Research and application of relative density test method for large coarse-grained soil
-
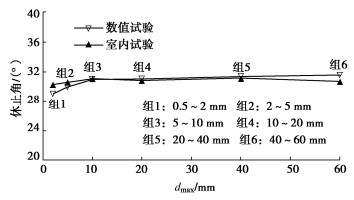
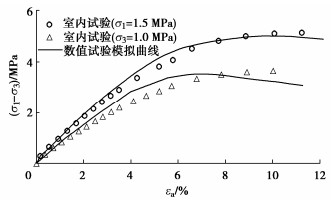
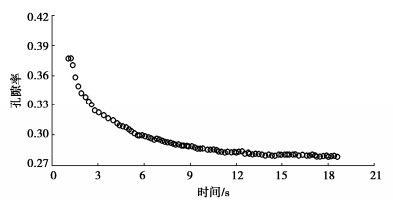
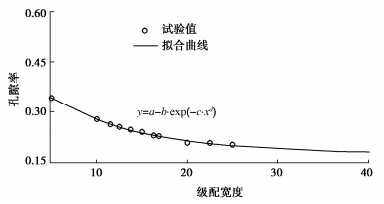
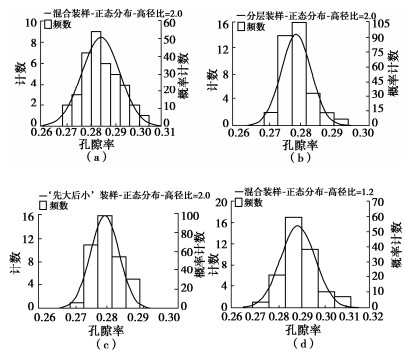
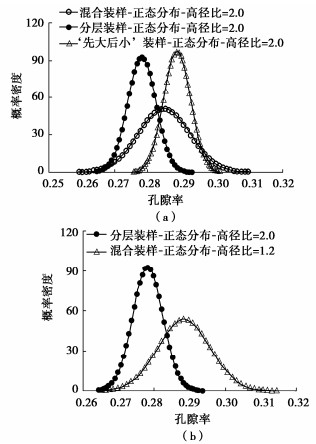
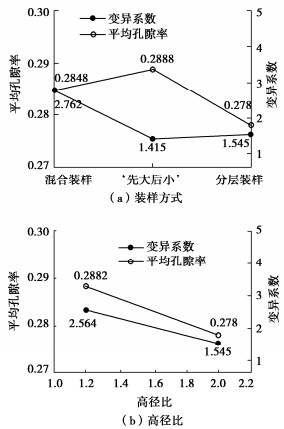
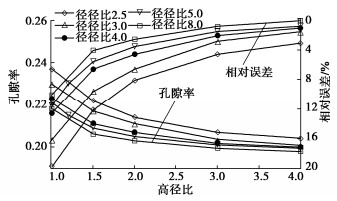
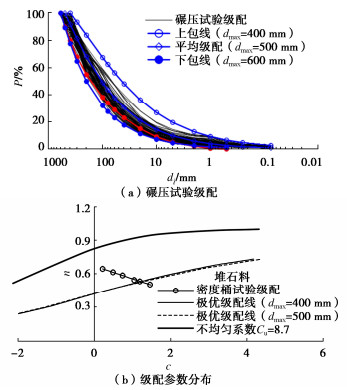
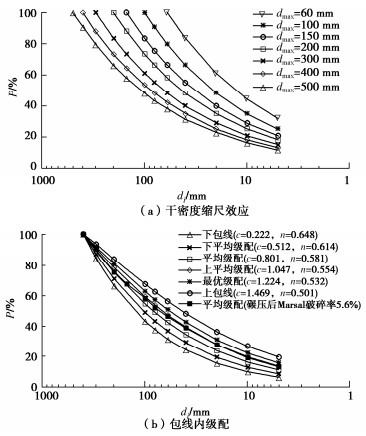
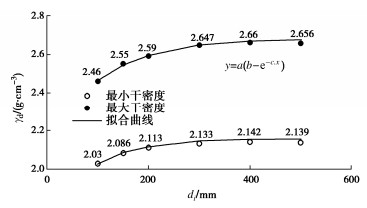
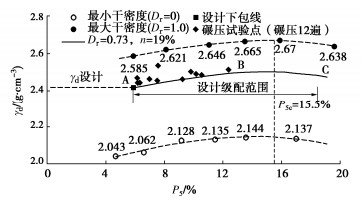
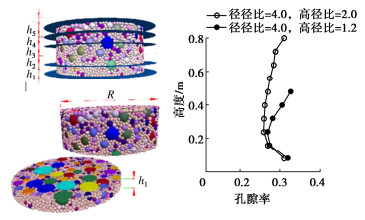
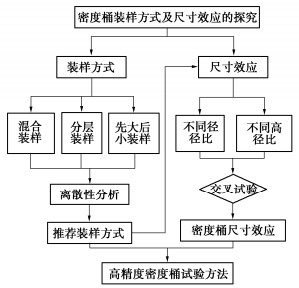
摘要: 结合拉哇特高面板坝堆石料的设计填筑级配,采用数值试验和现场试验手段,研究了影响大型密度桶试验精度的主要因素,提出了堆石料的孔隙率和相对密度双控填筑指标,并结合碾压试验成果验证其适用性。结果表明:①对于难以充分拌匀的大粒径粗粒土现场密度桶试验,采用人工分层装样方式,可有效减小试验结果的离散性。②密度桶尺寸的选择对试验结果影响较大,过大的尺寸带来较高的试验成本,甚至难以实施,过小的尺寸会带来明显的容器边界尺寸效应。综合现场实际情况,密度桶试验尺寸满足最小径径比和高径比分别在4.0,2.0左右时,试验结果的尺寸效应相对较小。③随着最大粒径的增加,密度桶试验的极值干密度均呈现增加的趋势,但当最大粒径达到300~400 mm以后,极值干密度基本稳定,试验结果可以作为压实设计和填筑质量控制的依据。④试验得到拉哇角闪片岩堆石料的双控填筑指标为:孔隙率不高于19%时相对密度不低于0.73。采用32 t振动碾振动碾压12遍,即可满足要求。⑤采用水平分层碾压的大粒径粗粒土,适当提高压实层厚度与最大粒径的比值,可以取得更佳的压实效率。堆石料取松铺层厚1.0 m左右、最大粒径400~600 mm,是一种较优的压实方案。研究成果可直接应用于大粒径粗粒土的填筑设计和评价,具有较强的应用价值。Abstract: Based on the design filling gradation of rockfill materials for Lawa super-high face dam, the main factors affecting the test accuracy of large density barrel are studied by means of numerical and field tests. The double-control index of rockfill porosity and relative density is proposed, and its applicability is verified by the results of rolling tests. The results show that: (1) For the field density barrel tests on the coarse-grained soil with a large particle size, which is difficult to be fully mixed, the method of artificial layering can effectively reduce the discreteness of the test results. (2) The selection of container size has a great influence on the test results, and too large size will bring higher test cost, even difficult to implement, while too small size will bring obvious container boundary size effect. Considering the actual situation in the field, the size effect of the test results is relatively small when the density barrel test size meets the minimum 'diameter to diameter ratio' and the 'height to diameter ratio' is about 4.0 and 2.0, respectively. (3) With the increase of the maximum particle size, the extreme dry density of density barrel tests shows an increasing trend. However, when the maximum particle size reaches 400 mm, the extreme dry density is basically stable. The test results can be used as the basis for compaction design and filling quality control. (4) The porosity is not higher than 19% and the relative density is not less than 0.75. The requirements can be met by using 32T vibration rolling 12 times. (5) For the soil with a large particle size with horizontal layered compaction, the ratio of the thickness of compaction layer to the maximum particle size can be appropriately increased, which can achieve better compaction efficiency. It is an optimal compaction scheme for rockfill materials to take a loose paving layer with a thickness of about 1.0 m and a maximum particle size of 400~600 mm. The research results can be directly applied to the compaction design and evaluation of coarse-grained soil with large particle size, which has a great application value.
-
Keywords:
- CFRD /
- coarse grained soil /
- filling standard /
- porosity rate /
- relative density /
- test method /
- dry density size effect
-
-
表 1 数值试验颗粒细观参数
Table 1 Micro-parameters of numerical tests
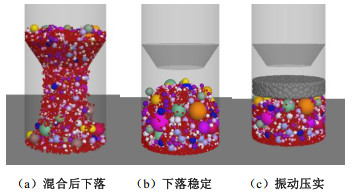
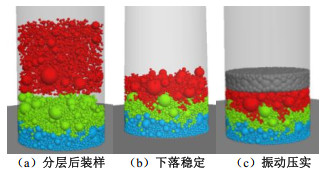
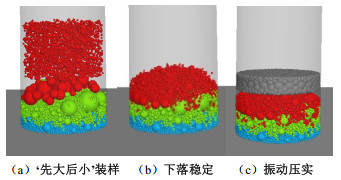
颗粒密度/(g·cm-3) 摩擦系数 抗转动系数 弹性模量/GPa 刚度比 2.975 0.4 0.4 1.6 2.0 表 2 不同装样方式试验方案
Table 2 Test schemes for different packing methods
密度桶尺寸 混合装样 分层装样 “先大后小”装样 合计/组 径径比=4.0 高径比=2.0 40 40 40 120 高径比=1.2 40 — — 40 表 3 填料施工摊铺碾压参数和压实效率
Table 3 Parameters and results of construction compaction
工程名 类型 最大粒径/mm H0/d0max 碾压遍数 孔隙率/% 两河口 堆石 800 1.0 8 ≤21 句容抽蓄 堆石 700 1.1 8 ≤19 阿尔塔什 堆石 600 1.5 8 ≤18 砂砾 400 2.0 10 ≤15 -
[1] Field and Laboratory Determination of Maximum Density in Coarse Sands and Gravels for Mica Dam: ASTM STP523—1973[S]. 1973.
[2] 史彦文. 大粒径砂卵石最大密度的研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 1981, 14(2): 53–58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC198102005.htm SHI Yan-wen. A study on maximum density of large sized sandy gravels[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 1981, 14(2): 53–58. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TMGC198102005.htm
[3] 朱晟, 钟春欣, 王京, 等. 高心墙堆石坝填筑标准的试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(3): 561–566. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201903019 ZHU Sheng, ZHONG Chun-xin, WANG Jing, et al. Experimental study on filling standard of high rockfill dams with soil core[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(3): 561–566. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201903019
[4] Relative Density Tests on Rock Fill at Carters Dam: ASTM STP523—1972[S]. 1972.
[5] BERTRAM G E. Field tests for compacted rockfill[M]//Embankment Dam Engineering. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 1973.
[6] Standard Test Methods for Maximum Index Density and Unit Weight of Soils Using A Vibratory Table : ASTM D4253-2016. [S]. 2016.
[7] 冯冠庆, 杨荫华. 堆石料最大指标密度室内试验方法的研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 1992, 14(5): 37–45. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1992.05.005 FENG Quan-qing, YANG Yin-hua. Laboratory test methods for maximum index density of rockfill materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1992, 14(5): 37–45. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.1992.05.005
[8] 朱晟, 王京, 钟春欣, 等. 堆石料干密度缩尺效应与制样标准研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2019, 38(5): 1073–1080. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201905021.htm ZHU Sheng, WANG Jing, ZHONG Chun-xin et al. Experimental study on scale effect of the dry density of rockfill material[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(5): 1073–1080. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201905021.htm
[9] 田堪良, 张慧莉, 张伯平, 等. 超径无粘性粗粒土填筑标准的确定方法[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 30(6): 193–197. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-9387.2002.06.047 SHI Xin-ling, CHEN Meng-hua, LIU Yun-peng. The combined circuit device of transducer and amplifier in water-measuring meter[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2002, 30(6): 193–197. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-9387.2002.06.047
[10] 土石筑坝材料碾压试验规程: NB/T 35016—2013[S]. 2013. Testing Specification on Material Compaction for Earth and Rock-Fill Dams: NB/T 35016—2013[S]. 2013. (in Chinese)
[11] 水电水利工程砂砾石料压实质量密度桶法检测技术规程: T/CEC 5001—2016[S]. 2016. Testing Technical Specification on Sand-Gravel Compaction Quality Test With Density Bucket Method for Hydropower Engineering: T/CEC 5001—2016[S]. 2016. (in Chinese)
[12] 王龙, 李彦坡, 王志坚, 等. 阿尔塔什水利枢纽混凝土面板堆石坝筑坝砂砾料相对密度试验及工程应用[J]. 水利水电技术, 2018, 49(增刊1): 21–26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJWJ2018S1004.htm WANG Long, LI Yan-po, WANG Zhi-jian, et al. Experiment on relative density of sand-gravel material for construction of concrete face rockfill dam for Altash Water Control Project and its engineering application[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2018, 49(S1): 21–26. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJWJ2018S1004.htm
[13] 张正勇, 包永侠, 唐德胜. 阿尔塔什大坝堆石料相对密度研究和施工应用[J]. 水力发电, 2018, 44(2): 40–42, 51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9342.2018.02.011 ZHANG Zheng-yong, BAO Yong-xia, TANG De-sheng. Study on relative density of rockfill material in aertashi dam and its application in dam construction[J]. Water Power, 2018, 44(2): 40–42, 51. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9342.2018.02.011
[14] 蔡加兴, 方德扬. 堆石料相对密度控制法试验及检测方法应用研究[J]. 人民长江, 2019, 50(12): 136–141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE201912025.htm CAl Jia-xing FANG De-yang. Controlling method of rockfill relative density and its detection method[J]. Yangtze River, 2019, 50(12): 136–141. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE201912025.htm
[15] 朱晟. 高面板坝堆石体的填筑质量控制指标研究与应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2020, 42(4): 610–615. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202004002 ZHU Sheng. Study and application of control indices for filling quality of high concrete face rockfill dams[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(4): 610–615. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202004002
[16] ZHOU B, HUANG R Q, WANG H B, et al. DEM investigation of particle anti-rotation effects on the micromechanical response of granular materials[J]. Granular Matter, 2013, 15(3): 315–326. doi: 10.1007/s10035-013-0409-9
[17] WENSRICH C M, KATTERFELD A. Rolling friction as a technique for modelling particle shape in DEM[J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 217: 409–417.
[18] Itasca Consulting Group Inc. Particle Flow Code in 3 Dimensions. User's Guide[R]. 1999.
[19] AI J, CHEN J F, ROTTER J M, et al. Assessment of rolling resistance models in discrete element simulations[J]. Powder Technology, 2011, 206(3): 269–282.
[20] 张宜, 周伟, 马刚, 等. 细颗粒截断粒径对堆石体力学特性影响的数值模拟[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2017, 50(3): 332–339. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSDD201703003.htm ZHANG Yi, ZHOU Wei, MA Gang, et al. Effect of minimum particle size on mechanical properties of rockfill materials by numerical simulation[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2017, 50(3): 332–339. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSDD201703003.htm
[21] 朱晟, 张露澄. 连续分布超径粗粒土的级配缩尺方法与适用条件[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2019, 38(9): 1895–1904. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201909017.htm ZHU Sheng, ZHANG Lu-cheng. A gradation scale method for continuously distributing super-diameter coarse-grained soils and its application conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(9): 1895–1904. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201909017.htm
[22] ICOLD. Concrete Face Rockfill Dams: Concepts for Design and Construction, Bulletin 141[R]. 2010.
[23] 朱晟, 卢知是, 刘纯, 等. 堆石体现场振动压实试验研究与应用[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(9): 2569–2577. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202109025.htm ZHU Sheng, LU Zhi-shi, LIU Chun, et al. Field vibration compaction test of rockfill and its application[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(9): 2569–2577. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX202109025.htm



 下载:
下载: