Rainfall infiltration model considering spatial variability of multiple layers in transition layer and its application in slope stability analysis
-
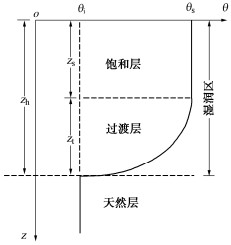
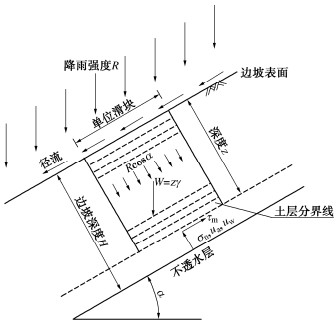
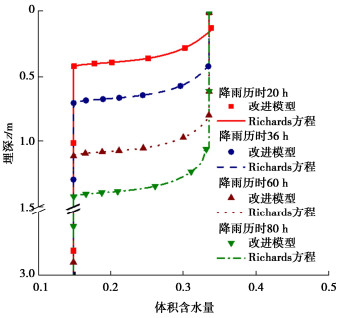
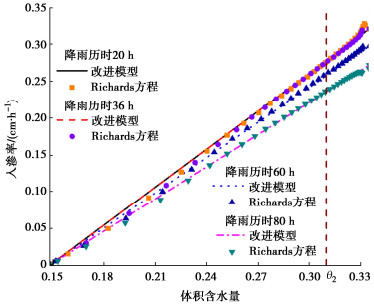
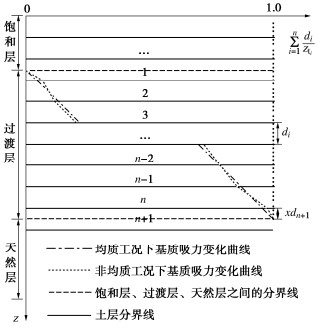
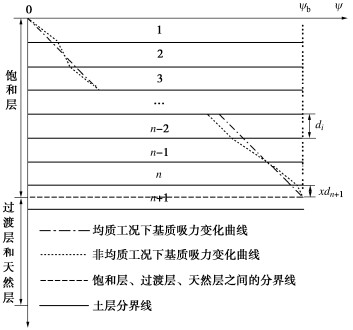
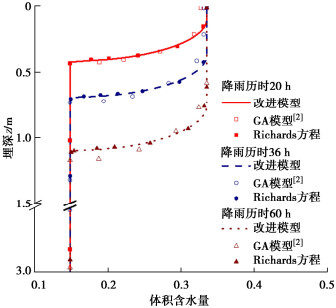
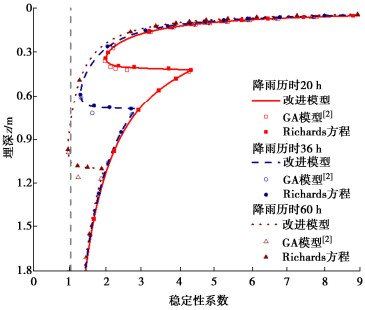
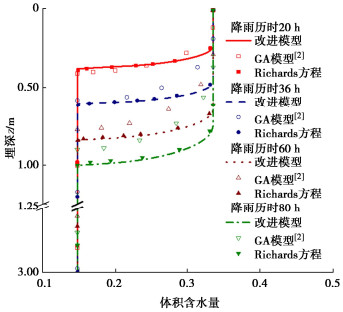
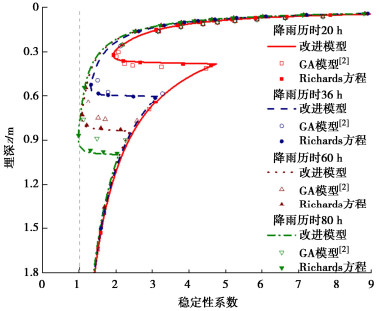
摘要: 建立合理的降雨入渗模型是揭示降雨诱发边坡失稳机制及灾害防控的重要前提。传统的Green-Ampt模型未考虑土壤分层及雨水入渗形成的过渡层分布,导致计算的入渗率存在较大偏差,难以适用于空间变异性边坡。提出土层入渗率的分层求解方法,可由不同土层间入渗率大小关系确定过渡层厚度,据此提出考虑土体饱和渗透系数空间变异性边坡降雨入渗分析的改进Green-Ampt模型。进而应用改进模型进行降雨入渗下均质和非均质无限长边坡渗流及稳定性分析,并与传统Green-Ampt模型计算结果和Richards方程数值解加以对比。分析结果表明:相比于传统的Green-Ampt模型,利用改进模型计算的边坡体积含水量分布和稳定性系数与Richards方程数值解更为吻合,可以更好地为非均质边坡降雨入渗分析及降雨型滑坡灾害防控提供理论依据。此外,发现过渡层厚度与土体饱和渗透系数、过渡层顶部入渗率和体积含水量之间存在依赖关系,而与雨水入渗的总深度无直接关系。
-
关键词:
- 边坡稳定性分析 /
- 空间变异性 /
- 降雨入渗 /
- 改进Green-Ampt模型 /
- 过渡层
Abstract: Establishing a reasonable rainfall infiltration model is an important prerequisite for revealing the rainfall-induced slope failure mechanism and disaster prevention and control. The traditional Green-Ampt model does not consider the distribution of soil stratification and transition layer formed by rainwater infiltration. This results in a large deviation on the calculated infiltration rate. Thus, the traditional model is difficult to apply to the spatially varying slopes. A method is proposed for calculating the infiltration rate of an arbitrary soil layer. The thickness of transition layer is estimated based on the relationship among the infiltration rates underlying different soil layers. Based on this, an improved Green-Ampt model is proposed to analyze the rainfall infiltration process in the slope considering the spatial variability of saturated hydraulic conductivity of soil. The improved Green-Ampt model is further applied to an infinite slope to analyze its seepage and stability for both homogeneous and heterogeneous soils under the rainfall infiltration. The results obtained from the improved model are systematically compared with those obtained from a traditional Green-Ampt model and the numerical solutions of Richards equation. The results indicate that the distribution of water content and factor of stability calculated from the proposed improved model are more consistent with the numerical solutions of Richards equation than those of the traditional Green-Ampt model. The proposed improved model can lay a solid theoretical foundation for analyzing the rainfall infiltration processes in the heterogeneous slopes, and formulating effective measures for the prevention and control of rainfall-induced landslide disasters. Additionally, it is found that there is a dependence between the thickness of transition layer and the saturated hydraulic conductivity as well as the infiltration rate and volumetric water content at its top, while it is not directly related to the total depth of rainwater infiltration. -
-
表 1 土体物理力学参数取值
Table 1 Values of physical mechanical parameters of soil
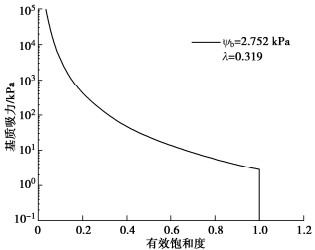
计算参数 单位 量纲 取值 饱和渗透系数ks cm/h LT-1 0.3 有效内摩擦角 ° 1 28 土体干重度 kN/m3 ML-2T-2 16.217 饱和体积含水量 1 0.335 初始体积含水量 1 0.148 残余体积含水量 1 0.068 有效黏聚力 kPa L-1MT-2 5 进气值 kPa L-1MT-2 2.752 初始基质吸力 kPa L-1MT-2 120.356 土体孔隙分布特征参数λ 1 0.319 注:是将初始体积含水量代入式(4)土水特征曲线函数中计算得到。 -
[1] FROUDE M J, PETLEY D N. Global fatal landslide occurrence from 2004 to 2016[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2018, 18(8): 2161-2181. doi: 10.5194/nhess-18-2161-2018
[2] 蒋水华, 刘贤, 黄劲松, 等. 多层非均质边坡降雨入渗分析的改进Green-Ampt模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2024, 46(6): 1177-1186. doi: 10.11779/CJGE20230205 JIANG Shuihua, LIU Xian, HUANG Jinsong, et al. An improved Green-Ampt model for rainfall infiltration analysis of multi-layered heterogeneous soil slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2024, 46(6): 1177-1186. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE20230205
[3] 王文焰, 汪志荣, 王全九, 等. 黄土中Green-Ampt入渗模型的改进与验证[J]. 水利学报, 2003, 34(5): 30-34. WANG Wenyan, WANG Zhirong, WANG Quanjiu, et al. Improvement and evaluation of the Green-Ampt model in loess soil[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2003, 34(5): 30-34. (in Chinese)
[4] 彭振阳, 黄介生, 伍靖伟, 等. 基于分层假设的Green-Ampt模型改进[J]. 水科学进展, 2012, 23(1): 59-66. PENG Zhenyang, HUANG Jiesheng, WU Jingwei, et al. Modification of Green-Ampt model based on the stratification hypothesis[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2012, 23(1): 59-66. (in Chinese)
[5] 王雪冬, 李世宇, 孙延峰, 等. 考虑非饱和浸润层厚度和累积入渗量的改进Green-Ampt模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2021, 48(6): 64-71. WANG Xuedong, LI Shiyu, SUN Yanfeng, et al. An improved Green-Ampt model for rainfall infiltration in the inner dumping site of an open pit coal mine[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(6): 64-71. (in Chinese)
[6] 黄良誉, 何廷全, 周成, 等. 边坡植被恢复中植被水泥土Green-Ampt入渗模型的改进与应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(增刊1): 183-188. doi: 10.11779/CJGE2022S1033 HUANG Liangyu, HE Tingquan, ZHOU Cheng, et al. Improvement and application of Green-Ampt infiltration model of vegetation cement soil in slope vegetation restoration[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(S1): 183-188. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE2022S1033
[7] ZHANG L L, ZHANG L M, TANG W H. Rainfall-induced slope failure considering variability of soil properties[J]. Géotechnique, 2005, 55(2): 183-188. doi: 10.1680/geot.2005.55.2.183
[8] DOU H Q, HAN T C, GONG X N, et al. Probabilistic slope stability analysis considering the variability of hydraulic conductivity under rainfall infiltration-redistribution conditions[J]. Engineering Geology, 2014, 183: 1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.09.005
[9] 蒋水华, 刘贤, 黄发明, 等. 考虑多参数空间变异性的降雨入渗边坡失稳机理及可靠度分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2020, 42(5): 900-907. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202005012 JIANG Shuihua, LIU Xian, HUANG Faming, et al. Failure mechanism and reliability analysis of soil slopes under rainfall infiltration considering spatial variability of multiple soil parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(5): 900-907. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202005012
[10] 马世国. 强降雨条件下基于Green-Ampt入渗模型的无限边坡稳定性研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2014. MA Shiguo. Study on Infinite Slope Stability under Heavy Rainfall Based on Green-Ampt Infiltration Model[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2014. (in Chinese)
[11] GREEN W H, AMPT G A. Studies on soil physics: flow of air and water through soils[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science, 1911, 4(1): 1-24.
[12] 雷志栋. 土壤水动力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1988. LEI Zhidong. Soil Hydrodynamics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1988. (in Chinese)
[13] FREDLUND D G, RAHARDJO H. Soil Mechanics for Unsaturated Soils[M]. New York: Wiley, 1993.
[14] BROOKS R H, COREY A T. Hydraulic Properties of Porous Media[M]. Fort Collins: Colorado State University, 1964.
[15] 李强, 贾森, 李鑫, 等. 考虑非饱和浸润区的改进Green-Ampt模型[J]. 岩土力学, 2022, 43(12): 3484-3492, 3502. LI Qiang, JIA Sen, LI Xin, et al. An improved Green-Ampt model considering unsaturated infiltration zone[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43(12): 3484-3492, 3502. (in Chinese)
[16] RICHARDS L A. Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums[J]. Physics, 1931, 1(5): 318-333.
[17] SIMUNEK J, VAN GENUCHTEN M T, SEJNA M. The Hydrus-1D software package for simulating the movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably saturated media, Version 4.16, HYDRUS Software Series 3[R]. California: Department of Environmental Sciences, University of California Riverside, 2013.
[18] CHO S E. Failure distribution analysis of shallow landslides under rainfall infiltration based on fragility curves[J]. Landslides, 2020, 17(1): 79-91.
[19] LU N, GODT J W, WU D T. A closed-form equation for effective stress in unsaturated soil[J]. Water Resources Research, 2010, 46(5): W05515.
[20] 陈正汉, 郭楠. 非饱和土与特殊土力学及工程应用研究的新进展[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(1): 1-54. CHEN Zhenghan, GUO Nan. New developments of mechanics and application for unsaturated soils and special soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(1): 1-54. (in Chinese)
[21] 赵振兴, 何建京. 水力学[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2010. ZHAO Zhenxing, HE Jianjing. Hydraulics[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2010. (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 黄娟,胡钟伟,余俊,李东凯. 基于黏性流体力学的液化土中桩基桩顶阻抗研究. 岩土工程学报. 2023(05): 1063-1071 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 柴少峰,王兰民,王平,郭海涛,夏晓雨,车高凤,王会娟. 石碑塬低角度黄土地层液化滑移特征与机理振动台试验研究. 岩土工程学报. 2023(12): 2565-2574 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)
-
其他相关附件



 下载:
下载: