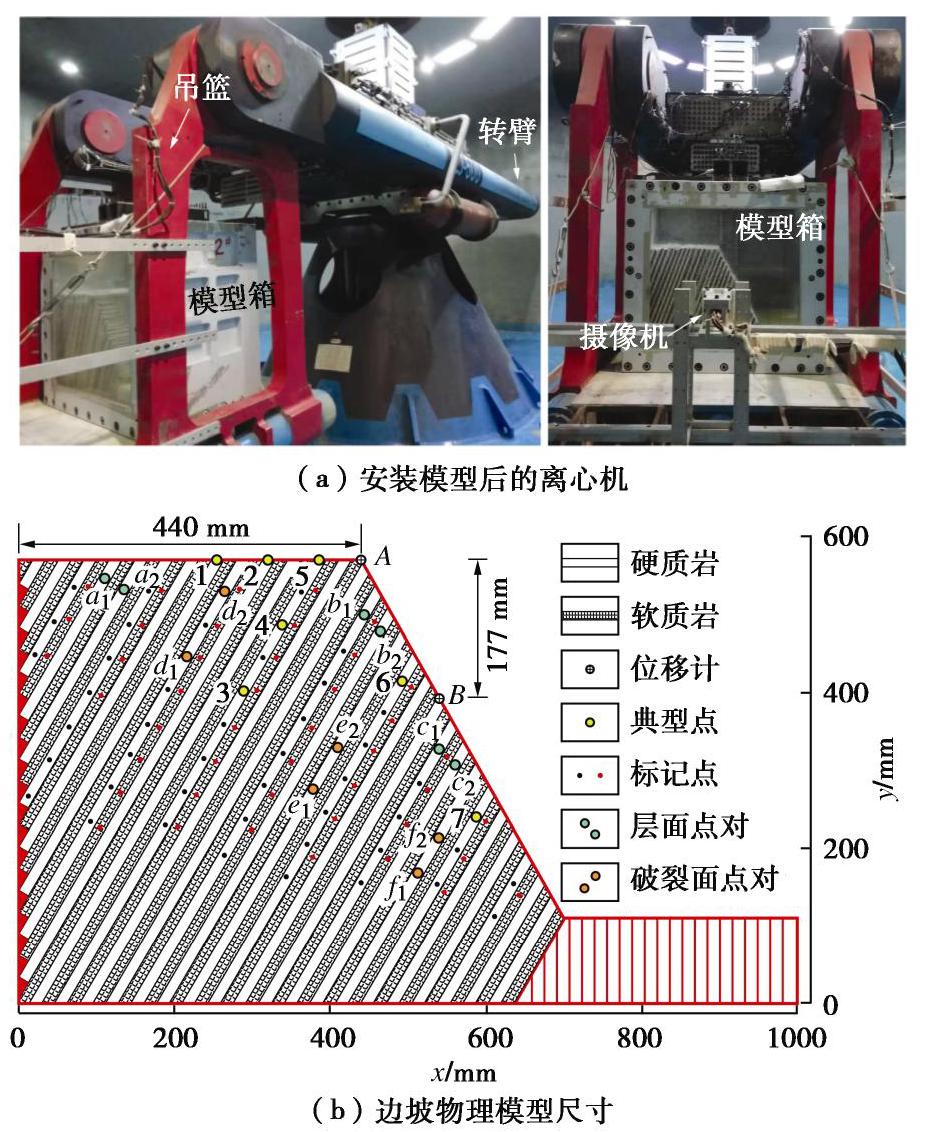
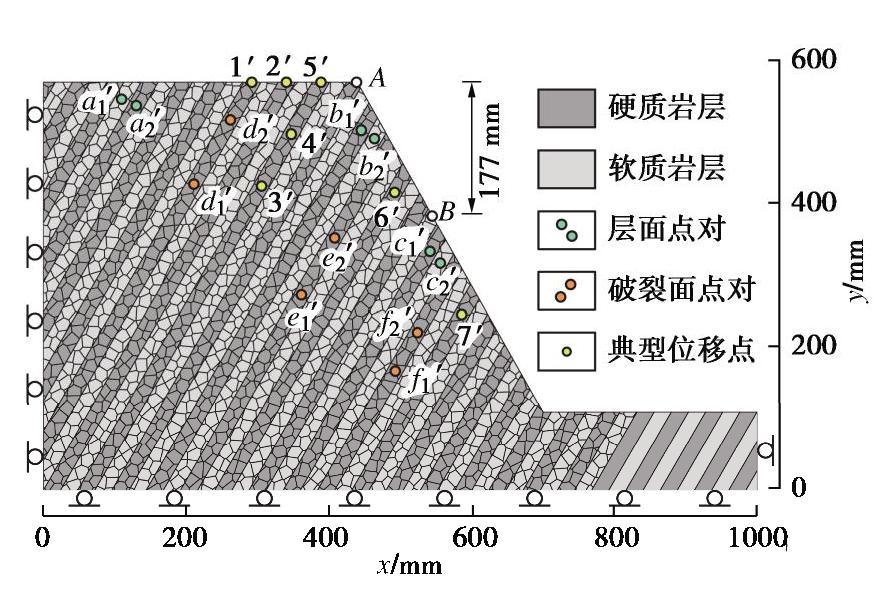
Centrifugal model test and numerical simulation for anaclinal rock slopes with soft-hard interbedded structures
-
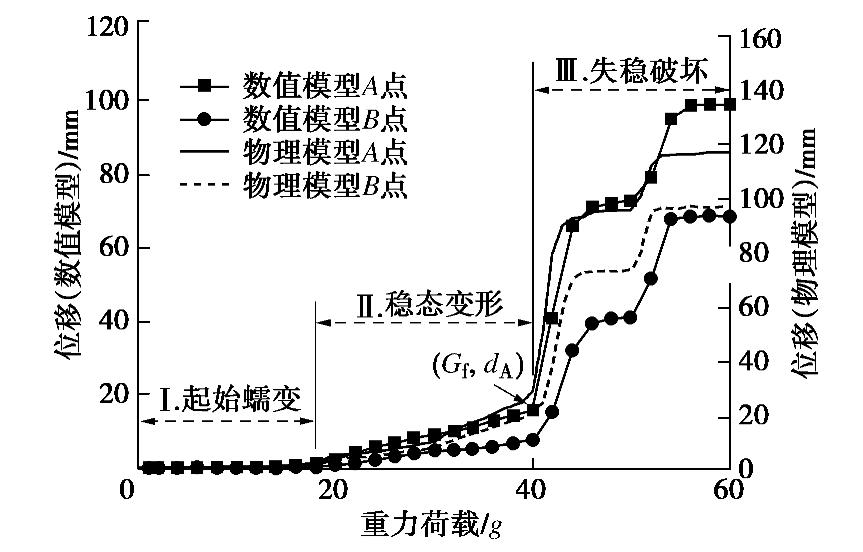
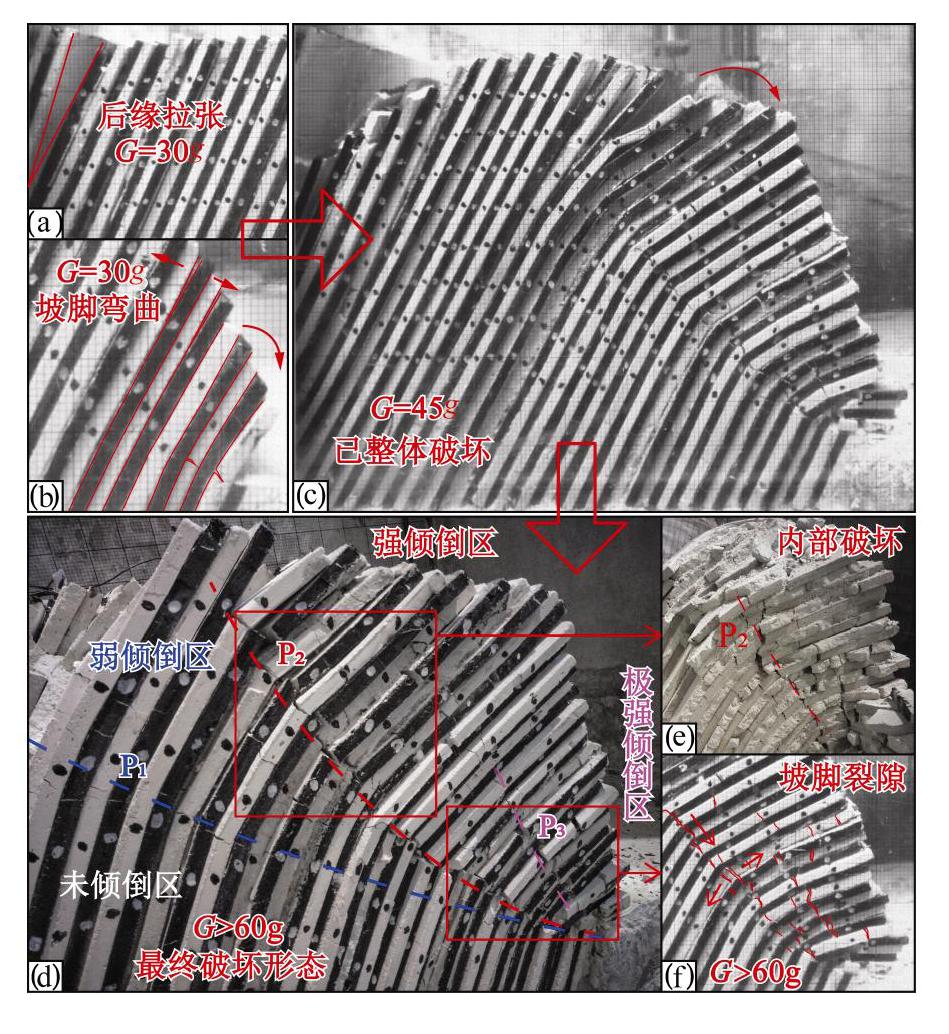
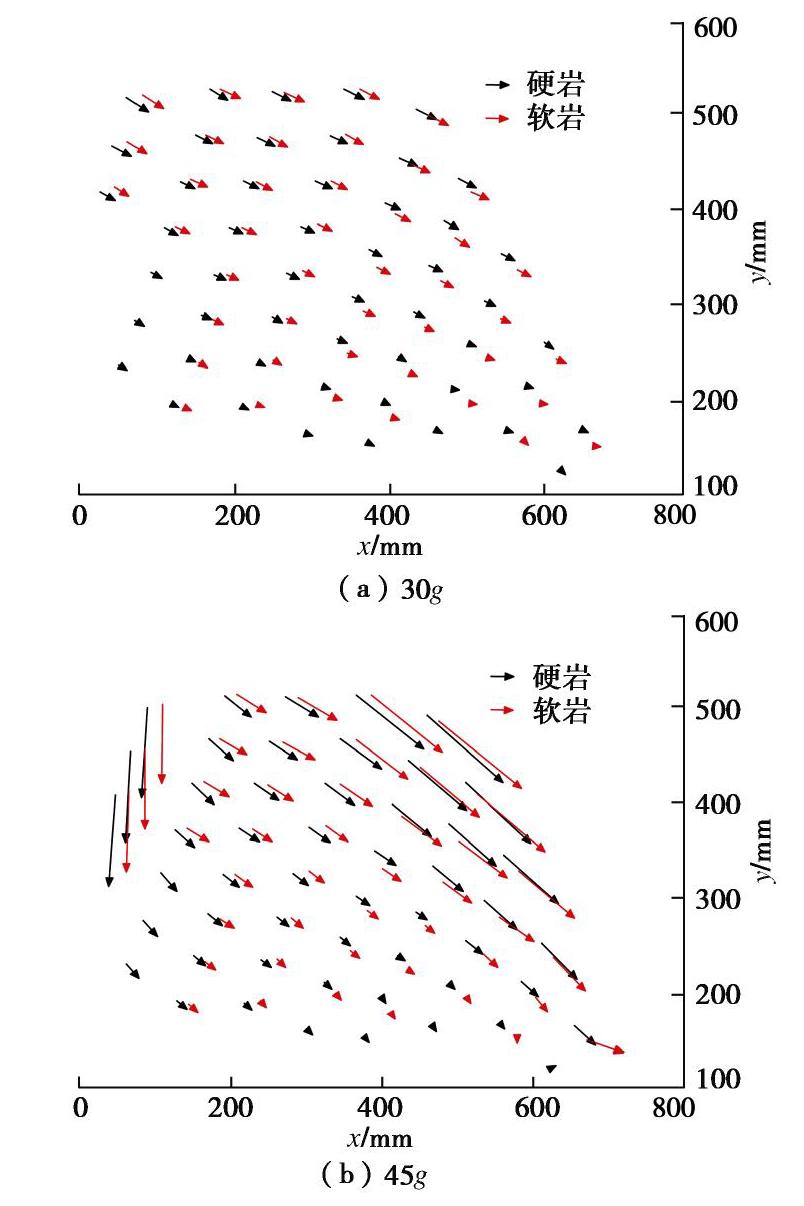
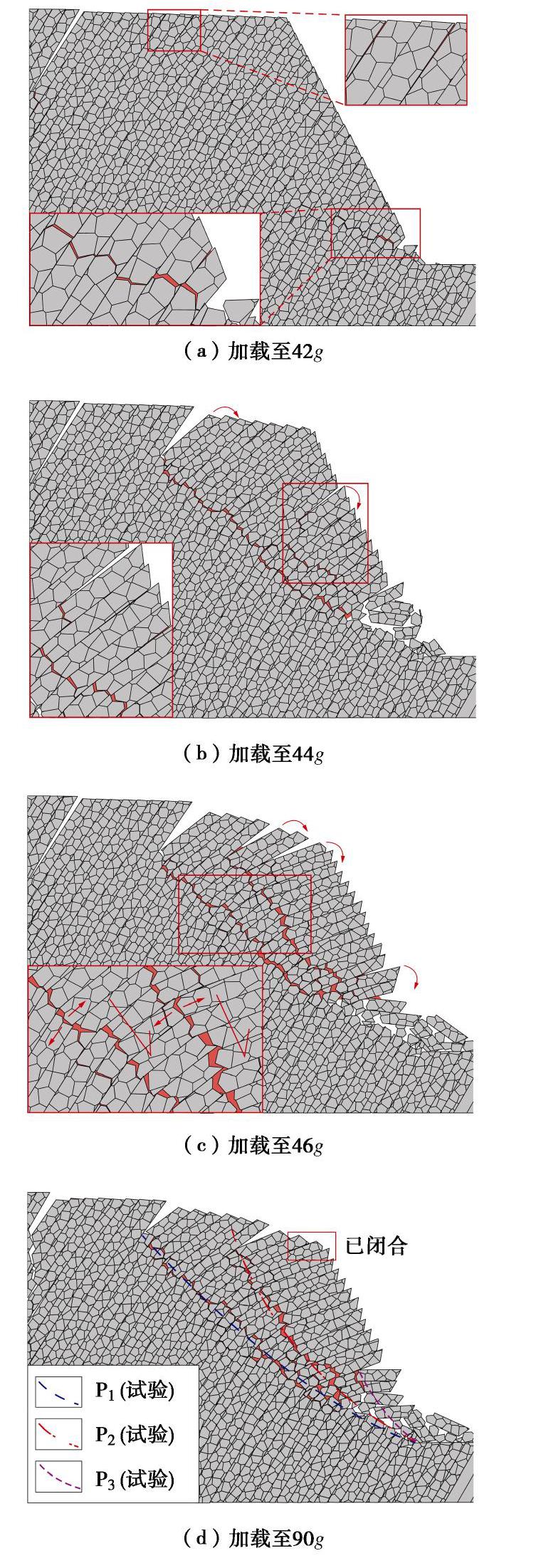
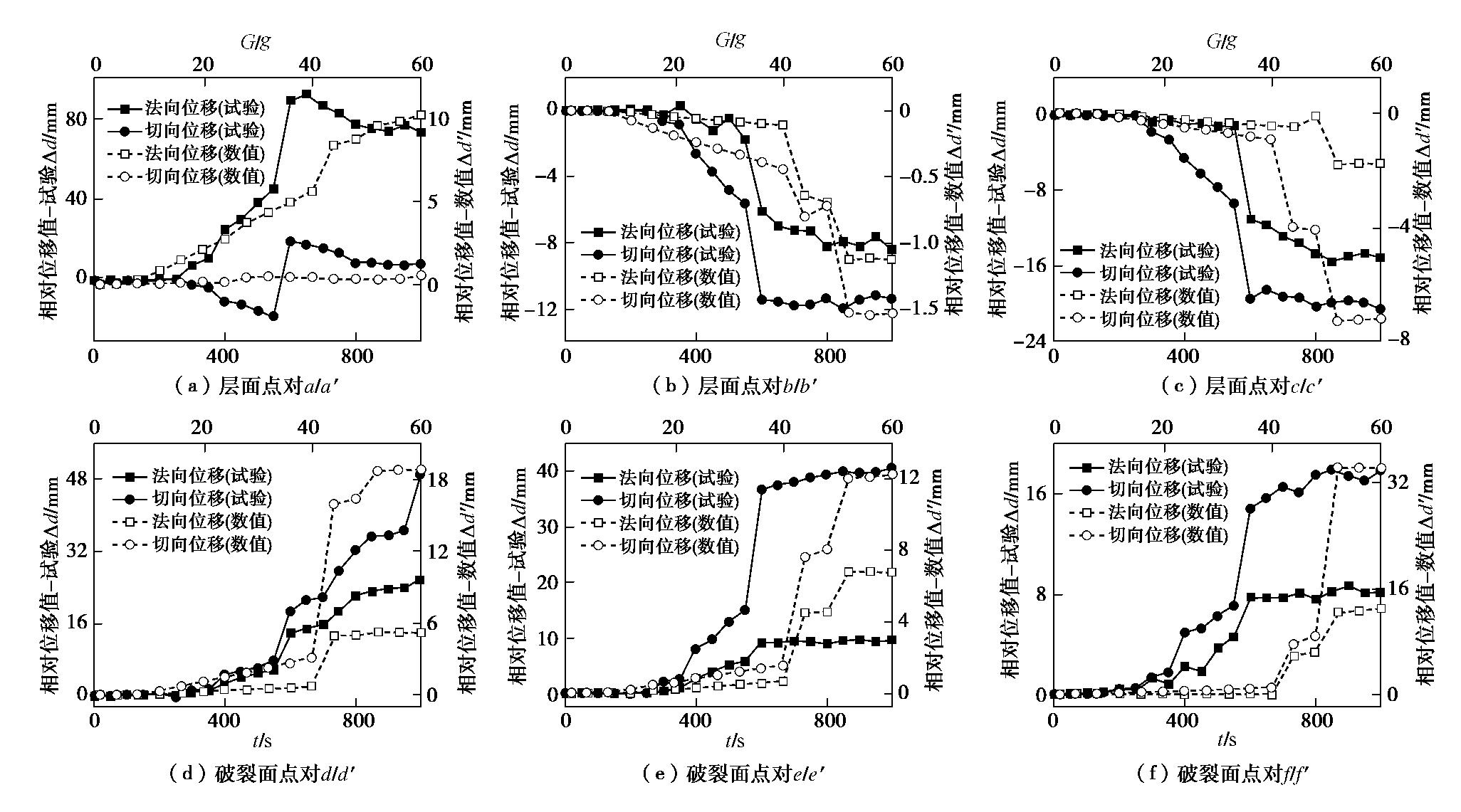
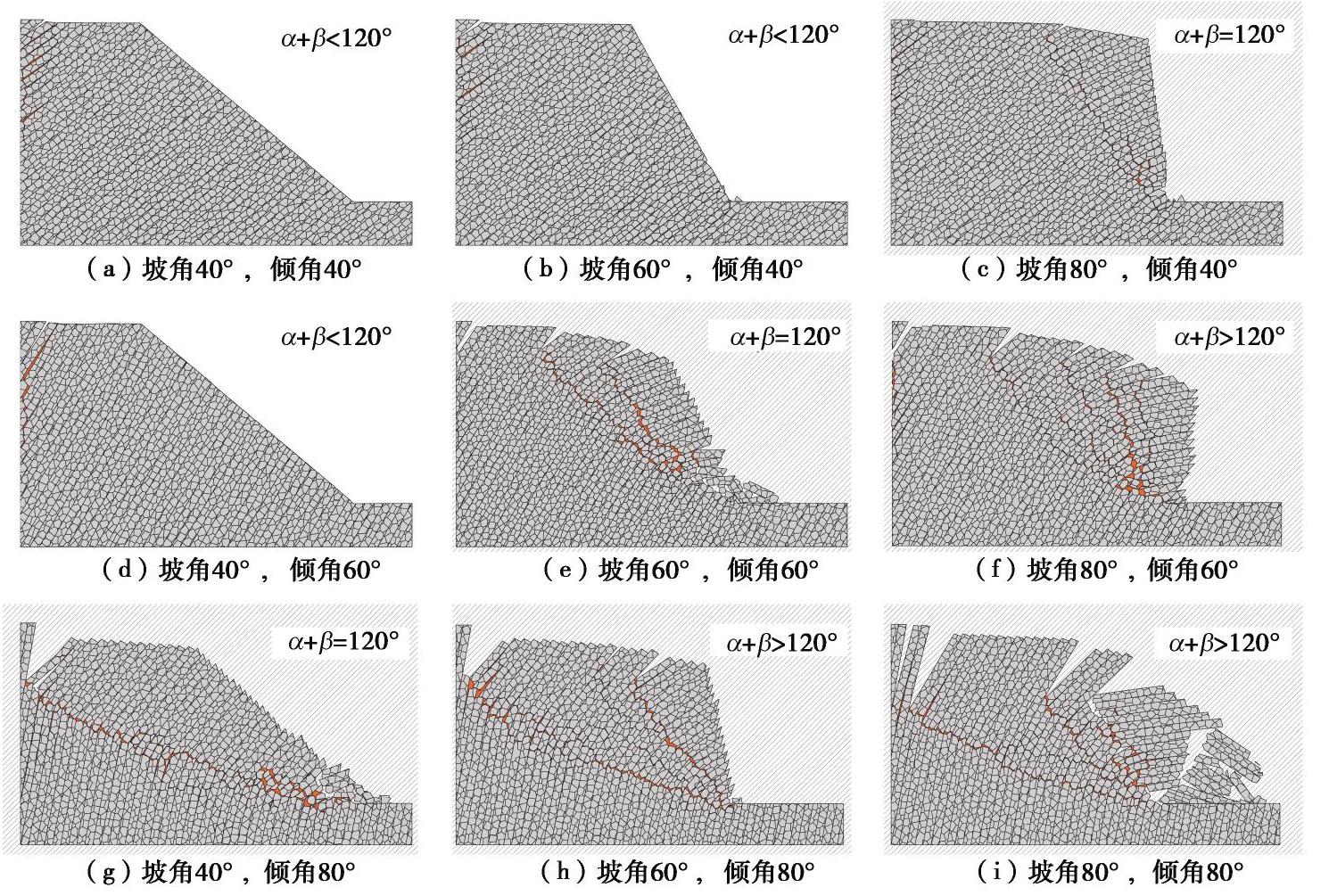
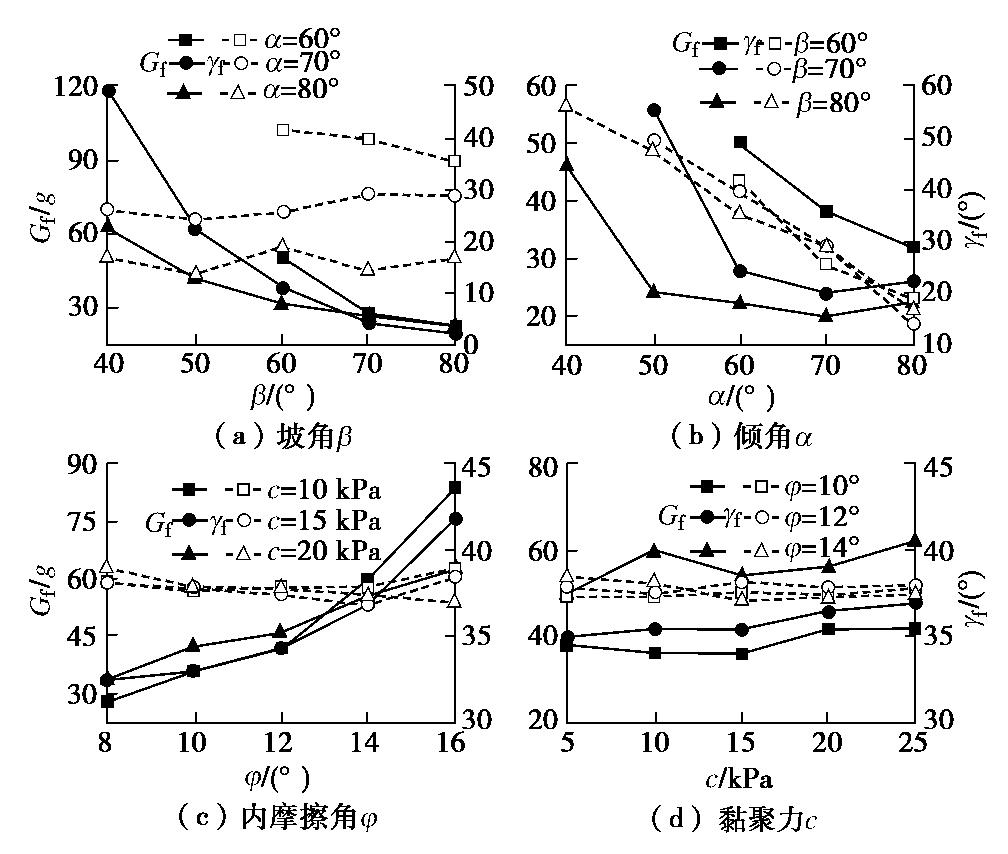
摘要: 西部山区工程建设揭露了众多大型弯曲倾倒变形体,多具有软硬互层结构,水平深度可达300 m。为进一步探明软硬互层反倾边坡的倾倒变形机制,融合离心模型试验与UDEC模拟,研究了此类边坡的破坏模式与影响因素,并通过点对分析,讨论了变形的力学机制。数值模拟时,在岩层内预置随机裂隙,获得了破裂面的演化规律。结果表明:数值模拟与试验的位移曲线及破裂面形态吻合较好,边坡变形可分为起始蠕变阶段、稳态变形阶段和失稳破坏阶段;坡体前部为压剪复合变形,后部则以拉张为主;边坡主破裂面呈弧形,由坡脚快速贯通至坡顶,整体为拉–剪性破裂面;坡体内发育3条破裂面,可作为分界线将变形体分为极强倾倒区、强倾倒区和弱倾倒区;坡脚岩体变形后期压致拉裂,逐渐折断脱离母岩,最终导致变形岩体沿不同的破裂面形成渐进后退式破坏;边坡在倾角与坡角之和大于等于120°时才较易破坏,坡角主要影响破坏难易,倾角则控制变形规模。Abstract: Most of the toppling deformations exposed in western China have soft-hard interlayer structures. The maximum depth even reaches 300 m. In order to further explore the toppling mechanism of soft-hard interbedded anaclinal slope, centrifugal model tests and UDEC simulation are combined. The mechanical mechanism of toppling is analyzed through point-to-point relative displacement. Random fissures are preset in rock plates of numerical slopes, and the evolution laws of failure surface are obtained. The results show that the displacement and fracture morphology of numerical model agree well with physical tests. The toppling process of slope can be divided into initial creep stage, steady deformation stage and failure stage. The front part of the slope is compression-shear composite deformation, while the rear part is tension-dominated. The main fracture surface runs through the whole slope rapidly from the slope toe with a curved shape, and is a tension-shear fracture surface. There are three fracture surfaces in the slope, which can be used as borders to divide the toppling slope into extremely strong toppling zone, strong toppling zone and weak toppling zone. At the anaphase of the deformation, the failure mode of slope toe turns into compression cracking, and the toe rocks gradually separate from parent rocks, leading to the progressive retrogressive failure of slope along different fracture surfaces. The slope is more likely to be damaged when the sum of the dip and slope angle is greater than or equal to 120°. The slope angle mainly affects the damage degree, and the dip controls the deformation scale.
-
-
表 1 相似材料最终配比
Table 1 Final ratios of similar materials
相似材料 石英砂 石膏 水泥 水 重晶石 硬岩 1 0.600 0.050 0.400 0 软岩 1 0.350 0.025 0.613 1 表 2 数值模型材料参数
Table 2 Material parameters of numerical model
材料 密度ρ/(kg·m-3) 法相刚度 kinkn/109 剪切刚度 kisks/109 黏聚力 cijkj/(104Pa) 抗拉强度 σitσt/(106Pa) 内摩擦角 φijφj /(°)残余摩擦角φijres/(°) 硬岩 2850 28 25 3.4×102 2.5 23 18 软岩 2250 14 12 1.4×102 1.1 15 10 层面 — 8 7.5 1.5 0 12 — -
[1] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(3): 433-454. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200703000.htm HUANG Run-qiu. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in china since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(3): 433-454. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200703000.htm
[2] 黄润秋, 李渝生, 严明. 斜坡倾倒变形的工程地质分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2017, 25(5): 1165-1181. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201705001.htm HUANG Run-qiu, LI Yu-sheng, YAN Ming. The implication and evaluation of toppling failure in engineering geology practice[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(5): 1165-1181. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201705001.htm
[3] 谭儒蛟, 杨旭朝, 胡瑞林. 反倾岩体边坡变形机制与稳定性评价研究综述[J]. 岩土力学, 2009, 30(增刊2): 479-484, 523. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2009S2104.htm TAN Ru-jiao, YANG Xu-zhao, HU Rui-lin. Review of deformation mechanism and stability analysis of anti-dipped rock slopes[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(S2): 479-484, 523. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2009S2104.htm
[4] 陈孝兵, 李渝生, 赵小平. 底摩擦重力试验在倾倒变形岩体稳定性研究中的应用[J]. 地学前缘, 2008, 15(2): 300-304. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200802038.htm CHEN Xiao-bing, LI Yu-sheng, ZHAO Xiao-ping. The application of bottom-friction gravity test to the study of the stability of the toppling rock mass[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(2): 300-304. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200802038.htm
[5] 郑达, 黄润秋, 黄刚. 地下开采作用下“反倾上硬下软”型斜坡崩塌形成机制研究——以贵州开阳磷矿崩塌为例[J]. 工程地质学报, 2014, 22(3): 464-473. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201403020.htm ZHENG Da, HUANG Run-qiu, HUANG Gang. Mechanism of rockfall with anti-dip and top hard-bottom soft rock by underground mining: a case study of rockfall in Kaiyang phosphorite, Guizhou[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(3): 464-473. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201403020.htm
[6] 包承纲. 我国岩土离心模拟技术的应用与发展[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2013, 30(11): 55-66, 71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJKB201311013.htm BAO Cheng-gang. Application and development of centrifugal modeling technology for geotechnical engineering in china[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2013, 30(11): 55-66, 71. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJKB201311013.htm
[7] ADHIKARY D P, DYSKIN A V, JEWELL R J, et al. A study of the mechanism of flexural toppling failure of rock slopes[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 1997, 30(2): 75-93.
[8] 汪小刚, 张建红, 赵毓芝, 等. 用离心模型研究岩石边坡的倾倒破坏[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1996, 18(5): 14-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC605.001.htm WANG Xiao-gang, ZHANG Jian-hong, ZHAO YU-zhi, et al. Investigations on mechanism of slope toppling failure by centrifuge model testing[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1996, 18(5): 14-21. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC605.001.htm
[9] 吴昊, 赵维, 年廷凯, 等. 反倾层状岩质边坡倾倒破坏的离心模型试验研究[J]. 水利学报, 2018, 49(2): 223-231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB201802009.htm WU Hao, ZHAO Wei, NIAN Ting-kai, et al. Study on the anti-dip layered rock slope toppling failure based on centrifuge model test[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2018, 49(2): 223-231. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB201802009.htm
[10] 蒋金阳. 软硬互层边坡倾倒变形破坏特征及支护效果的大型离心机试验研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2017. JIANG Jin-yang. Experimental Study on Failure Characteristics and Support Effect of Soft and Hard Interbedded Slope Toppling Deformation in Large Scale Centrifuge: A Case Study of the Right Bank Slope of the Right Bank of the Miao Tail[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2017. (in Chinese)
[11] ORR M C, SWINDELLS C F. Open pit toppling failures: Experience versus analysis[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Congress on Computer Method and Advance in Geomechanics, 1991, Cairus: 505-510.
[12] LEANDRO R A, IVÁN G, ROBERTO M. Analysis of a complex toppling-circular slope failure[J]. Engineering Geology, 2010, 114(1): 93-104.
[13] COGGAN J S, PINE R J. Application of distinct-element modelling to assess slope stability at Delabole slate quarry[C]//Cornwall, England: Trans Inst Min Metall (Sec A: Mining Industry), 1996.
[14] 孙东亚, 彭一江, 王兴珍. DDA数值方法在岩质边坡倾倒破坏分析中的应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2002, 21(1): 39-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200201007.htm SUN Dong-ya, PENG Yi-jiang, WANG Xing-zhen. Application of dda method in stability analysis of topple rock slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2002, 21(1): 39-42. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200201007.htm
[15] 马昊, 黄达, 石林. 基于断距–层厚特征统计的反倾边坡S型破坏演化数值模拟[J/OL]. 工程地质学报: 1-11[2020-05-09]. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-042. MA Hao, HUANG Da, SHI Lin. Numerical simulation of s-shaped failure evolution of anti-dip slope based on statistics of broken length and layerthickness[J/OL]. Journal of Engineering Geology. [2020-05-09] doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-042. (in Chinese)
[16] 程东幸, 刘大安, 丁恩保, 等. 层状反倾岩质边坡影响因素及反倾条件分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2005, 27(11): 1362-1366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC200511027.htm CHENG Dong-xing, LIU Da-an, DING En-bao, et al. Analysis on influential factors and toppling conditions of toppling rock slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2005, 27(11): 1362-1366. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC200511027.htm
[17] 赵华, 李文龙, 卫俊杰, 等. 反倾边坡倾倒变形演化过程的模型试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2018, 26(3): 749-757. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201803022.htm ZHAO Hua, LI Wen-long, WEI Jun-jie, et al. Model test study on toppling deformation evolution process of counter-tilt slope[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(3): 749-757. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201803022.htm
[18] Itasca Consulting Group Inc. UDEC (Universal Distinct Element Code), Version 6.0[M]. Minneapolis: Itasca Consulting Group Inc, 2014.
[19] DIEDERICHS M S, KAISER P K. Stability of large excavation in laminated hard rock masses: the voussoir analogue revisited[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 1999, 36(1): 97-117.
[20] ZHENG Y, CHEN C X, LIU T T, et al. Study on the mechanisms of flexural toppling failure in anti-inclined rock slopes using numerical and limit equilibrium models[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 237: 116-128.
[21] CHO N, MARTIN C D, SEGO D C. A clumped particle model for rock[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2007, 44(7): 997-1010.
[22] 左保成, 陈从新, 刘小巍, 等. 反倾岩质边坡破坏机理模型试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(19): 107-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200519016.htm ZUO Bao-cheng, CHEN Cong-xin, LIU Xiao-wei, et al. Modeling experiment study on failure mechanism of counter-tilt rock slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(19): 107-113. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200519016.htm
[23] 李世俊, 马昌慧, 刘应明, 等. 离心模型试验与数值模拟相结合研究采空边坡渐进破坏特性[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(4): 1577-1583, 1595. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201904041.htm LI Shi-jun, MA Chang-hui, LIU Ying-ming, et al. Centrifuge model tests and numerical simulation on progressive failure behavior of slope above a mine-out area[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(4): 1577-1583, 1595. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201904041.htm



 下载:
下载: