Experimental investigation on evolution process of suffusion in gap-graded cohesionless soil
-
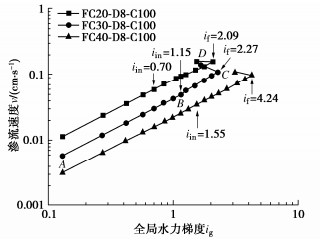
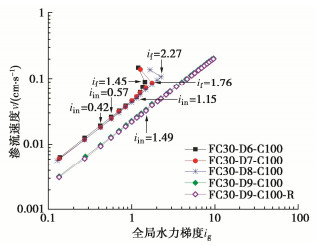
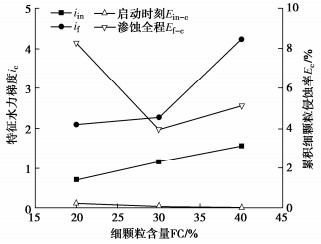
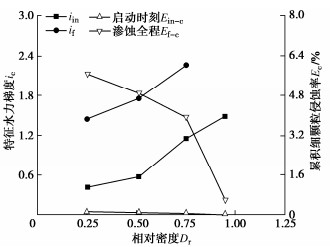
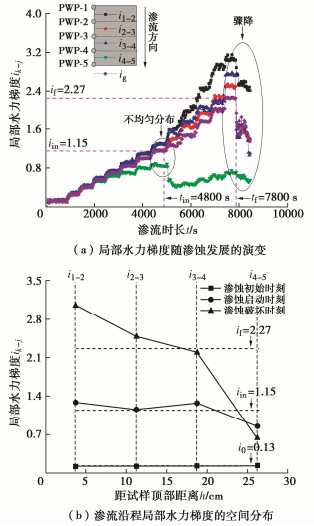
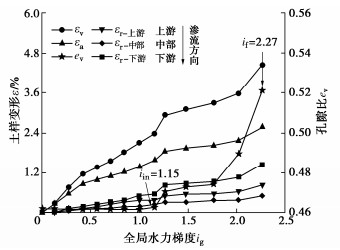
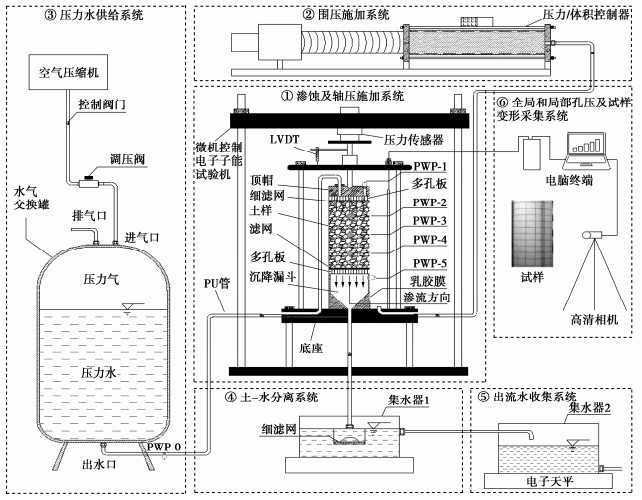
摘要: 渗蚀是指土体内部细颗粒在渗流作用下克服粒间作用力逐步脱离,在粗颗粒骨架孔隙中发生迁移,并可能引起土骨架应力重分布和变形的侵蚀过程。利用自制局部孔压可测的三轴渗蚀装置,研究了细颗粒含量和相对密度对不连续级配无黏性土渗蚀行为的影响,并根据渗流沿程局部水力梯度的时空演变揭示了土体渗蚀发展的演变特征。结果表明:不连续级配无黏性土启动和破坏水力梯度随细颗粒含量/相对密度的增大而增大;相对密度越大侵蚀程度越小,且等向应力下相对密度增大到一定值后,土体会由渗流不稳定状态转变为稳定状态;土体渗蚀启动的内部表现是局部水力梯度的突变及渗流沿程上的不均匀分布。土体渗蚀导致细颗粒流失,土体孔隙比增大,在等向应力条件下,会引发体积收缩现象。Abstract: The suffusion involves selective erosion and gradual migration of fine particles through the voids of soil skeleton formed by coarse particles under seepage flow. As a result, redistribution of soil skeleton stress and deformation of soil may be induced. In this study, a series of suffusion tests are carried out using the triaxial erosion apparatus with measurable local pore pressure. The effects of the initial fine particle content and initial relative density on the suffusion of a gap-graded cohesionless soil are investigated. According to the spatial-temporal evolution of local hydraulic gradients along seepage path, the evolution process of the suffusion is revealed. Test results show that both the initiation and the failure hydraulic gradients of the gap-graded cohesionless soil increase with the increase of the fine particle content and relative density. The cumulative loss of fine particles decreases significantly with the increase of the relative density. When the relative density increases to a certain value under isotropic stress condition, the gap-graded cohesionless soil will change from an unstable state of seepage to a stable one. Additionally, the internal manifestation of suffusion initiation of soil is the mutation and uneven distribution of local hydraulic gradient along seepage path. The suffusion will cause the loss of fine particles, as well as the increase of the void ratio. Under the isotropic stress condition, the volume shrinkage is induced.
-
-
表 1 试验材料基本物性参数
Table 1 Physical properties of test soils
基本物
性参数细粒
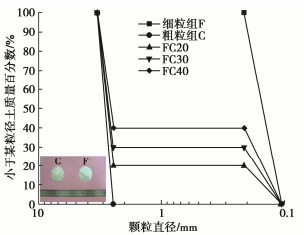
含量FC/%颗粒相对质量密度Gs 不均匀系数Cu 曲率系数Cc 最大孔隙比emax 最小孔隙比emin 细粒组 100 2.65 1.45 0.96 1.306 0.706 粗粒组 0 2.65 1.16 0.98 1.053 0.697 FC20 20 2.65 19.20 15.41 0.764 0.428 FC30 30 2.65 21.69 0.12 0.748 0.378 FC40 40 2.65 22.83 0.10 0.729 0.336 表 2 试验工况
Table 2 Test program
试验系列 方案编号 FC /% 干密度ρd/
(g·cm-3)相对密度Dr 初始孔隙比e 有效围压/kPa 固结后孔隙比e0 内部稳定性判定 Kézdi K-L FC20-D8-C100 20 0.87 0.461 U U FC30-D8-C100 30 0.78 0.462 U U 系列Ⅰ FC40-D8-C100 40 1.8 0.65 0.472 100 0.466 U U FC30-D8-C100-R1 30 0.75 0.462 U U FC30-D8-C100-R2 30 0.75 0.462 U U FC30-D6-C100 1.6 0.25 0.656 0.600 U U FC30-D7-C100 1.7 0.50 0.559 0.518 U U 系列Ⅱ FC30-D8-C100 30 1.8 0.75 0.472 100 0.462 U U FC30-D9-C100 1.9 0.95 0.395 0.388 U U FC30-D9-C100-R1 1.9 0.95 0.395 0.388 U U 注:方案编号中,FC为细颗粒含量;D为干密度;C(confining pressure)为等向应力即围压数值;R为重复性试验。内部稳定性判定中,U表示内部不稳定。Kézdi法中dc15/df85 > 4为内部不稳定,其中dc15为土体粗粒组15%质量百分数所对应粒径;df85为土体细粒组85%质量百分数所对应粒径。K-L法(Kenney和Lau方法)中(H/F)min<1为内部不稳定,其中H为土体任意粒径d对应质量百分数;F为土体任意粒径d~4d之间颗粒对应质量百分数。 表 3 可重复性试验结果
Table 3 Results of repeatability tests
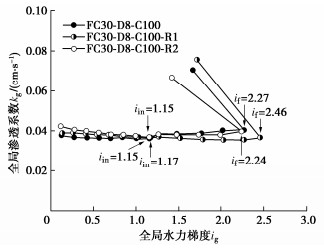
试验工况 iin Cv/% if Cv/% k0/(cm·s-1) Cv/% kin/(cm·s-1) Cv/% kav/(cm·s-1) Cv/% FC30-D8-C100 1.15 0.8 2.27 4.2 0.0381 4.5 0.0365 0.5 0.0378 1.8 FC30-D8-C100-R1 1.17 2.46 0.0392 0.0366 0.0375 FC30-D8-C100-R2 1.15 2.24 0.0423 0.0369 0.0389 -
[1] FOSTER M, FELL R, SPANNAGLE M. The statistics of embankment dam failures and accidents[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2000, 37(5): 1000-1024. doi: 10.1139/t00-030
[2] Iternational Commiss on Large Dams. Internal Erosion of Existing Dams, Levees and Dikes, and Their Toundations (ICOLD Bulletin 164)[R]. Paris: Iternational Commiss on Large Dams, 2017.
[3] KÉZDI, A. Soil Physics[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, 1979.
[4] 李伟一, 钱建固, 尹振宇, 等. 间断级配砂土渗流侵蚀现象的CFD-DEM模拟[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(11): 3191-3201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202111028.htm LI Weiyi, QIAN Jiangu, YIN Zhenyu, et al. Simulation of seepage erosion in gap graded sand soil using CFD-DEM[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(11): 3191-3201. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202111028.htm
[5] OUEIDAT M, BENAMAR A, BENNABI A. Effect of fine particles and soil heterogeneity on the initiation of suffusion[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 2021, 39(3): 2359-2371. doi: 10.1007/s10706-020-01632-8
[6] 宋林辉, 黄强, 闫迪, 等. 水力梯度对黏土渗透性影响的试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2018, 40(9): 1635-1641. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201809009 SONG Linhui, HUANG Qiang, YAN Di, et al. Experimental study on effect of hydraulic gradient on permeability of clay[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(9): 1635-1641. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201809009
[7] PACHIDEH V, MIR MOHAMMAD HOSSEINI S M. A new physical model for studying flow direction and other influencing parameters on the internal erosion of soils[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 2019, 42(6): 20170301. doi: 10.1520/GTJ20170301
[8] CHANG D S, ZHANG L M. Critical hydraulic gradients of internal erosion under complex stress states[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2013, 139(9): 1454-1467. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000871
[9] 陈勇, 闵泽鑫, 夏振尧, 等. 渗流作用下粉土质砂潜蚀演化特征与预测模型[J/OL]. 土木与环境工程学报(中英文), 2023: 1-9. CHEN Yong, MING Zexin, XIA Zhenyao, et al. Evolution characteristics and prediction model on suffusion of silty-sand subjected to seepage[J/OL]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2023: 1-9. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1218.TU.20210816.1145.003.html. (in Chinese)
[10] 刘杰, 谢定松. 砾石土渗透稳定特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(9): 2632-2638. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2012.09.009 LIU Jie, XIE Dingsong. Research on seepage stability experiment of gravelly soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(9): 2632-2638. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2012.09.009
[11] 陈生水, 凌华, 米占宽, 等. 大石峡砂砾石坝料渗透特性及其影响因素研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(1): 26-31. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201901002 CHEN Shengshui, LING Hua, MI Zhankuan, et al. Experimental study on permeability and its influencing factors for sandy gravel of Dashixia Dam[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(1): 26-31. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201901002
[12] 陈群, 谷宏海, 何昌荣. 砾石土防渗料-反滤料联合抗渗试验[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2012, 44(1): 13-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLH201201004.htm CHEN Qun, GU Honghai, HE Changrong. Combination seepage failure test of gravelly soil and the filter[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 2012, 44(1): 13-18. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLH201201004.htm
[13] LIANG Y, YEH T C J, ZHA Y Y, et al. Onset of suffusion in gap-graded soils under upward seepage[J]. Soils and Foundations, 2017, 57(5): 849-860. doi: 10.1016/j.sandf.2017.08.017
[14] LIU K W, QIU R Z, SU Q, et al. Suffusion response of well graded gravels in roadbed of non-ballasted high speed railway[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 284: 122848. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122848
[15] 袁涛, 蒋中明, 刘德谦, 等. 粗粒土渗透损伤特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(4): 1311-1316, 1336. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201804022.htm YUAN Tao, JIANG Zhongming, LIU Deqian, et al. Experiment on the seepage damage coarse grain soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(4): 1311-1316, 1336. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201804022.htm
[16] KE L, TAKAHASHI A. Strength reduction of cohesionless soil due to internal erosion induced by one-dimensional upward seepage flow[J]. Soils and Foundations, 2012, 52(4): 698-711. doi: 10.1016/j.sandf.2012.07.010
[17] WANG J J, QIU Z F. Anisotropic hydraulic conductivity and critical hydraulic gradient of a crushed sandstone–mudstone particle mixture[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2017, 35(1): 89-97.
[18] MOFFAT R, FANNIN R J, GARNER S J. Spatial and temporal progression of internal erosion in cohesionless soil[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2011, 48(3): 399-412. doi: 10.1139/T10-071
[19] 谷敬云, 罗玉龙, 张兴杰, 等. 基于平面激光诱导荧光的潜蚀可视化试验装置及其初步应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(6): 1287-1296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202106019.htm GU Jingyun, LUO Yulong, ZHANG Xingjie, et al. A suffusion visualization apparatus based on planar laser induced fluorescence and the preliminary application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(6): 1287-1296. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202106019.htm
[20] 梁越, 代磊, 魏琦. 基于透明土和粒子示踪技术的渗流侵蚀试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(6): 1133-1140. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202206018 LIANG Yue, DAI Lei, WEI Qi. Experimental study on seepage erosion based on transparent soil and particle tracing technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(6): 1133-1140. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202206018
[21] 常东升, 张利民. 土体渗透稳定性判定准则[J]. 岩土力学, 2011, 32(增刊1): 253-259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2011S1045.htm CHANG Dongsheng, ZHANG Limin. Internal stability criteria for soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(S1): 253-259. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2011S1045.htm
[22] 朱秦, 苏立君, 刘振宇, 等. 颗粒迁移作用下宽级配土渗透性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(1): 125-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202101014.htm ZHU Qin, SU Lijun, LIU Zhenyu, et al. Study of seepage in wide-grading soils with particles migration[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(1): 125-134. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202101014.htm
[23] 周健, 姚志雄, 张刚. 基于散体介质理论的砂土管涌机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(4): 749-756. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200804016.htm ZHOU Jian, YAO Zhixiong, ZHANG Gang. Research on piping mechanism in sandy soils based on discrete element theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(4): 749-756. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200804016.htm
[24] KE L, TAKAHASHI A. Experimental investigations on suffusion characteristics and its mechanical consequences on saturated cohesionless soil[J]. Soils and Foundations, 2014, 54(4): 713-730.
[25] 陈锐, 谭润锵, 赵燕茹, 等. 一种用于乳胶膜开孔后的密封装置及其使用方法: CN111042097A[P]. 2020-04-21. CHEN Rui, TAN Runqiang, ZHAO Yanru, et al. Sealing Device Used after Hole Forming of Latex Film and Application Method of Sealing Device: CN111042097A[P]. 2020-04-21. (in Chinese)
[26] KENNEY T C, LAU D. Internal stability of granular filters[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1985, 22(2): 215-225.
[27] CHANG D S, ZHANG L M, et al. A stress-controlled erosion apparatus for studying internal erosion in soils[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 2011, 34(6): 103889.
[28] CHEN C, ZHANG L M, ZHU H. A photographic method for measuring soil deformations during internal erosion under triaxial stress conditions[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 2018, 41(1): 20170031.
[29] RICHARDS K S, REDDY K R, et al. True triaxial piping test apparatus for evaluation of piping potential in earth structures[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 2010, 33(1): 102246.
[30] LIANG Y, ZENG C, WANG J J, et al. Constant gradient erosion apparatus for appraisal of piping behavior in upward seepage flow[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 2017, 40(4): 630-642.
[31] DENG G, ZHANG L L, CHEN R, et al. Experimental investigation on suffusion characteristics of cohesionless soils along horizontal seepage flow under controlled vertical stress[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2020, 8: 195.
-
其他相关附件



 下载:
下载: