Experimental study on chemical damage and mechanical property degradation of reservoir rocks during process of CO2 geological storage in a saline aquifer
-
摘要:
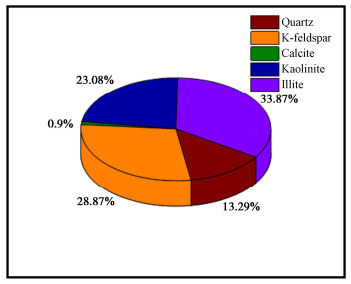
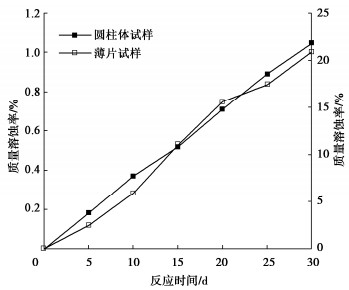
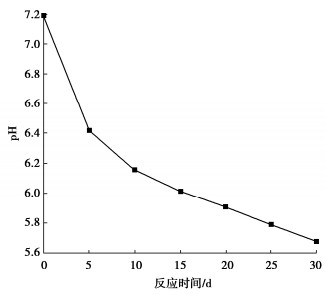
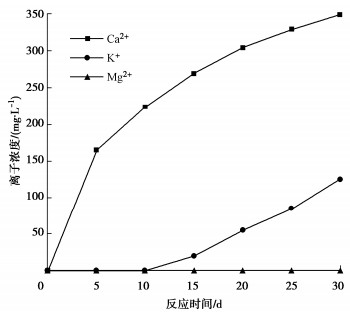
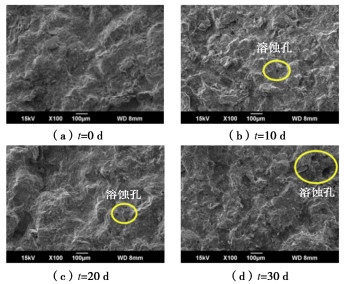
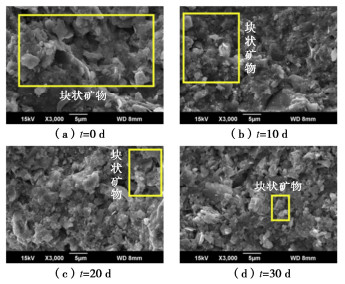
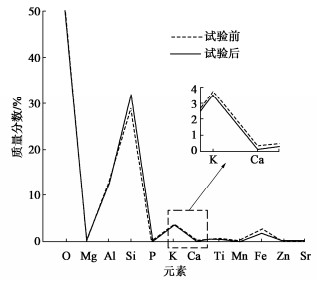
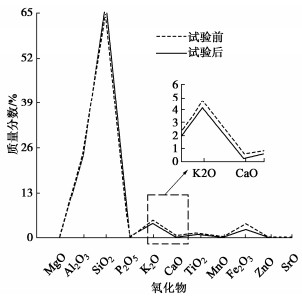
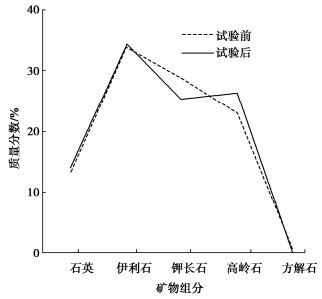
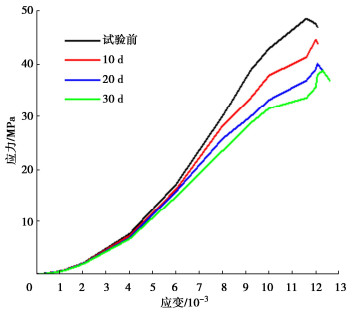
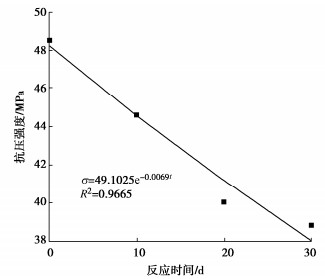
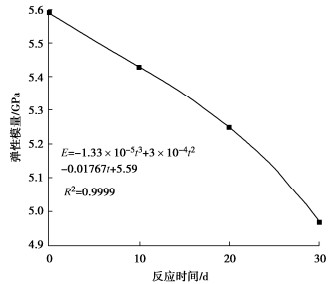
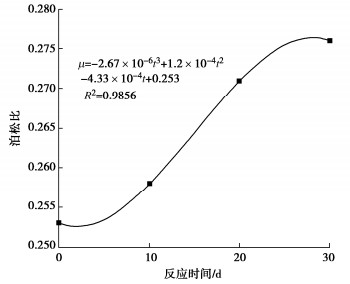
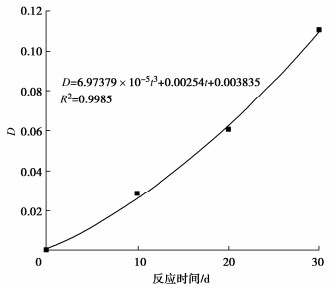
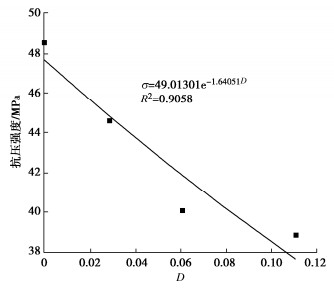
为了探究超临界二氧化碳注入咸水层后储层岩石的化学损伤规律,利用自制的恒温恒压超临界CO2-水-岩石热流固化耦合试验系统,测试反应前后储层岩心矿物组分、微观结构、矿物元素及氧化物的变化,分析反应溶液pH值和钙、钾、镁离子浓度的变化规律,研究反应前后储层岩心试样质量、单轴抗压强度、弹性模量、泊松比等物理力学参数演化规律,揭示超临界二氧化碳注入咸水层后储层岩石的化学损伤特征和力学性质劣化规律。研究结果表明:随着反应时间延长,方解石和钾长石的质量分数逐渐减少,钙元素、钾元素及其氧化物的质量分数也随之减少,试样表面粗糙度增大,产生了溶蚀孔;反应溶液的pH值从7.19降至5.68,方解石溶解速率最快,其次是钾长石,最后是伊利石;反应时间内,试样的质量溶蚀率、泊松比逐渐增大,单轴抗压强度和弹性模量逐渐减小。此外,试样的单轴抗压强度与化学作用时间呈指数函数关系,弹性模量、泊松比与化学作用时间呈三次多项式函数关系,据此建立了化学损伤作用下储层岩石的强度预测模型。以弹性模量为损伤变量,得到了岩心的单轴抗压强度和损伤变量之间的关系,揭示了储层岩石的化学损伤机制。
Abstract:To investigate the chemical damage mechanism of reservoir rocks following the injection of the supercritical CO2 into a saline aquifer, a self-made thermal-hydrological-mechanical-chemical coupled experimental system of the supercritical CO2-water-rock at constant temperature and pressure is established, which is used to test the changes of mineral components, microstructure, mineral elements and oxides of reservoir rocks before and after the reaction. And the changes of pH value and concentrations of Ca2+, K+, Mg2+ ions of the reaction solution are analyzed. Furthermore, this study focuses on elucidating the evolutionary patterns of physical and mechanical parameters, including mass, uniaxial compressive strength, elastic modulus, and Poisson's ratio. The experimental study reveals the chemical damage characteristics and mechanical property degradation of reservoir rocks after the supercritical CO2 injected into a saline aquifer. The results show that the mass fractions of calcite and K-feldspar decrease gradually as the reaction time increases, and those of calcium, potassium and their oxides also decrease, resulting in the presence of corrosion cavities. The pH value of the reaction solution decreases from 7.19 to 5.68, and the corrosion rate of calcite is the fastest, followed by that of K-feldspar, and finally that of illite. During the reaction time, the mass corrosion rate and Poisson's ratio of reservoir rocks gradually increase, and the uniaxial compressive strength and elastic modulus gradually decrease. The uniaxial compressive strength of reservoir rocks shows an exponential function relationship with reaction time. The elastic modulus and Poisson's ratio show a cubic polynomial function relationship with reaction time. The strength prediction model for the reservoir rocks under chemical reaction is established. Taking the elastic modulus as the damage variable, the relationship between the uniaxial compressive strength and the damage variable of reservoir rocks is obtained, which reveals the chemical damage mechanism of reservoir rocks.
-
-
[1] 王焰新, 毛绪美, Donald DePaolo. CO2地质储存的纳米尺度流体-岩石相互作用研究[J]. 地球科学, 2011, 36(1): 163-171. WANG Yanxin, MAO Xumei, DEPAOLO D. Nanoscale fluid-rock interaction in CO2 geological storage[J]. Earth Science, 2011, 36(1): 163-171. (in Chinese)
[2] 任岚, 于志豪, 赵金洲, 等. 碳酸溶蚀对致密砂岩储层流动特征的影响: 以鄂尔多斯盆地长6致密砂岩为例[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2023, 42(2): 50-58. REN Lan, YU Zhihao, ZHAO Jinzhou, et al. Impact of carbonic acid dissolution on flow characteristics of tight sandstone reservoir: taking Chang 6 tight sandstone in Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2023, 42(2): 50-58. (in Chinese)
[3] 杨术刚, 蔡明玉, 张坤峰, 等. CO2-水-岩相互作用对CO2地质封存体物性影响研究进展及展望[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2023, 30(6): 80-91. YANG Shugang, CAI Mingyu, ZHANG Kunfeng, et al. Research progress and prospect of CO2-water-rock interaction on petrophysical properties of CO2 geological sequestration[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2023, 30(6): 80-91. (in Chinese)
[4] 李宁, 金之钧, 张士诚, 等. 水/超临界二氧化碳作用下的页岩微观力学特性[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2023, 50(4): 872-882. LI Ning, JIN Zhijun, ZHANG Shicheng, et al. Micro-mechanical properties of shale due to water/supercritical carbon dioxide-rock interaction[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(4): 872-882. (in Chinese)
[5] 李颖, 马寒松, 李海涛, 等. 超临界CO2对碳酸盐岩储层的溶蚀作用研究[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2023, 13(3): 288-295, 357. LI Ying, MA Hansong, LI Haitao, et al. Dissolution of supercritical CO2 on carbonate reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2023, 13(3): 288-295, 357. (in Chinese)
[6] 陈晨, 何邢益, 牛庆合, 等. 超临界CO2注入煤层对顶板岩石纵波速度及力学响应特征研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2021, 49(5): 98-104. CHEN Chen, HE Xingyi, NIU Qinghe, et al. Study on P-wave velocity and mechanical response characteristic of rock in coal seam roof with supercritical CO2 injection[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(5): 98-104. (in Chinese)
[7] 李四海, 马新仿, 张士诚, 等. CO2-水-岩作用对致密砂岩性质与裂缝扩展的影响[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(3): 312-318. LI Sihai, MA Xinfang, ZHANG Shicheng, et al. Experimental investigation on the influence of CO2-brine-rock interaction on tight sandstone properties and fracture propagation[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(3): 312-318. (in Chinese)
[8] FOROUTAN M, GHAZANFARI E, AMIRLATIFI A, et al. Variation of pore-network, mechanical and hydrological characteristics of sandstone specimens through CO2-enriched brine injection[J]. Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 2021, 26: 100217. doi: 10.1016/j.gete.2020.100217
[9] ZHANG Y H, ZAHNG Z K, ARIF M, et al. Carbonate rock mechanical response to CO2 flooding evaluated by a combined X-ray computed tomography-DEM method[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 84: 103675. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2020.103675
[10] AN Q Y, ZHANG Q S, LI X H, et al. Experimental study on alteration kinetics for predicting rock mechanics damage caused by SC-CO2[J]. Energy, 2022, 259: 1225026.
[11] 要丹, 刘财, 张民志. 海拉尔盆地非典型沉积岩中柯绿泥石和钠板石组合的发现及其石油地质意义[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2006, 21(3): 949-956. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2006.03.039 YAO Dan, LIU Cai, ZHANG Minzhi. Discovery of corrensite and allevardite in the extremely special reservers of Hailaer Basin and it's mining to genesis mineralogy[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2006, 21(3): 949-956. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2006.03.039
[12] 刘钦甫, 付正, 候丽华, 等. 海拉尔盆地贝尔凹陷兴安岭群储层黏土矿物组成及成因研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2008, 28(1): 43-47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2008.01.007 LIU Qinfu, FU Zheng, HOU Lihua, et al. Clay complexes and geneses of the Xing'anling group in the beier depression of the Hailar basin[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2008, 28(1): 43-47. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2008.01.007
[13] 田成, 李艳军, 曾卫东, 等. 海拉尔盆地贝尔凹陷储层成岩与储渗结构特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 2004, 23(4): 83-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2004.04.017 TIAN Cheng, LI Yanjun, ZENG Weidong, et al. Character of reservoir diagenesis and reservoir-permeater units in beir depression, Hailaer basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2004, 23(4): 83-87. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2004.04.017
[14] LIU S Q, MA J S, SANG S X, et al. The effects of supercritical CO2 on mesopore and macropore structure in bituminous and anthracite coal[J]. Fuel, 2018, 223: 32-43. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.03.036
[15] DU Y, SANG S X, WANG W F, et al. Experimental study of the reactions of supercritical CO2 and minerals in high-rank coal under formation conditions[J]. Energy & Fuels 2018, 32(2): 1115-1125.
[16] KASZUBA J P, JANECKY D R, SNOW M G. Carbon dioxide reaction processes in a model brine aquifer at 200℃ and 200 bars: implications for geologic sequestration of carbon[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2003, 18(7): 1065-1080. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00239-1
[17] KETZER J M, IGLESIAS R, EINLOFT S, et al. Water-rock-CO2 interactions in saline aquifers aimed for carbon dioxide storage: experimental and numerical modeling studies of the Rio Bonito Formation(Permian), southern Brazil[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2009, 24(5): 760-767. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2009.01.001
[18] XU T F, APPS J A, PRUESS K. Mineral sequestration of carbon dioxide in a sandstone-shale system[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005, 217(3/4): 295-318.
[19] 朱子涵, 李明远, 林梅钦, 等. 储层中CO2-水-岩石相互作用研究进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2011, 30(1): 104-112. ZHU Zihan, LI Mingyuan, LIN Meiqin, et al. Review of the CO2-water-rock interaction in reservoir[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2011, 30(1): 104-112. (in Chinese)
[20] HE B G, WANG J, ZHANG Y, et al. Microscopic failure of yellow sandstone with different-sized grains and mineral composition[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2023, 30(6): 2035-2047.
[21] HUO R K, LI S G, DING Y. Experimental study on physicochemical and mechanical properties of mortar subjected to acid corrosion[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2018(1): 3283907.
-
其他相关附件



 下载:
下载: