Review on researches on horizontal swelling pressure of expansive soils after humidification
-
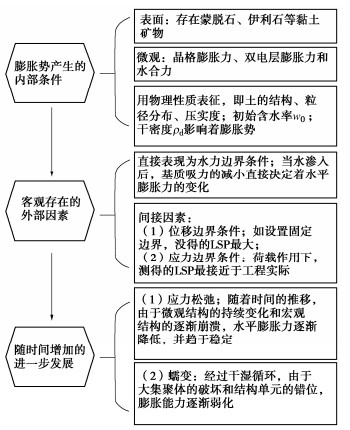
摘要: 膨胀土是一种富含蒙脱石、伊利石及高岭石的高塑性黏土,在增湿作用下会发生体积膨胀。若其横向膨胀变形受到约束,将会产生水平膨胀力,对岩土工程设施造成巨大危害。近年来,为减少相关损失,学者们通过大量室内试验,开发了新型理论方法及预测模型对水平膨胀力进行了深入研究。归纳总结并分析了膨胀土膨胀特性的影响因素和各因素对膨胀特性的影响规律,并从微观结构角度分析了各因素的影响机理。最后提出了降低侧向水平膨胀力的实用措施,分析了研究裂隙膨胀土水平膨胀力的重要性,并对其未来研究方向进行了展望。Abstract: The expansive soil is a kind of high plastic clay rich in montmorillonite, illite and kaolinite, in which volume expansion will occur under humidification. If the lateral swelling deformation is constrained, the horizontal swelling pressure will be generated, which will cause great harm to geotechnical engineering facilities. In recent years, in order to reduce the relative losses, domestic and foreign scholars have performed a large number of laboratory tests and developed new theoretical methods and prediction models for horizontal swelling pressure. The influence factors of swelling characteristics of expansive soils and the influence laws of various factors on the swelling characteristics are analyzed, and the influence mechanism of various factors is studied from the perspective of microstructure. Finally, the practical measures to reduce the lateral horizontal swelling force are proposed, the importance of studying the horizontal swelling force of fissured expansive soils is analyzed, and the future research direction is prospected.
-
-
表 1 水平膨胀力测量的试验装置
Table 1 Test devices for measuring horizontal swelling prossure
来源 仪器类型 仪器示意图 创新点 要点 Bag等[7] 改进的固结仪 
增加了加热
装置适用于膨胀土温度剧烈变化的工程情况,如膨胀土作核废料处置库时。 Zhang等[8] 改进的固结仪 
设计了可调节固结环,使用塑料丙烯酸分离器 静态压实后会产生初始径向应力,固结环可以消除静态压实产生的误差,分离器可提高传感器的精度 Liu等[9] 改进的固结仪 
通过气泵和水泵控制孔隙气压和孔隙水压 可测量特定净法向应力和基质吸力作用下的垂直膨胀应变和水平膨胀力,适用于深入非饱和土力学机理的膨胀试验研究 Puppala等[3] 改进的液压三轴仪 
使用乳胶膜将土水隔离,并用实心金属圆筒进行校准 可测量不同围压下的体积应变 谢云等[4] 改进的三维胀缩仪 
采用薄钢板作为平衡膨胀力的测力元件 可同时量测三向的变形和膨胀力 Ikizler等[5] 改进的三维胀缩仪 
设计了一个刚性钢制立方体盒 可测量恒体积下横向和垂直方向的膨胀力,所测值即为不容许地基发生变形条件下建筑物所受膨胀力,较符合工程实际。 李胜杰等[6] 改进的三维胀缩仪 
添加了边界条件切换系统 通过调整仪器拉杆松紧可模拟恒体积、恒应力和柔性等刚度边界条件。如恒体积条件为固定所有拉杆,恒应力条件控制拉杆1号、3号,松开拉杆2号、4号,柔性等刚度边界条件为松开拉杆1号,固定其余拉杆。 表 2 半经验和经验模型相关理论方法
Table 2 Theoretical methods of semi-empirical and empirical models
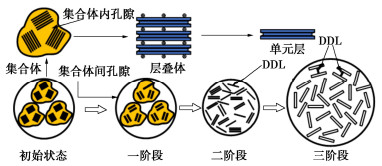
参考文献 公式 要点 Jiang等[10] 为了确定含水率系数,需进行系列试验;变形系数是一个经验参数,因土壤而不同。 Hong等[11] 半经验公式较为可靠,可用于工程实践,但参数的确定复杂。 Nelson等[12] 仅用于忽略摩擦表面上的侧向土压力的估算 Liu等[13] 可预测自由膨胀下考虑水平膨胀力的侧向土压力,但从初始不饱和状态到饱和状态的垂直膨胀压力难以预测。 Liu等[14] 仅需土水特征曲线(SWCC)和少量土壤性质(饱和土的弹性模量、最大干密度、泊松比),即可预测非饱和状态的水平膨胀力。 Abdollahi等[15] 只需要土壤水分特征曲线、泊松比以及初始和最终土壤含水率,即可预测非饱和状态下的水平膨胀力。但未考虑弹性模量随基质吸力的变化。 式中,为侧向土压力;为防止垂直膨胀所需的最小应力;为非饱和条件下的LSP;为含水率系数,即当前含水率与最大LSP的含水率之比;为变形系数,即当前变形与最大LSP时的变形之比;为试验中的最大LSP;为平均主应力的初始值;为水平膨胀应变;为平均主应力压缩指数;为饱和度从~1的系数;为体积含水率;为土壤的单位重量;z为计算点的深度;为静止土压力;为被动土压力;为参数,取值为0.7~1;为随基质吸力变化范围的平均弹性模量,为泊松比,为恒定体积的垂直膨胀压力(VSP);Sr为饱和度,为吸力为零时的垂直膨胀压力(压实膨胀土建议取55 kPa),为拟合参数;为土的最大干密度,为塑性指数,为土的吸力;为上覆压力引起的水平压力;分别为最终吸力和初始吸力。 -
[1] 廖世文. 膨胀土与铁路工程[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 1984. LIAO Shi-wen. Expansive Soil and Railway Engineering[M]. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House, 1984. (in Chinese)
[2] PUPPALA A J, CERATO A. Heave distress problems in chemically-treated sulfateladen materials[J]. Geo-Strata, 2009, 10(2): 28–32. https://cedb.asce.org/CEDBsearch/record.jsp?dockey=0169992
[3] PUPPALA A J, PEDARLA A, HOYOS L R, et al. A semi-empirical swell prediction model formulated from 'clay mineralogy and unsaturated soil' properties[J]. Engineering Geology, 2016, 200: 114–121. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.12.007
[4] 谢云, 陈正汉, 孙树国, 等. 重塑膨胀土的三向膨胀力试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2007, 28(8): 1636–1642. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.08.020 XIE Yun, CHEN Zheng-han, SUN Shu-guo, et al. Test research on three-dimensional swelling pressure of remolded expansive clay[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(8): 1636–1642. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.08.020
[5] IKIZLER S B, VEKLI M, DOGAN E, et al. Prediction of swelling pressures of expansive soils using soft computing methods[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2014, 24(2): 473–485. doi: 10.1007/s00521-012-1254-1
[6] 李胜杰, 唐朝生, 王东伟, 等. 多边界条件下缓冲/回填材料的膨胀特性[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(4): 700–706. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201904017.htm LI Sheng-jie, TANG Chao-sheng, WANG Dong-wei, et al. Effects of boundary conditions on swelling behavior of buffer/backfill materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(4): 700–706. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201904017.htm
[7] BAG R, RABBANI A. Effect of temperature on swelling pressure and compressibility characteristics of soil[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2017, 136: 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2016.10.043
[8] ZHANG R, LIU Z, ZHENG J, et al. Experimental evaluation of lateral swelling pressure of expansive soil fill behind a retaining wall[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2020, 32(2): 04019360. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0003032
[9] LIU Z N, ZHANG R, LIU Z J, et al. Experimental study on swelling behavior and its anisotropic evaluation of unsaturated expansive soil[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2021, 2021: 1–13.
[10] JIANG Z X, QIN X L. A new method for calculating lateral swell pressure in expansive soil[C]// Proc 7th Int Conf on Expansive Soils, ASCE, Reston, 1991: 233–238.
[11] HONG G T. Earth Pressures and Deformations in Civil Infrastructure in Expansive Soils[D]. Texas: Texas A & M University, 2008.
[12] NELSON J D, CHAO K C, OVERTON D D. Foundation Engineering for Expansive Soils[M]. John Wiley & Sons, 2015.
[13] LIU Y L, VANAPALLI S K. Influence of lateral swelling pressure on the geotechnical infrastructure in expansive soils[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2017, 143(6): 04017006. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001651
[14] LIU Y L, VANAPALLI S K. Load displacement analysis of a single pile in an unsaturated expansive soil[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2019, 106: 83–98. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2018.10.007
[15] ABDOLLAHI M, VAHEDIFARD F. Prediction of lateral swelling pressure in expansive soils[C]//Geo-Congress 2020. Minneapolis, 2020: 367–376.
[16] IKIZLER S B, VEKLI M, DOGAN E, et al. Prediction of swelling pressures of expansive soils using soft computing methods[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2014, 24(2): 473–485. doi: 10.1007/s00521-012-1254-1
[17] JALAL F E, XU Y F, IQBAL M, et al. Predictive modeling of swell-strength of expansive soils using artificial intelligence approaches: ANN, ANFIS and GEP[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 289: 112420. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112420
[18] SCHANZ T, KHAN M I, AL-BADRAN Y. An alternative approach for the use of DDL theory to estimate the swelling pressure of bentonites[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2013, 83/84: 383–390. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2013.07.018
[19] BHARAT T V, SIVAPULLAIAH P V, ALLAM M M. Novel procedure for the estimation of swelling pressures of compacted bentonites based on diffuse double layer theory[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 70(1): 303–314. doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-2128-7
[20] MITCHELL J, SOGA K. Fundamentals of Soil Behavior[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2005.
[21] GUO Y, (BILL) YU X. Characterizing the surface charge of clay minerals with Atomic Force Microscope (AFM)[J]. AIMS Materials Science, 2017, 4(3): 582–593. doi: 10.3934/matersci.2017.3.582
[22] 叶云雪, 邹维列, 韩仲, 等. 考虑初始状态影响的膨胀土一维膨胀特性研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(8): 1518–1525. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202108019.htm YE Yun-xue, ZOU Wei-lie, HAN Zhong, et al. One-dimensional swelling characteristics of expansive soils considering influence of initial states[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(8): 1518–1525. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC202108019.htm
[23] 刘海明, 赵超, 姚美良. 膨胀土改良技术研究进展[J]. 低温建筑技术, 2016, 38(11): 95–96, 100. doi: 10.13905/j.cnki.dwjz.2016.11.036 LIU Hai-ming, ZHAO Chao, YAO Mei-liang. Advances in the research on the improvement of expansive soil[J]. Low Temperature Architecture Technology, 2016, 38(11): 95–96, 100. (in Chinese) doi: 10.13905/j.cnki.dwjz.2016.11.036



 下载:
下载: