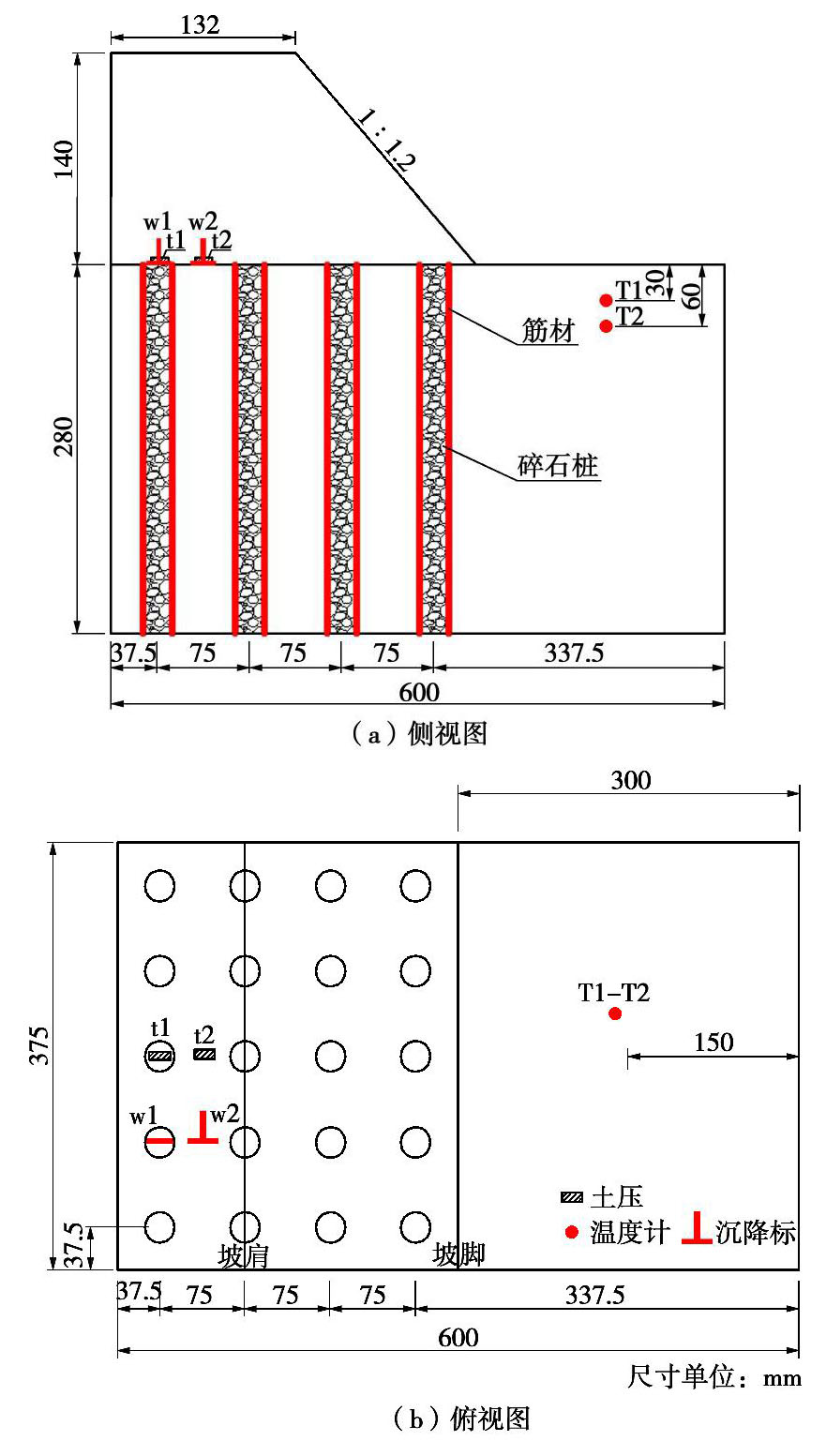
Behaviour of embankment on composite foundation with geosynthetic-encased stone columns under freeze-thaw condition
-
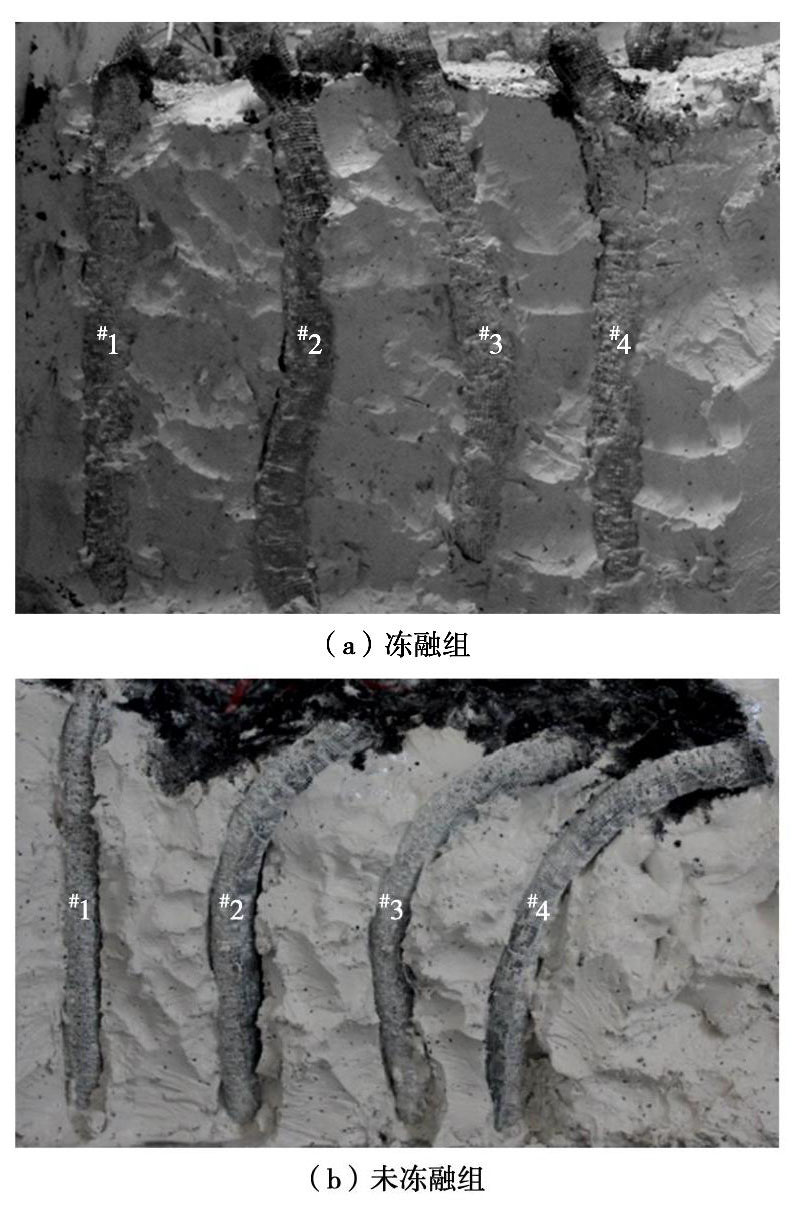
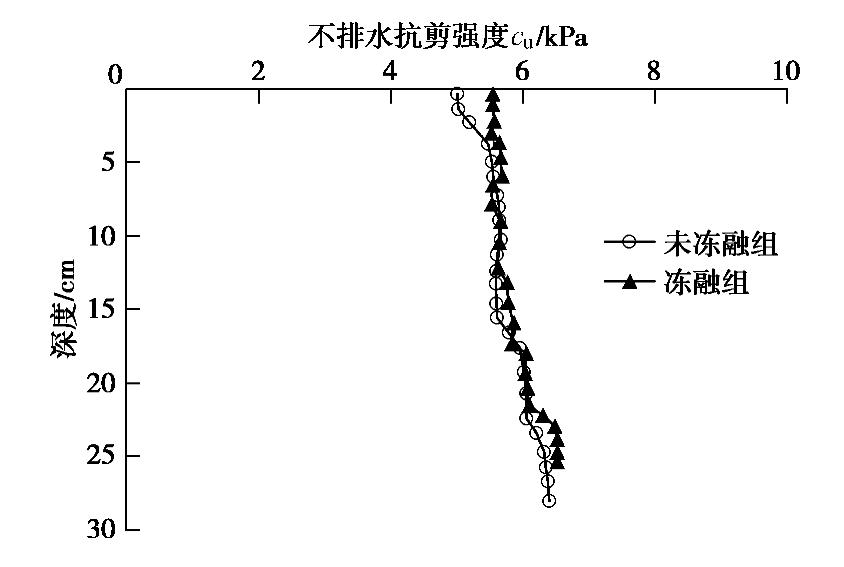
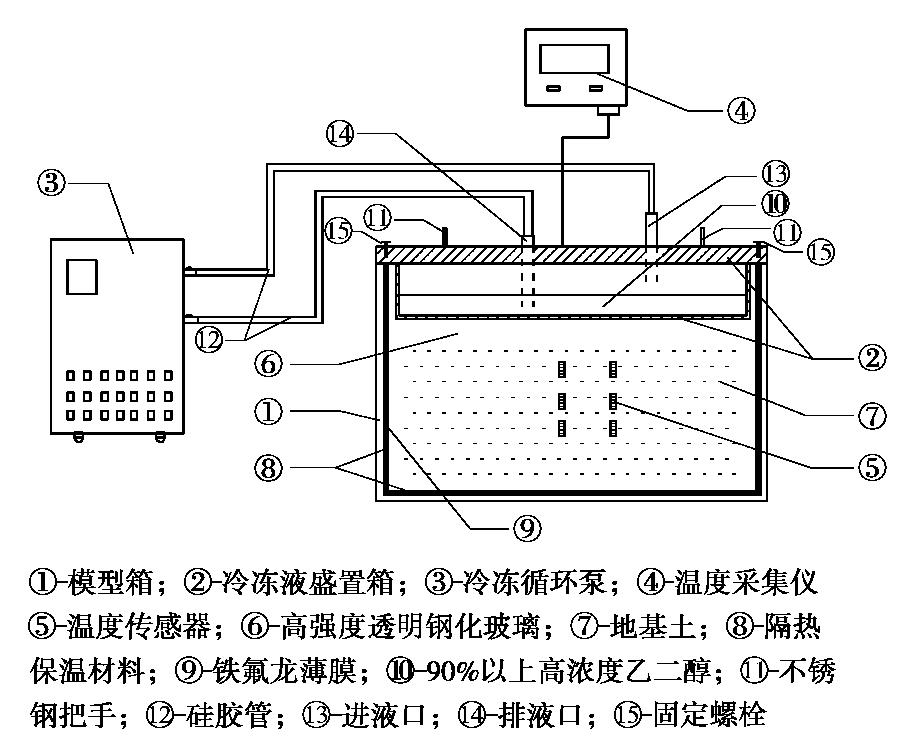
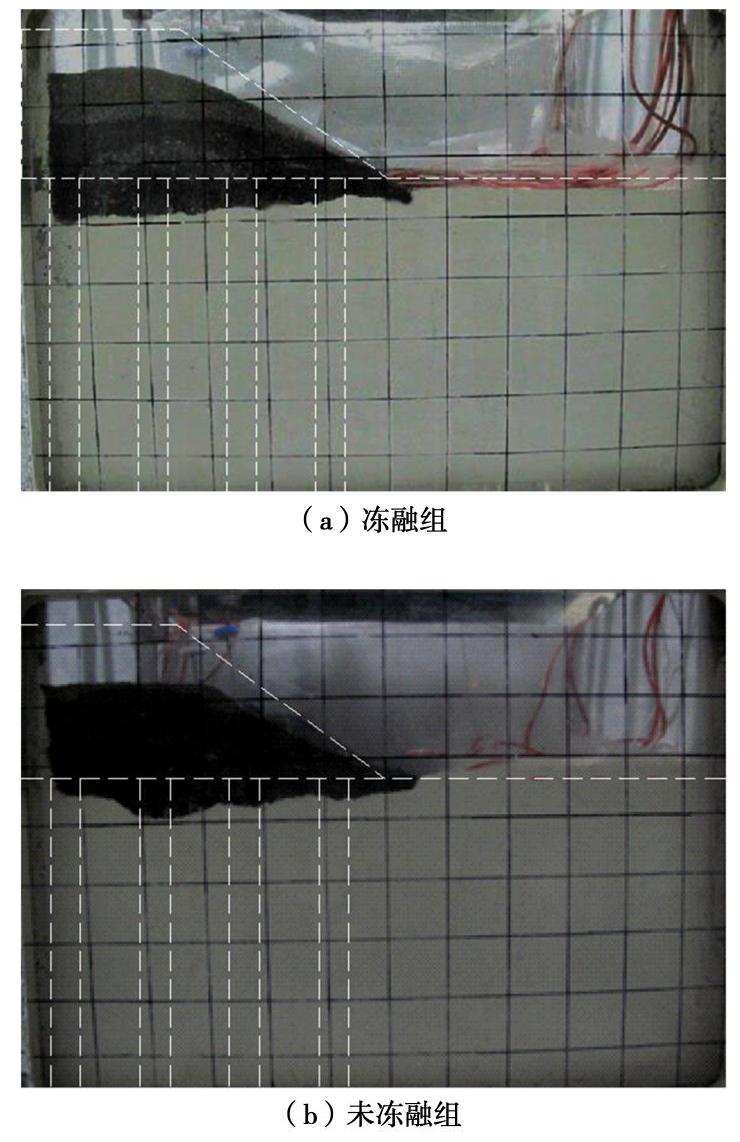
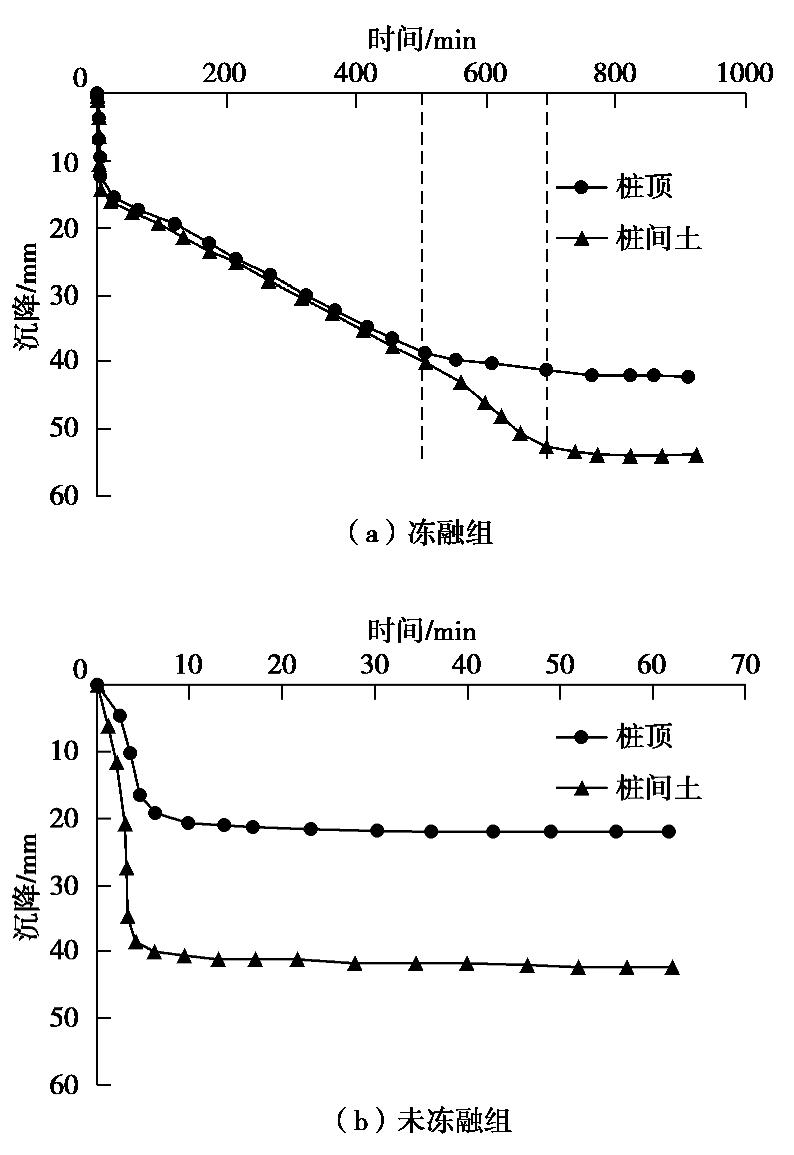
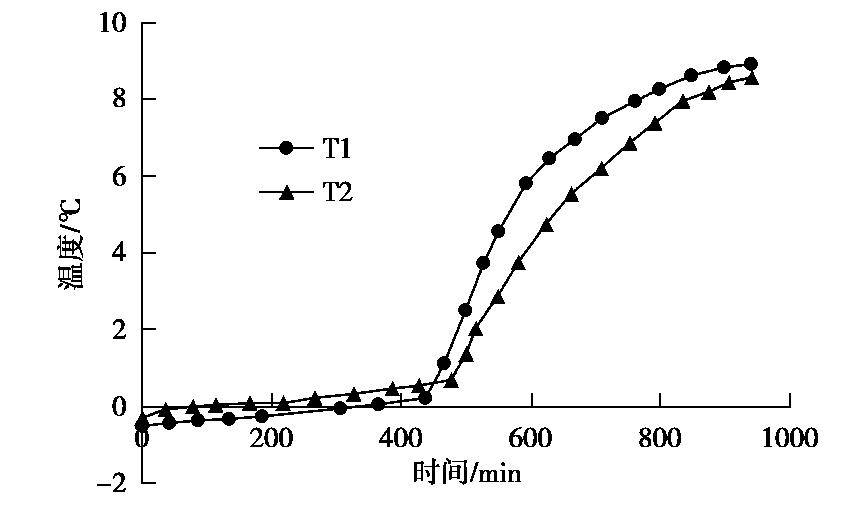
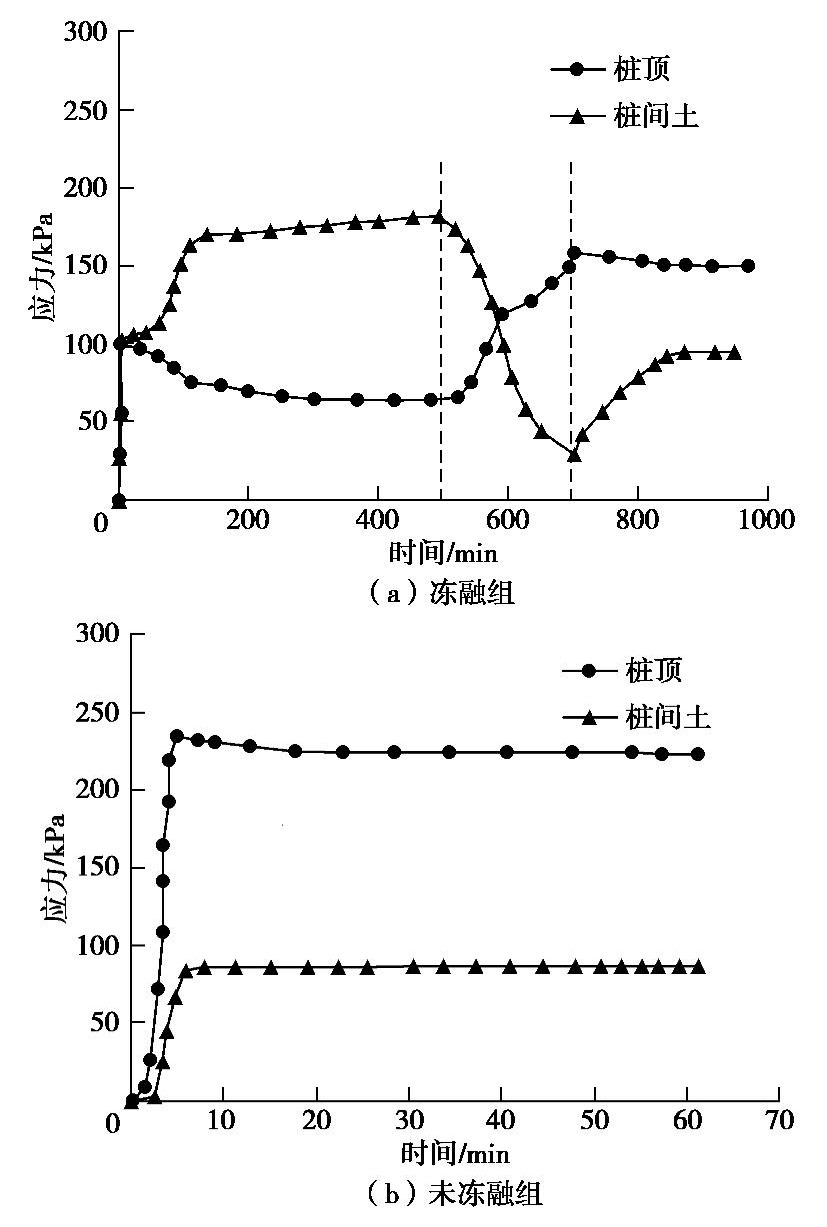
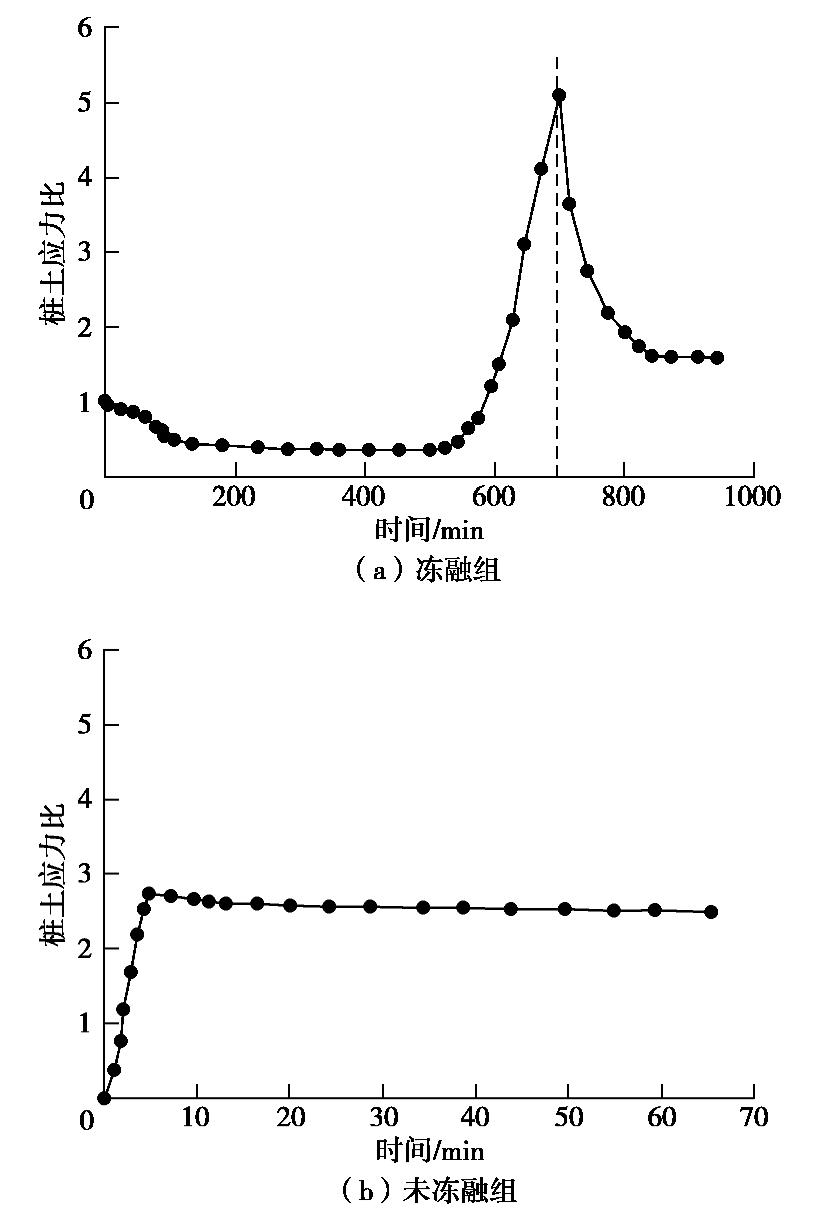
摘要: 制作了一套加筋碎石桩复合地基冷冻试验系统,开展了1组加筋碎石桩复合地基路堤冻融离心模型试验和1组未冻融的对比试验,以研究加筋碎石桩复合地基经历季节性冻土后填筑的路堤在冻融条件下的性状。研究结果表明:冻融条件下加筋碎石桩复合地基在地基土未融化前,其桩顶和桩间土沉降基本一致,而在地基土全部融化后,桩间土沉降显著增大;冻融条件下路堤边坡基本保持初始坡度,路堤下地基沉降比较均匀,而未冻融组路堤边坡明显变缓,路堤下地基不均匀沉降明显;在复合地基和桩体均处于冰冻状态时,其桩顶和桩间土应力一致,当桩体先于桩间土融化后,桩顶应力减小而桩间土应力增大,而当地基土开始全部融化后,桩间土应力快速下降而桩顶应力快速增大,冻融条件下复合地基沉降稳定时的桩土应力比是未冻融条件下桩土应力比的2/3左右;冻融条件下由于路堤加载过程中桩顶周围土体处于冰冻状态,限制了桩顶侧向位移,而冻土层以下土体推动下部桩体向外位移,使得靠近路堤边坡下的桩体向路堤内弯曲,但弯曲变形量较小,而未冻融条件下的桩体则向路堤外弯曲且弯曲变形量较大;加筋碎石桩适合用于季节性冻土区湿地软土地基处理,其复合地基经历季节性冻土后填筑的路堤整体性能较好。Abstract: A set of freezing test system for composite foundation with geosynthetic-encased stone columns (GESCs) is developed. The centrifugal model tests are conducted on an embankment on composite foundation with GESCs under freeze-thaw condition, and the comparative tests under non-freezing condition are also conducted. The behavior of embankment built on composite foundation with GESCs subjected to seasonal freezing is studied under freeze-thaw condition. The results show that under freeze-thaw condition, the consistent settlement is found on the top of the columns and on the soil when the soil and the columns are in the frozen state, while that on the soil increases significantly after complete melting. The embankment slope remains the original slope angle and has relatively uniform settlement under freeze-thaw condition, while the significant decrease in slope angle and differential settlement are observed under non-freezing condition. When the soil and the columns are in the frozen state, the stresses on the top of the columns and on the soil between the columns are consistent. However, columns melt before the soil, the stress on the top of the columns decreases while that on the soil increases. After the soil melts completely, the stress on the soil decreases rapidly while that on the top of the columns increases rapidly. Under the freeze-thaw condition, the stress concentration ratio is relatively small, which is about 2/3 of that under non-freezing condition. Because the soil around the top of the columns is in a frozen state during the embankment loading, the lateral displacement of the top of the columns is restricted. However, the soil below the frozen soil layer pushes the lower part of the columns outward that makes the columns under the embankment slope bend inward, but small bending deformation is observed. Inversely, the columns bend outward under non-freezing condition, and the bending deformation is obvious. The GESCs are suitable for the soft soil foundation treatment of wetlands in the seasonal frozen soil areas, and the overall performance of embankment built on the composite foundation with GESCs subjected to seasonal freezing is satisfactory.
-
-
表 1 桩顶和桩间土沉降
Table 1 Settlements on top of columns and soil
(mm) 试验 桩顶沉降 桩间土沉降 差异沉降 加载期末 休止期末 加载期末 休止期末 加载期末 休止期末 冻融组 12 42 14 54 2 12 未冻融组 19 22 37 42 18 20 -
[1] ALEXIEW D, BROKEMPER D, LOTHSPEICH S. Geotextile encased columns (GEC): load capacity, geotextile selection and pre-design graphs[C]//Proceedings of the Geo-frontiers Conference, 2005, Austin: 497-510.
[2] 陈建峰, 李良勇, 徐超, 等. 路堤荷载下土工织物散体桩复合地基离心模型试验[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2018, 40(5): 932-938. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201805023.htm CHEN Jian-feng, LI Liang-yong, XU Chao, et al. Centrifuge model tests of composite foundation reinforced with geosynthetic-encased stone columns under embankment load[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(5): 932-938. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201805023.htm
[3] LO S R, ZHANG R, MAK J. Geosynthetic-encased stone columns in soft clay: a numerical study[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2010, 28(3): 292-302. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2009.09.015
[4] YOO C. Performance of geosynthetic-encased stone columns in embankment construction: numerical investigation[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2010, 136(8): 1148-1160. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000316
[5] ELSAWY M B D. Behaviour of soft ground improved by conventional and geogrid-encased stone columns, based on FEM study[J]. Geosynthetics International, 2013, 20(4): 276-285. doi: 10.1680/gein.13.00017
[6] RAJESH S, JAIN P. Influence of permeability of soft clay on the efficiency of stone columns and geosynthetic-encased stone columns–a numerical study[J]. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 9(5): 483-493. doi: 10.1179/1939787914Y.0000000088
[7] YOO C. Settlement behavior of embankment on geosynthetic-encased stone column installed soft ground: a numerical investigation[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2015, 43(6): 484-492. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2015.07.014
[8] RAJESH S. Time-dependent behaviour of fully and partially penetrated geosynthetic encased stone columns[J]. Geosynthetics International, 2016, 24(1): 1-12.
[9] MOHAPATRA S R, RAJAGOPAL K. Undrained stability analysis of embankments supported on geosynthetic encased granular columns[J]. Geosynthetics International, 2017, 24(5): 465-479. doi: 10.1680/jgein.17.00015
[10] CHEN J F, LI L Y, XUE J F, et al. Failure mechanism of geosynthetic-encased stone columns in soft soils under embankment[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2015, 43(5): 424-431. doi: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2015.04.016
[11] ALMEIDA M S S, HOSSEINPOUR I, RICCIO M, et al. Behavior of geotextile-encased granular columns supporting test embankment on soft deposit[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2014, 141(3): 04014116.
[12] 赵明华, 顾美湘, 张玲, 等. 竖向土工加筋体对碎石桩承载变形影响的模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(9): 1587-1593. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201409006.htm ZHAO Ming-hua, GU Mei-xiang, ZHANG Ling, et al. Model tests on influence of vertical geosynthetic-encasement on performance of stone columns[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(9): 1587-1593. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201409006.htm
[13] GU M, ZHAO M, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of geogrid encasement on lateral and vertical deformations of stone columns in model tests[J]. Geosynthetics International, 2015, 23(2): 100-112.
[14] 陈建峰, 王波, 魏静, 等. 加筋碎石桩复合地基路堤模型试验[J]. 中国公路学报, 2015, 28(9): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL201509002.htm CHEN Jian-feng, WANG Bo, FENG Shou-zhong, et al. Model tests of embankments on soft foundation reinforced with geosynthetic-encased stone columns[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2015, 28(9): 1-8. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL201509002.htm
[15] FATTAH M Y, ZABAR B S, HASSAN H A. Experimental analysis of embankment on ordinary and encased stone columns[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 16(4): 1-13.
[16] 梁波, 张贵生, 刘德仁. 冻融循环条件下土的融沉性质试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2006, 28(10): 1213-1217. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.10.007 LIANG Bo, ZHANG Gui-sheng, LIU De-ren. Experimental study on thawing subsidence characters of permafrost under frost heaving and thawing circulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2006, 28(10): 1213-1217. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.10.007
[17] 王天亮, 卜建清, 王扬, 等. 多次冻融条件下土体的融沉性质研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(4): 625-632. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201404006.htm WANG Tian-liang, BU Jian-qing, WANG Yang, et al. Thaw subsidence properties of soils under repeated freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(4): 625-632. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201404006.htm
[18] 张玉芝, 杜彦良, 孙宝臣, 等. 季节性冻土地区高速铁路路基冻融变形规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2014, 33(12): 2546-2553. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201412021.htm ZHANG Yu-zhi, DU Yan-liang, SUN Bao-chen, et al. Roadbed deformation of high-speed railway due to freezing-thawing process in seasonally frozen regions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(12): 2546-2553. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201412021.htm
[19] 陈湘生, 濮家骝, 殷昆亭, 等. 地基冻–融循环离心模型试验研究[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2002(4): 531-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHXB200204028.htm CHEN Xiang-sheng, PU Jia-liu, YIN Kun-ting, et al. Centrifuge modelling tests of foundation undergoing two cycles of frost heave and thaw sett lement[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science & Technology), 2002(4): 531-534. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHXB200204028.htm
[20] ZHOU J, TANG Y Q. Centrifuge experimental study of thaw settlement characteristics of mucky clay after artificial ground freezing[J]. Engineering Geology, 2015, 190: 98-108.
[21] 蔡正银, 张晨, 黄英豪. 冻土离心模拟技术研究进展[J]. 水利学报, 2017, 48(4): 398-407. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB201704003.htm CAI Zheng-yin, ZHANG Chen, HUANG Ying-hao. A review on the development of geotechnical centrifuge modeling technique on frozen ground engineering[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2017, 48(4): 398-407. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB201704003.htm
[22] 陈建峰, 柳军修, 马君. 实验室用小型单桥静力触探探头的标定[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 40(4): 549-552, 588. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDZ201204009.htm CHEN Jian-feng, LIU Jun-xiu, MA Jun. Calibration of a mniature cone penetrometer for geotechnicalmodel test[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2012, 40(4): 549-552, 588. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDZ201204009.htm
[23] 陈建峰, 王兴涛, 曾岳, 等. 土工织物散体桩桩体大三轴试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2017, 39(12): 2212-2218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201712011.htm CHEN Jian-feng, WANG Xing-tao, ZENG Yue, et al. Large triaxial compression tests on geosynthetic-encased granular columns[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(12): 2212-2218. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201712011.htm
[24] 王静, 刘寒冰, 吴春利. 冻融循环对不同塑性指数路基土弹性模量的影响研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(12): 3665-3668. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201212023.htm WANG Jing, LIU Han-bing, WU Chun-li. Influence of freeze-thaw cycles on elastic modulus of subgrade soil with different plasticity indices[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(12): 3665-3668. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201212023.htm



 下载:
下载: