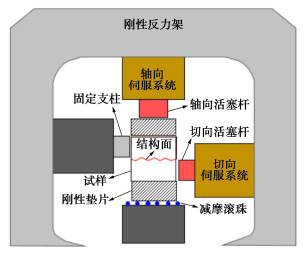
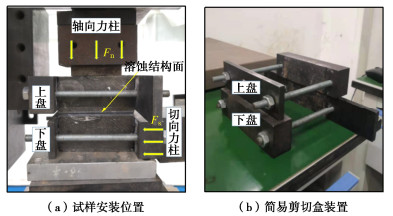
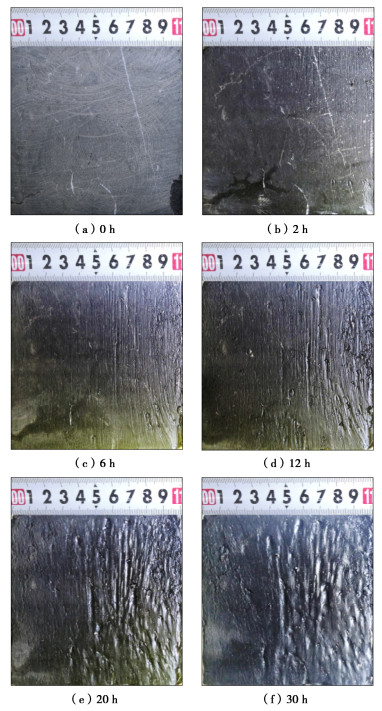
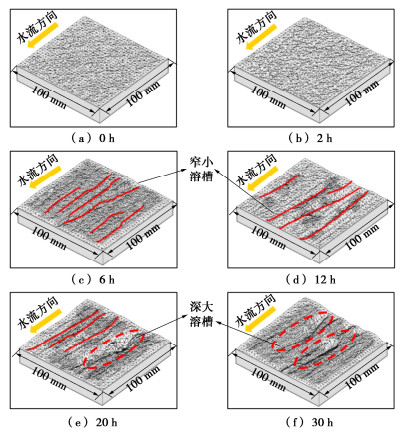
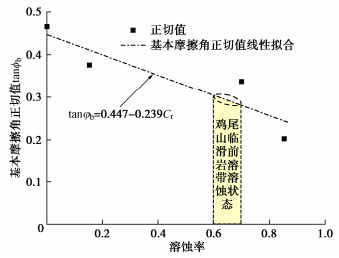
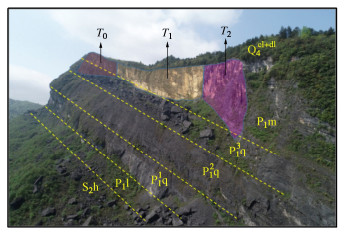
摘要: 中国西南地区溶蚀岩体分布广泛。岩溶作用下,结构面强度持续劣化是影响岩体稳定性的重要因素之一。为探究溶蚀作用下结构面的演化特征,揭示岩溶作用对灰岩结构面剪切力学特性的影响,以武隆鸡尾山溶蚀岩质坡体为例,采用室内结构面渗流溶蚀试验和结构面直接剪切试验,并结合三维形貌光学扫描技术,阐明了水动力-溶蚀作用灰岩结构面的表观演化模式和剪切力学特性演化规律,揭示了水动力-溶蚀作用下结构面劣化机理。结果表明:灰岩结构面在化学溶蚀和物理冲蚀双重作用下,先后经历“点式选择性溶蚀—细槽线式稳定渗流溶蚀—优势管道流强烈溶蚀—壁面缓慢溶蚀”4个阶段;溶蚀过程中,灰岩结构面表面粗糙度指数和溶蚀率指标随时长增大而增大,并呈收敛趋势;直剪过程中,溶蚀结构面表现出初期锁固、后期剪摩阻滑的两阶段特征,且时间越长、应力水平越高,剪切硬化特征越显著;随溶蚀时间增长,结构面主要抗滑结构由刚性稳定微凸体发展为细微溶槽并最终演变为深大岩溶管道,其极限抗剪强度呈现出“先减小,后增大”的趋势;基于Barton公式建立了灰岩溶蚀结构面抗剪强度预测模型。Abstract: The dissolved rock mass is widely distributed in Southwest China. Under the action of karst, the continuous deterioration of structural plane strength is one of the important factors affecting the stability of rock mass. In order to explore the evolution characteristics of structural plane under dissolution and to reveal the influences of karstification on the shear mechanical properties of limestone structural plane, based on the example of the dissolution rock slope of Jiwei Mountain in Wulong, the apparent evolution patterns of limestone structural plane and the evolution laws of shear mechanical properties as well as the deterioration mechanism of structural plane are expounded by using the indoor seepage dissolution and direct shear tests on the structural plane and the three-dimensional morphology optical scanning technology. The results show that under the dual action of chemical corrosion and physical erosion, the limestone structural plane has experienced four stages: point selective dissolution, thin groove linear stable seepage dissolution, strong dissolution of dominant pipeline flow and wall slow dissolution. During the dissolution process, the surface roughness index and dissolution rate index of limestone structural plane increase with the increase of dissolution time, and exhibit a convergence trend. During the direct shear process, the corrosion structural plane shows two-stage characteristics of the initial locking and the later shear friction and sliding, and the longer the corrosion time and the higher the stress level, the more obvious the shear hardening characteristics. With the increase of the corrosion time, the main anti-sliding structure of the structural plane develops from a rigid stable microconvex to a fine solution groove and finally evolves into a deep karst pipeline, and its ultimate shear strength shows a trend of " first decreasing, then increasing". The prediction model for shear strength of limestone dissolution structural plane is established based on the Barton's formula.
-
Keywords:
- karst /
- structural plane /
- shear characteristic /
- strength prediction model /
- roughness /
- Jiwei Mountain
-
-
表 1 不同工况下的溶蚀时长分布情况
Table 1 Dissolution duration distribution under different working conditions
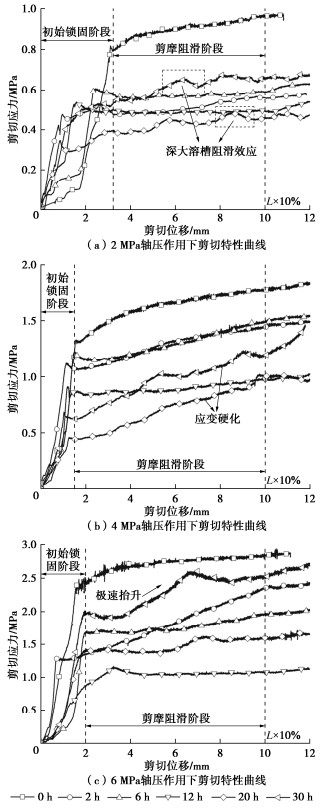
工况编号 工况1 工况2 工况3 工况4 工况5 工况6 溶蚀时长/h 0 2 6 12 20 30 表 2 结构面直接剪切试验轴压试验值
Table 2 Axial compression test values of structural plane direct shear tests
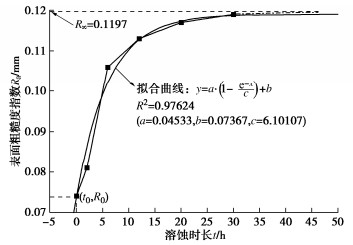
轴压 低水平轴压 中等水平轴压 高水平轴压 压力值/MPa 2 4 6 表 3 溶蚀结构面表面粗糙度演化特征
Table 3 Evolution characteristics of surface roughness of dissolved.discontinuities
溶蚀时长t/h 最大峰高Rp/mm 最大谷深Rv/mm 最大溶槽深度hmax/mm 表面粗糙度指数Ra/mm 0 0.153 0.282 0.435 0.074 2 0.274 0.323 0.597 0.081 6 0.387 0.924 1.311 0.106 12 0.485 1.001 1.486 0.113 20 0.495 1.250 1.745 0.117 30 0.506 1.681 2.187 0.119 表 4 结构面溶蚀率与溶蚀时长对应关系表
Table 4 Relation between discontinuity dissolution rate and dissolution time
溶蚀时长/h 0 2 6 12 20 30 Ra 0.074 0.081 0.106 0.113 0.117 0.119 Cr 0.000 0.153 0.700 0.853 0.941 0.985 表 5 不同溶蚀时长结构面极限抗剪强度
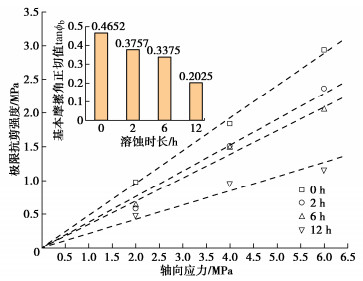
Table 5 Ultimate shear strengths of structural plane with different dissolution durations
溶蚀时长t/h 各轴压下极限抗剪强度τ/MPa 溶蚀率Cr 2 MPa 4 MPa 6 MPa 0 0.977 1.841 2.938 0 2 0.581 1.502 2.360 0.153 6 0.633 1.490 2.045 0.700 12 0.490 0.970 1.169 0.853 20 0.479 1.023 1.712 0.941 30 0.672 1.465 2.520 0.985 表 6 预测值-试验结果对比情况
Table 6 Comparison between predicted values and test results
溶蚀时长/h 2 MPa 4 MPa 6 MPa 平均误
差/MPa试验值 预测值 试验值 预测值 试验值 预测值 0 0.977 0.973 1.841 1.946 2.938 2.920 0.043 2 0.581 0.797 1.502 1.594 2.360 2.390 0.113 6 0.633 0.744 1.490 1.488 2.045 2.231 0.100 12 0.490 0.477 0.970 0.955 1.169 1.432 0.097 -
[1] 殷跃平, 朱继良, 杨胜元. 贵州关岭大寨高速远程滑坡—碎屑流研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2010, 18(4): 445-454. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201004003.htm YIN Yueping, ZHU Jiliang, YANG Shengyuan. Investigation of a high speed and long Run-out rockslide-debris flow at dazhai in Guanling of Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(4): 445-454. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201004003.htm
[2] 郭静芸, 李守定, 李滨, 等. 岩溶山区崩滑灾害变形破坏地质模式分类[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(4): 478-491. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202004003.htm GUO Jingyun, LI Shouding, LI Bin, et al. Geological models classification of deformation and failures for collapses and landslides in Karst mountainous areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(4): 478-491. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202004003.htm
[3] 许强, 邓茂林, 李世海, 等. 武隆鸡尾山滑坡形成机理数值模拟研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2018, 40(11): 2012-2021. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201811007 XU Qiang, DENG Maolin, LI Shihai, et al. Numerical simulation for formation of Jiweishan landslide in Wulong County, Chongqing City of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(11): 2012-2021. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201811007
[4] 崔芳鹏, 李滨, 杨忠平, 等. 贵州纳雍普洒滑坡动力触发机制离散元模拟分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(4): 524-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202004008.htm CUI Fangpeng, LI Bin, YANG Zhongping, et al. Discrete element modelling on dynamic triggering mechanism of the Pusa landslide in Nayong County, Guizhou Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(4): 524-534. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202004008.htm
[5] 余逍逍, 史文兵, 王小明, 等. 基于数字图像处理技术的溶蚀岩体细观变形破坏机制模拟研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(3): 409-416. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202003015.htm YU Xiaoxiao, SHI Wenbing, WANG Xiaoming, et al. Simulation on mesoscopic deformation and failure mechanism of dissolved rock mass using digital image processing technology[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(3): 409-416. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202003015.htm
[6] TAO M, WANG J, ZHAO H T, et al. The influence of acid corrosion on dynamic properties and microscopic mechanism of marble[J]. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources, 2022, 8(1): 36.
[7] QIAO L P, WANG Z C, HUANG A D. Alteration of mesoscopic properties and mechanical behavior of sandstone due to hydro-physical and hydro-chemical effects[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2017, 50(2): 255-267.
[8] LI S G, HUO R K, WANG B, et al. Experimental study on physicomechanical properties of sandstone under acidic environment[J/OL]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2018: 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5784831.
[9] 熊绍真, 史文兵, 王小明. 单轴压缩条件下岩溶化裂隙岩体损伤破坏特征研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2022, 30(4): 1098-1110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202204011.htm XIONG Shaozhen, SHI Wenbing, WANG Xiaoming. Damage and failure characteristics of Karst fractured rock mass under uniaxial compression[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(4): 1098-1110. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202204011.htm
[10] PAN J L, CAI M F, LI P, et al. A damage constitutive model of rock-like materials containing a single crack under the action of chemical corrosion and uniaxial compression[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2022, 29(2): 486-498.
[11] CHEN Y L, XIAO P, DU X, et al. Study on damage statistical constitutive model of triaxial compression of acid-etched rock under coupling effect of temperature and confining pressure[J]. Materials (Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 14(23): 7414.
[12] HUO R K, LIANG Y L, LI S G, et al. The damage mechanism and deterioration characteristics of acid-corroded sandstone: an experimental study[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2022, 15(6): 537.
[13] LI S G, WU Y M, HUO R K, et al. Mechanical properties of acid-corroded sandstone under uniaxial compression[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2021, 54(1): 289-302.
[14] 穆成林, 李华东, 裴向军, 等. 溶蚀岩体各向异性力学性质的试验研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2022, 57(5): 1070-1076, 1112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT202205018.htm MU Chenglin, LI Huadong, PEI Xiangjun, et al. Experimental study on anisotropy mechanical properties of corroded rock mass[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022, 57(5): 1070-1076, 1112. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNJT202205018.htm
[15] 朱雷, 王小群, 聂德新, 等. 基于随机模型溶蚀岩体强度参数研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2014, 22(6): 1034-1038. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201406003.htm ZHU Lei, WANG Xiaoqun, NIE Dexin, et al. Stochastic method based evaluation of corrosion rock strength parameters[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(6): 1034-1038. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201406003.htm
[16] GU D M, HUANG D, ZHANG W G, et al. A 2D DEM-based approach for modeling water-induced degradation of carbonate rock[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2020, 126: 104188.
[17] WANG L Q, WANG C S, KHOSHNEVISAN S, et al. Determination of two-dimensional joint roughness coefficient using support vector regression and factor analysis[J]. Engineering Geology, 2017, 231: 238-251.
[18] 尹宏, 王述红, 董卓然, 等. 引入因子分析的结构面粗糙度RBF复合参数模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(4): 721-730. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202204015 YIN Hong, WANG Shuhong, DONG Zhuoran, et al. RBF composite parameter model for structural surface roughness with factor analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(4): 721-730. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202204015
[19] LIU X G, ZHU W C, YU Q L, et al. Estimation of the joint roughness coefficient of rock joints by consideration of two-order asperity and its application in double-joint shear tests[J]. Engineering Geology, 2017, 220: 243-255.
[20] 陈冲, 陈胜宏. 结构面轮廓不等间距采样、向量表征与粗糙度[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(增刊1): 2798-2805. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2021S1022.htm CHEN Chong, CHEN Shenghong. Unequal interval sampling, vector representation and roughness of joint profile[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(S1): 2798-2805. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2021S1022.htm
[21] 刘新荣, 许彬, 黄俊辉, 等. 多形态贯通型岩体结构面宏细观剪切力学行为研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(3): 406-415. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202103002 LIU Xinrong, XU Bin, HUANG Junhui, et al. Macro-meso shear mechanical behaviors of coalescent rock joints with different morphologies[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(3): 406-415. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202103002
[22] LIU X R, KOU M M, LU Y M, et al. An experimental investigation on the shear mechanism of fatigue damage in rock joints under pre-peak cyclic loading condition[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2018, 106: 175-184.
[23] 刘佑荣, 唐辉明. 岩体力学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1999. LIU Yourong, TANG Huiming. Rock Mechanics[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1999. (in Chinese)
[24] 邓建伟. 岩溶发育带岩体强度特征研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2014. DENG Jianwei. The Rock Strength Characteristics Research of Karst Belt[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2014. (in Chinese)
[25] 王旭东, 俞作辉, 裴强强, 等. 砂岩制样方法及误差影响研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2020, 41(增刊2): 1-10. WANG Xudong, YU Zuohui, PEI Qiangqiang, et al. Research on preparation method of sandstone sample and its error influence[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(S2): 1-10. (in Chinese)
[26] BANDIS S C, LUMSDEN A C, BARTON N R. Fundamentals of rock joint deformation[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1983, 20(6): 249-268.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 何潇,周建伟,彭鑫. 复杂地下水环境下石膏岩溶蚀特性分析. 黑龙江科学. 2025(02): 84-86+91 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. LIU Xinrong,WANG Hao,XIONG Fei,LUO Xinyang. Deformation and failure mechanism of karst mountain with deep and large fissures under multi-coal seam mining: Insight from DEM simulation. Journal of Mountain Science. 2025(03): 950-965 .  必应学术
必应学术
3. 刘新荣,郭雪岩,周小涵,罗新飏,王浩,李沛瑶,周福川. 库岸危岩剪切带—基岩界面宏细观剪切贯通机制及力学特性研究. 岩石力学与工程学报. 2024(05): 1096-1109 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)
-
其他相关附件



 下载:
下载: