Influences of typical inorganic flocculants on flocculation effects of dredging materials and quality of effluent water
-
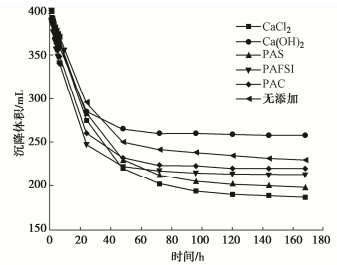
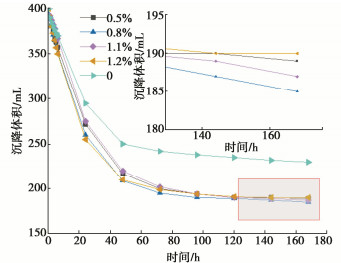
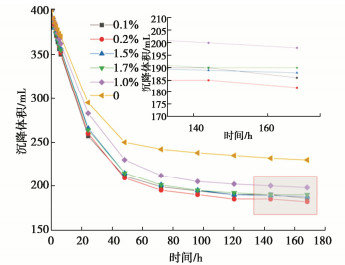
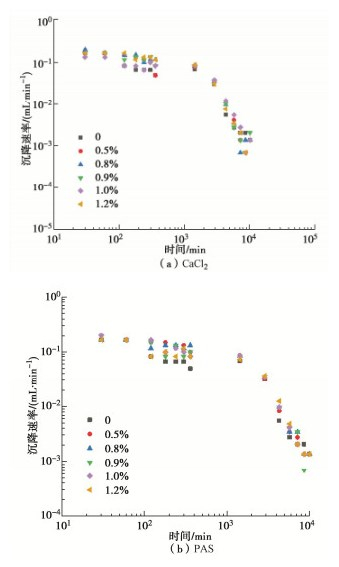
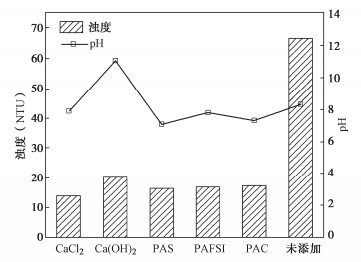
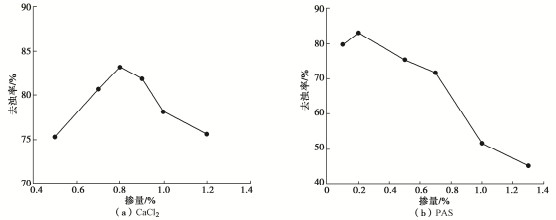
摘要: 针对淤泥堆场堆填处置中,天然底泥自重落淤固结缓慢等问题,工程中常添加化学药剂来加快泥水分离过程。利用量筒沉积柱试验研究了5种典型无机絮凝剂对高含水率疏浚淤泥的絮凝沉积效果及上覆水水质(浊度值)的影响规律。5种典型的无机絮凝剂中,CaCl2,PAS(聚合硫酸铝)的絮凝效果相对较好。在此基础上,探明了这两种絮凝剂在不同掺量下对疏浚淤泥沉积规律的影响。试验结果表明,CaCl2,PAS掺量不同,泥浆自重沉积固结稳定后沉降量、沉降速率、沉积稳定时间不同,得到CaCl2和PAS的最优掺量分别为0.8%,0.2%。在最优掺量下上覆水的去浊率可达到84%左右。CaCl2通过Ca2+的交换作用和电性中和作用发挥絮凝作用;PAS主要通过土颗粒表面的电性中和作用发挥絮凝作用。结果可为大规模疏浚淤泥的快速絮凝和余水排放研究和设计提供参考借鉴。Abstract: In view of the problems such as slow siltation and solidification of natural bottom sludge in the landfill disposal of sludge yards, the chemical agents are often added in the project to speed up the process of sludge-water separation. The influences of five typical inorganic flocculants on the flocculation sedimentation effects of dredged materials with high water content and the quality of overlying water (turbidity) are studied through the measuring cylinder sedimentation tests. Among the five typical inorganic flocculants, CaCl2 and PAS (polyaluminum sulfate) have relatively good flocculation effects. On this basis, the influences of these two flocculants on the sedimentation laws of dredged sludge under different dosages are investigated. The test results show that with different contents of CaCl2 and PAS, the settlement amount, rate and stabilization time of the sludge after self-weight sedimentation and consolidation are different. The optimum contents of CaCl2 and PAS obtained in this study are 0.8% and 0.2%, respectively. Under the optimal dosage, the turbidity removal rate of the overlying water can reach about 84%. CaCl2 plays a role of flocculation through Ca2+ exchange and electrical neutralization; and PAS mainly plays a role of flocculation through electrical neutralization on the surface of soil particles. The results may provide a referencees for the research and design of rapid flocculation and residual water discharge of large-scale dredged materials.
-
Keywords:
- dredged material /
- inorganic flocculant /
- turbidity
-
-
表 1 淤泥的基本物理性质
Table 1 Basic physical properties of dredged materials
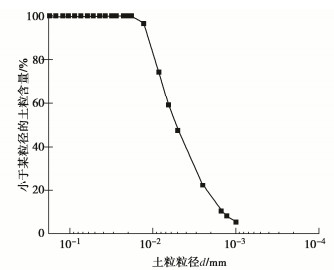
含水率/% 液限/% 塑限/% 塑性指数 黏粒含量①/% 相对质量密度 有机质含量②/% 100.4 55.9 20.6 35.3 28.00 2.72 0.75 注:①粒径小于5 μm;②重铬酸钾容量法。 表 2 量筒沉积试验方案
Table 2 Schemes of measuring cylinder sedimentation tests
加药种类 絮凝剂掺量/% CaCl2 0,0.5,0.8,0.9,1.0,1.2 PAS 0,0.1,0.2,0.5,0.7,1.0 表 3 不同絮凝剂掺量下淤泥自重沉积稳定时间
Table 3 Stabilization time of self-weight sedimentation of sludge under different flocculant dosages
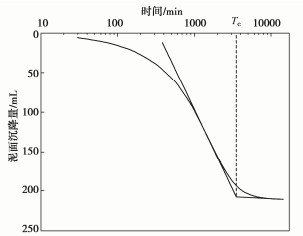
絮凝剂 CaCl2/PAS 掺量/% 0 0.5/0.1 0.8/0.2 0.9/0.5 1.0/0.7 1.2/1.0 Tc/d 3.39 2.63/2.65 2.54/2.58 2.58/2.60 2.77/2.61 2.80/2.63 -
[1] XU G Z, GAO Y F, HONG Z S, et al. Sedimentation behavior of four dredged slurries in China[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2012, 30(2): 143-156.
[2] 朱伟, 闵凡路, 吕一彦, 等. "泥科学与应用技术"的提出及研究进展[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(11): 3041-3054. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201311001.htm ZHU Wei, MIN Fanlu, LÜ Yiyan, et al. Subject of "mud science and application technology"and its research progress[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(11): 3041-3054. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201311001.htm
[3] 黄英豪, 戴济群, 徐锴. 新拌固化淤泥的流动性和黏滞性试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(2): 235-244. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202202004 HUANG Yinghao, DAI Jiqun, XU Kai. Flowability and viscosity of freshly solidified dredged materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(2): 235-244. (in Chinese) doi: 10.11779/CJGE202202004
[4] 苏德纯, 胡育峰, 宋崇渭, 等. 官厅水库坝前疏浚底泥的理化特征和土地利用研究[J]. 环境科学, 2007, 28(6): 1319-1323. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200706027.htm SU Dechun, HU Yufeng, SONG Chongwei, et al. Physicochemical properties of Guanting Reservoir sediment and its land application[J]. Environmental Science, 2007, 28(6): 1319-1323. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ200706027.htm
[5] 金雪林, 薛路阳, 金杰. 生态清淤及淤泥快速处置一体化技术的应用[J]. 人民黄河, 2013, 35(9): 43-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RMHH201309016.htm JIN Xuelin, XUE Luyang, JIN Jie. Application of ecological dredging silt and rapid disposal of the integration technology[J]. Yellow River, 2013, 35(9): 43-45. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RMHH201309016.htm
[6] 李晓威, 吕鹏, 彭万里. 湖泊环保疏浚工程中泥浆絮凝效率的优化研究[J]. 人民黄河, 2016, 38(9): 64-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RMHH201609017.htm LI Xiaowei, LÜ Peng, PENG Wanli. Optimization study on the mud flocculation efficiency in the lake environmental dredging engineering[J]. Yellow River, 2016, 38(9): 64-67. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RMHH201609017.htm
[7] 章荣军, 蒋达飞, 郑俊杰. 絮凝调理对淤泥(浆)固结特性的影响[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(7): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG202107001.htm ZHANG Rongjun, JIANG Dafei, ZHENG Junjie. Effect of flocculation conditioning on consolidation characteristics of mud(slurry)[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(7): 1-6. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG202107001.htm
[8] 袁国辉, 胡秀青, 刘飞禹, 等. 絮凝-逐级加压电渗法改良疏浚淤泥试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(增刊1): 2995-3003. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2020S1040.htm YUAN Guohui, HU Xiuqing, LIU Feiyu, et al. Experimental study on the improvement of dredged slurry by flocculation-step-by-step loading voltage electro-osmosis method[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(S1): 2995-3003. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2020S1040.htm
[9] 刘飞禹, 吴文清, 海钧, 等. 絮凝剂对电渗处理河道疏浚淤泥的影响[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(2): 56-63, 72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL202002005.htm LIU Feiyu, WU Wenqing, HAI Jun, et al. Effect of flocculants on electro-osmotic treatment of river dredged sludge[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(2): 56-63, 72. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGGL202002005.htm
[10] IMAI G. Experimental studies on sedimentation mechanism and sediment formation of clay materials[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1981, 21(1): 7-20.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 陈祎,刘明昊,赵智慧. 钻孔灌注桩废弃泥浆快速絮凝脱水技术与机理研究. 建筑施工. 2025(01): 6-11 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 原媛,刘丝丝,崔勇涛,赖智龙,廖德祥. 生物酶用于河湖底泥脱水减量调理的对比研究. 水资源与水工程学报. 2025(01): 154-162 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 孙万吉,陈建,梁志学,李朝阳,赵永享. 碱渣-矿渣-水玻璃对流态固化土的影响研究. 中国新技术新产品. 2024(19): 116-118+140 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 唐伟超,赵东平,王风,朱龙,汤青山,和琦. 砂卵土-泥岩复合地层土压平衡盾构渣土脱水试验. 现代隧道技术. 2024(S1): 684-693 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张达志. 基桩施工产生的废弃泥浆絮凝脱水后的土体工程性质研究. 四川水力发电. 2024(S2): 29-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: