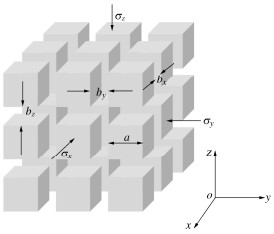
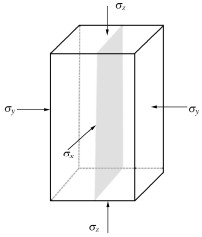
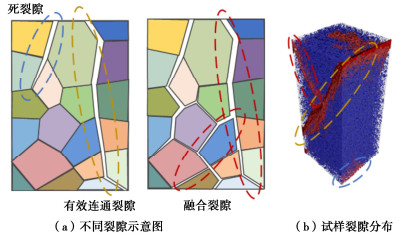
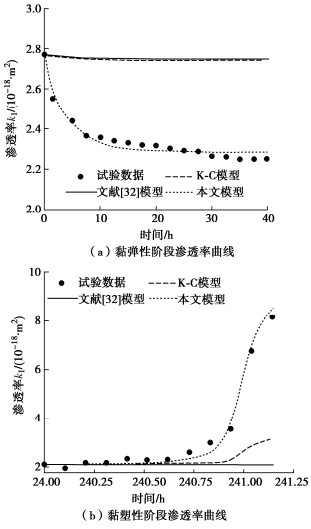
An anisotropic creep-permeability model for rock
-
摘要: 地下工程服役期较长,富水环境下围岩蠕变变形加剧,三向应力下围岩渗透性各向异性特征凸显,为了描述围岩蠕变过程中渗透率各向异性特征,将岩石简化为立方体模型,结合蠕变曲线特征分阶段建立岩石正交各向异性蠕变-渗透率模型。黏弹性阶段定义裂隙与岩石的黏滞系数比、引入侧向影响系数表示侧向应力对裂隙开度影响,黏塑性阶段引入表示裂隙对渗流通道影响的修正系数,结合岩石各向异性蠕变损伤模型、立方定律、含裂隙岩石渗透率方程,建立岩石正交各向异性蠕变-渗透率模型。利用真三轴条件下岩石蠕变-渗流试验结果对各向异性蠕变-渗透率模型进行验证,模拟了不同条件下渗透率演化。结果表明:与传统Kozeny-Carman(K-C)模型及已有各向异性蠕变-渗透率模型相比,提出的正交各向异性蠕变-渗透率模型精度更高,可以描述黏弹性阶段渗透率因岩石孔裂隙逐渐被压密而逐渐降低、加速蠕变阶段渗透率在裂隙逐渐汇聚影响下突增的变化趋势。对正交各向异性蠕变-渗透率模型的关键参数进行了敏感性分析,随着裂隙与岩石的黏滞系数比增加,渗透率衰减越快,渗透率稳定值越低,随着侧向影响系数越高渗透率初始衰减速率越高,渗透率稳定值越低;黏塑性阶段修正系数越高,加速蠕变阶段渗透率开始大幅增加。Abstract: The service life of underground engineering is so long that the creep deformation of the surrounding rock can be intensified in the water environment. The permeability shows an anisotropic trend under the three-dimension stresses. The rock is simplified as a cube model, and a rock creep permeability model is established in stages based on the creep characteristics. At the viscoelastic stage, the ratio of viscosity coefficients between cracks and rocks is defined, and a lateral influence coefficient is introduced to represent the influence of lateral stress on crack opening. In the viscoplastic stage, a correction coefficient is defined to represent the influences of cracks on seepage channels. An anisotropic creep-permeability model is established combined with the anisotropic creep damage model for rock, cubic law, and the permeability model for fractured rock. The creep-seepage tests under true triaxial conditions are performed, and the anisotropic creep-permeability model is validated. The parameters can be determined and the permeability evolution under different conditions is analyzed. The proposed model shows the higher accuracy by comparing with the traditional K-C model and the previously anisotropic creep-permeability model. It can be used to describe the trend that the permeability decreases due to the gradual compaction of pores and cracks at the viscoelastic stage, and it increases suddenly caused by the gradual convergence of cracks at the accelerated creep stage. The sensitivity analysis is conducted on the parameters in the anisotropic creep-permeability model. As the viscosity coefficient ratio increases, the permeability decays fast and the stable permeability decreases. As the viscosity coefficient increases, the initial decay rate of permeability increases, and the stable permeability decreases. At the accelerated creep stage, as the correction coefficient increases, the permeability increases significantly.
-
Keywords:
- creep-seepage /
- creep model /
- permeability model /
- orthogonal anisotropy
-
0. 引言
非饱和状态下的土体具有很高的强度[1],然而遇水湿化强度会迅速降低,局部可能达到饱和,该状态下的土压力值与非饱和条件下的值差别很大。多名学者统计显示大部分基坑事故都与水有关,此外,2019年6月8日南宁绿地中心基坑塌陷也是因为场地管道爆裂,非饱和土遇水湿化,作用在支护结构的土压力增大[2]。因此,亟需定量评估浸湿作用对非饱和土侧向土压力的影响,提出计算方法,减少此类事故发生。
目前,对非饱和土压力研究获得了很大进展,但现有研究多从理论出发进行公式推导,1961年Coleman等[3]提出双变量理论,Fredlund便得到净应力与吸力的双变量理论,之后得到了扩展的朗肯土压力理论,但是在平时的设计和研究中,仍然采用朗肯土压力理论[4]计算非饱和土压力。姚攀峰等[5]提出了与扩展型朗肯土压力不同的计算方法广义朗肯土压力计算方法,陈铁林等[6]解决水位变化及降水条件下的土压力计算问题,根据K0定义推导K0求解式。任传健等[7]结合Fredlund非饱和土抗剪切与强化准则和经典的朗肯土压计算公式,得出考虑降水变化的土压计算公式。汪丁建等[8]在饱和土朗肯土压力分析基础上,推导出降雨条件下非饱和朗肯土压力。王晓亮等[9]将降雨和蒸发对基质吸力的影响引入到非饱和土抗剪强度公式中,得到K0随降雨定性变化,但没有定量结果。
已有的大量研究充分表明水对静止土压力的影响不可忽略,但已有的计算公式复杂不实用,结果有待验证。导致现有非饱和土体仍采用饱和土理论的计算结果加安全储备来设计计算[10],安全系数是否足够不明确。为了使湿化条件下静止土压力增量的演化规律更明确,本文通过室内试验确定了其相关的变化规律、建立相应的计算模型,减小对安全施工的威胁。
1. 试验材料与方法
1.1 土料特性
取北京延庆地区原状粉质黏土进行烘干、碾碎、过0.25 mm筛备用,进行基本物理性质测试,依据《土工试验方法标准:GB/T50123—2019》[11],结果见表 1。
表 1 土的基本物理性质Table 1. Basic physical properties of soil最大干
密度/
(g·cm-3)最优含水率/% 液限
wL/%塑限wP/% 塑性指数IP 土粒相对密度GS 1.80 16.5 30.7 15.2 15.5 2.73 1.2 试验方案
选择干密度1.53 g/cm3(压实度0.85)、高度40 mm的标准环刀试样开展K0压缩试验,设5个不同的初始饱和度与4个不同的上覆荷载,具体方案见表 2。
表 2 浸水条件下非饱和粉质黏土试验方案Table 2. Test schemes under water immersion conditions上覆荷载/kPa 加载过程 初始饱和度 100/200/
300/400100(200/300/400)kPa→湿化→逐级加载至1600kPa 0.2/0.3/0.4/
0.5/0.61.3 试验过程
(1)仪器标定。本文采用JCY型K0固结仪来完成K0压缩试验,在气囊中充入与试样等体积的水,利用水各向等压特性标定仪器在竖向压力下对土压力的测量,根据试验数据拟合得到两仪器的标定系数[12]。
(2)制样并养护得到不同初始含水率试样。用饱和再风干的土样模拟经过了干湿循环的天然非饱和土,通过7 d密闭养护保证孔隙水分布均匀,见图 1。
(3)加上覆荷载待稳定后进行湿化饱和,湿化稳定后养护7 d,再完成后续设定加载至试验结束。
(4)卸压并整理仪器装置,将不同初始饱和度湿化前与湿化压缩后试样进行对比,如图 2所示。
2. 试验结果及规律
K0固结仪连接压力传感器采集数据,得到侧压力随时间变化关系[12],从而得到粉质黏土在5个不同初始饱和度Sr和4个不同上覆荷载P作用下发生湿化与湿化后继续加载的水平静止土压力-竖向压力的关系曲线,见图 3,因篇幅关系只展示Sr=0.2结果[12]。对于非饱和土一般采用水土合算计算土压力,此时侧压力传感器测量得到的相当于水土合算下的土压力。
湿化静止土压力增量Δσh统计见表 3,计算式为
Δσh=σw−σd。 (1) 表 3 湿化静止土压力增量计算值统计Table 3. Statistics of calculated increment static earth pressure初始饱和度Sr 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 100 kPa下增量值 35.14 25.10 17.41 12.5 3.53 200 kPa下增量值 68.95 48.38 33.32 22.97 6.31 300 kPa下增量值 95.01 68.95 47.86 29.99 8.98 400 kPa下增量值 118.02 90.00 60.99 35.97 10.11 式中:σd为上覆荷载作用下湿化前静止土压力大小;σw湿化饱和后静止土压力大小。
3. 静止土压力增量计算模型
3.1 湿化过程中静止土压力演变规律
不同初始饱和度湿化过程的增湿水平不同,可使用湿化前初始饱和度表示增湿水平,即:Sr=1的增湿水平为0,Sr越小增湿水平越大。
由表 3可以看到湿化时静止土压力都有不同程度的增大,且初始饱和度Sr越低或上覆荷载P越大,静止土压力增量越大。图 3数据显示,湿化后继续加载呈线性且斜率基本一致,表明K0值大小近似一致,Sr与P的不同不会影响湿化饱和后K0大小。可能原因是:静止土压力系数主要由有效内摩擦角决定,饱和后有效内摩擦角接近,因此湿化饱和后K0近似一致。
土体强度理论认为土颗粒间存在综合作用,包括吸力、胶结作用、德华力以及化学键等[4],非饱和土研究学者[13]一般认为土骨架受压为保证完整性依靠两部分力平衡:一是土颗粒间的基质吸力,取决于土体的含水量;另外是土颗粒间的胶结力,取决于土体内部的黏粒微量物质。静止土压力增量是由颗粒间胶结作用的减弱和基质吸力减小两方面原因引起的[14]。为推导计算模型引出中间变量0.65-Sr,如图 4所示,初始饱和度越小,湿化导致基质吸力减少量就越大,静止土压力增量就越大;湿化饱和后上覆荷载越大,对土体胶结力破坏就越大,如图 5所示,湿化饱和后的静止土压力增量,随上覆荷载增加而变大。
3.2 湿化过程中静止土压力增量计算模型
土压力增量Δσh与上覆荷载P,初始饱和度Sr都呈线性关系,双线性模型见式(2),P和Sr确定时有一次函数式(3),(4)。当变量n=(Sr+b1)=0.65−Sr时,土压力增量Δσh与n成正比例,k1k2m为斜率,见图 4。
Δσh=k1n×k2m, (2) k1n=k1(Sr+b1), (3) k2m=k2(P+b2)。 (4) P与其对应的k1k2m拟合得k1k2m = 0.60P+19.76,再将n代入式(2)中,得到式(5)。当初始饱和度Sr较大接近饱和土时,静止土压力增量为0,观察式(5),当饱和度Sr>0.65时,湿化不会引起静止土压力增加。
Δσh={(0.60P + 19.76)(0.65−Sr)(Sr⩽0.65)0 (Sr>0.65)。 (5) 为了更直观的表现增量的含义,将ΔSr=1−Sr代入式(5),得到最终的增量表达式如下:
Δσh={(0.60P+19.76)(ΔSr−0.35)(ΔSr⩾0.35)0(ΔSr<0.35)。 (6) 4. 挡土墙静止土压力计算案例分析
以延庆某深基坑为背景,结合勘察数据,对上文的模型进行试算。该基坑开挖深度23 m,上表面有8 kPa的均布荷载,施工阶段饱和度0.25,已勘测到自然地面以下34 m地层特性,土体基本为粉质黏土。
根据划分土层的重度与厚度计算出土层下表面荷载,并根据K0算出湿化前静止土压力σhi,K0按经验值取0.3。根据式(6)算出静止土压力增量Δσhi,接着计算出湿化后静止土压力σwi和σwi/σhi比值,计算值随深度变化绘制在图 6中,发现比值随深度增大而减小,但始终大于1.8,说明湿化对静止土压力影响较大。
由于本文采用重塑土进行试验,和天然土体湿化时侧压力变化结果不同,特别是黄土等结构性非饱和土,其湿化可能发生湿陷等行为,导致土压力演化较为复杂。本文研究结果仅适用于非结构性的非饱和土。
5. 结论
本文通过开展室内试验,定量评估浸湿作用对非饱和土侧向土压力的影响,实测浸湿饱和作用下静止土压力增量的变化规律,建立相应的计算模型,通过应用发现设计时必须重视湿化的影响,并得到以下3点结论。
(1)湿化饱和后,土体的静止土压力系数K0值与初始饱和度、上覆荷载无关。推测土体静止土压力系数K0值主要由有效内摩擦角决定,饱和后有效内摩擦角基本一致,故K0值大小近似一致。
(2)湿化前的初始饱和度越低,湿化饱和后的静止土压力增量越大;且湿化饱和后的静止土压力增量,随湿化时的上覆荷载增加而变大。
(3)基于试验数据和机理分析,得到了湿化条件下考虑上覆荷载与初始饱和度的双线性土压力增量计算模型;将其应用于某支挡工程,发现湿化后的土压力可达初始土压力1.8倍以上,设计时必须予以重视。
-
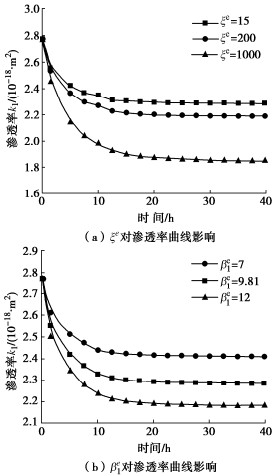
表 1 σ3=5 MPa,σ2=20 MPa条件下渗透率模型参数
Table 1 Parameters of permeability model under σ3=5 MPa and σ2=20 MPa
蠕变应力比 ξe βe1 βe2 βe3 ωp1 ωp2 ωp3 0.4 18 9.81 9.81 9.81 0.5 4.18 4.95 4.95 0.6 2.06 4.30 4.30 0.7 0.94 3.37 3.37 0.8 11.01 13.85 13.85 0.9 8.72 8.72 8.72 0.95 0.81 2.11 2.11 -
[1] 赵阳升. 岩体力学发展的一些回顾与若干未解之百年问题[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(7): 1297-1336. ZHAO Yangsheng. Retrospection on the development of rock mass mechanics and the summary of some unsolved centennial problems[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(7): 1297-1336. (in Chinese)
[2] LIU Z B, SHAO J F, XIE S Y, et al. Gas permeability evolution of clayey rocks in process of compressive creep test[J]. Materials Letters, 2015, 139: 422-425. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2014.10.139
[3] LIU Z B, SHAO J F. Strength behavior, creep failure and permeability change of a tight marble under triaxial compression[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2017, 50(3): 529-541. doi: 10.1007/s00603-016-1134-6
[4] ZHANG Y, SHAO J F, XU W Y, et al. Creep behaviour and permeability evolution of cataclastic sandstone in triaxial rheological tests[J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2015, 19(4): 496-519. doi: 10.1080/19648189.2014.960103
[5] 王如宾, 徐卫亚, 王伟, 等. 坝基硬岩蠕变特性试验及其蠕变全过程中的渗流规律[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(5): 960-969. WANG Rubin, XU Weiya, WANG Wei, et al. Experimental investigation on creep behaviors of hard rock in dam foundation and its seepage laws during complete process of rock creep[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(5): 960-969. (in Chinese)
[6] 张玉, 徐卫亚, 赵海斌, 等. 渗流-应力-流变耦合作用下破碎带砂岩渗透演化规律试验研究[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(4): 154-161. ZHANG Yu, XU Weiya, ZHAO Haibin, et al. Experimental investigation on permeability evolution of sandstone from fractured zone under coupling action of hydro-mechanical-creep[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2014, 38(4): 154-161. (in Chinese)
[7] 蔡婷婷, 冯增朝, 姜玉龙, 等. 不同温度应力下煤体蠕变中的渗流规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(增刊2): 101-107. CAI Tingting, FENG Zengchao, JIANG Yulong, et al. Seepage evolution in coal creep under different temperatures and different stresses[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(S2): 101-107. (in Chinese)
[8] XU P, YANG S Q. Permeability evolution of sandstone under short-term and long-term triaxial compression[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2016, 85: 152-164. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.03.016
[9] YANG S Q, HU B. Creep and permeability evolution behavior of red sandstone containing a single fissure under a confining pressure of 30 MPa[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 1900. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58595-2
[10] 马丹, 段宏宇, 张吉雄, 等. 断层破碎带岩体突水灾害的蠕变-冲蚀耦合力学特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(9): 1751-1763. MA Dan, DUAN Hongyu, ZHANG Jixiong, et al. Experimental investigation of creep-erosion coupling mechanical properties of water inrush hazards in fault fracture rock masses[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(9): 1751-1763. (in Chinese)
[11] 王凯, 郭阳阳, 王刚, 等. 真三轴路径下含瓦斯复合煤岩体渗流及力学破坏特性[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(1): 226-237. WANG Kai, GUO Yangyang, WANG Gang, et al. Seepage and mechanical failure characteristics of gas-bearing composite coal-rock under true triaxial path[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(01): 226-237. (in Chinese)
[12] 岳少飞, 王开, 张小强, 等. 不同加载速率无烟煤蠕变特性及能量演化规律[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(8): 3060-3075. YUE Shaofei, WANG Kai, ZHANG Xiaoqiang, et al. Creep properties and energy evolution of anthracite coal with different loading rates[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(8): 3060-3075. (in Chinese)
[13] 于冰冰, 李清, 赵桐德, 等. 基于应力与时间双阈值的岩石全时态非线性蠕变损伤模型[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(8): 1928-1944. YU Bingbing, LI Qing, ZHAO Tongde, et al. Full-time nonlinear creep damage model of fractured rock mass based on stress-time double threshold[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(8): 1928-1944. (in Chinese)
[14] 程爱平, 付子祥, 刘立顺, 等. 胶结充填体蠕变硬化-损伤特征及非线性本构模型[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2022, 39(3): 449-457. CHENG Aiping, FU Zixiang, LIU Lishun, et al. Creep hardening-damage characteristics and nonlinear constitutive model of cemented backfill[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2022, 39(3): 449-457. (in Chinese)
[15] 程爱平, 戴顺意, 舒鹏飞, 等. 考虑应力水平和损伤的胶结充填体蠕变特性及本构模型[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(2): 439-449. CHENG Aiping, DAI Shunyi, SHU Pengfei, et al. Creep characteristics and constitutive model of cemented backfill considering stress and damage[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(2): 439-449. (in Chinese)
[16] LIU X Y, YU J, ZHANG J Z, et al. Anisotropic time-dependent deformation and damage constitutive model of rock under true triaxial compression[J]. Mechanics of Time-Dependent Materials, 2024, 28: 2177-2203. doi: 10.1007/s11043-023-09617-9
[17] 康红普, 伊康. 深部软岩巷道围岩扩容与流变特性模拟研究及应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(1): 15-33. KANG Hongpu, YI Kang. Simulation study on dilatant and rheologic properties of soft rocks surrounding deep roadway and its application[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(1): 15-33. (in Chinese)
[18] 贾善坡, 陈卫忠, 于洪丹, 等. 泥岩隧道施工过程中渗流场与应力场全耦合损伤模型研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2009, 30(1): 19-26. JIA Shanpo, CHEN Weizhong, YU Hongdan, et al. Research on seepage-stress coupling damage model of Boom clay during tunneling[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(1): 19-26. (in Chinese)
[19] 李祥春, 张良, 赵艺良. 常规三轴压力下含瓦斯煤蠕变-渗流演化规律[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2018, 50(4): 55-62. LI Xiangchun, ZHANG Liang, ZHAO Yiliang. Evolution of gas-filled coal creep-seepage under conventional triaxial compression[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2018, 50(4): 55-62. (in Chinese)
[20] ZHOU H W, WANG L J, RONG T L, et al. Creep-based permeability evolution in deep coal under unloading confining pressure[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2019, 65: 185-196. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2019.03.010
[21] ZHOU H W, ZHANG L, WANG X Y, et al. Effects of matrix-fracture interaction and creep deformation on permeability evolution of deep coal[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2020, 127: 104236.
[22] 刘帅奇, 马凤山, 郭捷, 等. 致密页岩缝网蠕变-渗流耦合规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(增): 9-18. LIU Shuaiqi, MA Fengshan, GUO Jie, et al. Study on the rules of creep-seepage coupling of dense shale fracturing network[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(S): 9-18. (in Chinese)
[23] 张雷, 周宏伟, 王向宇, 等考虑蠕变影响的深部煤体分数阶渗透率模型研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2020, 42(8): 1516-1524. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202008017 ZHANG Lei, ZHOU Hongwei, WANG Xiangyu, et al. Fractional permeability model for deep coal considering creep effect[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(8): 1516-1524. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202008017
[24] 王路军, 曹志国, 程建超, 等. 煤矿地下水库坝基层间岩体破坏及突渗力学模型[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(3): 1192-1208. WANG Lujun, CAO Zhiguo, CHENG Jianchao, et al. Failure analysis of rock strata between upper and lower coals under underground reservoir in coal mine and its critical percolation model of jumping permeability[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(3): 1192-1208. (in Chinese)
[25] 亓宪寅. 各向异性煤岩气-固耦合机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2017. QI Xianyin. Study on Gas-Solid Coupling Mechanism of Anisotropic Coal and Rock[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. (in Chinese)
[26] 刘文博, 张树光, 李若木. 一种基于能量耗散理论的岩石加速蠕变模型[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(9): 2741-2750. LIU Wenbo, ZHANG Shuguang, LI Ruomu. Accelerated creep model of rock based on energy dissipation theory[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(9): 2741-2750. (in Chinese)
[27] 沈才华, 张兵, 王文武. 一种基于应变能理论的加速蠕变本构模型[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(11): 2195-2200. SHEN Caihua, ZHANG Bing, WANG Wenwu. A new accelerated creep constitutive model based on the strain energy theory[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(11): 2195-2200. (in Chinese)
[28] 蒋邦友, 谭云亮, 王连国, 等. 基于Mogi-Coulomb准则的弹塑性损伤本构模型及其数值实现[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2019, 48(4): 784-792. JIANG Bangyou, TAN Yunliang, WANG Lianguo, et al. Development and numerical implementation of elastoplastic damage constitutive model for rock based on Mogi-Coulomb criterion[J]. Journal of China University of Ming & Technology, 2019, 48(4): 784-792. (in Chinese)
[29] REN C H, YU J, CAI Y Y, et al. A novel constitutive model with plastic internal and damage variables for brittle rocks[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2021, 248: 107731.
[30] REN C H, YU J, LIU X Y, et al. Cyclic constitutive equations of rock with coupled damage induced by compaction and cracking[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2022, 32(5): 1153-1165.
[31] REN C H, YU J, LIU S Y, et al. A plastic strain-induced damage model of porous rock suitable for different stress paths[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2022, 55(4): 1887-1906.
[32] YAO W, YU J, LIU X Y, et al. Experimental and theoretical investigation of coupled damage of rock under combined disturbance[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2023, 164: 105355.
[33] COOK N G W. Natural joints in rock: Mechanical, hydraulic and seismic behaviour and properties under normal stress[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1992, 29(3): 198-223.
[34] 张玉军, 琚晓冬. 双重孔隙-裂隙岩体中地下洞室稳定性的瞬弹-黏弹-黏塑性二维有限元分析[J]. 中国科学, 2016, 46(3): 276-285. ZHANG Yujun, JU Xiaodong. 2D transient elastic- viscoelastic-viscoplastic FEM analyses for stability of underground cavern located in dual-pore-fracture rock mass[J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2016, 46(3): 276-285. (in Chinese)
[35] 刘才华, 陈从新. 三轴应力作用下岩石单裂隙的渗流特性[J]. 自然科学进展, 2007, 17(7): 989-994. LIU Caihua, CHEN Congxin. Scepage characteristics of rcok single fracture under triaxial stress[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2007, 17(7): 989-994. (in Chinese)
[36] 孔洋, 朱珍德, 阮怀宁. 三向应力作用下节理岩体渗流-应力耦合特性[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(6): 2008-2016. KONG Yang, ZHU Zhende, RUAN Huaining. Stress- seepage coupling characteristics of jointed rock mass under three principal stresses[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(6): 2008-2016. (in Chinese)
[37] 蒋长宝, 余塘, 段敏克, 等. 瓦斯压力和应力对裂隙影响下的渗透率模型研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(2): 115-121. JIANG Changbao, YU Tang, DUAN Minke, et al. Study on permeability model under the influence of gas pressure and stress on fracture[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(2): 115-121. (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 叶帅华,辛亮亮. 基于桩-土界面剪切特性的单桩沉降和承载问题研究. 岩土力学. 2024(05): 1457-1471 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: