Experimental study on electrokinetic remediation of cadmium-contaminated clayey soil
-
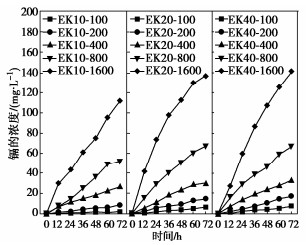
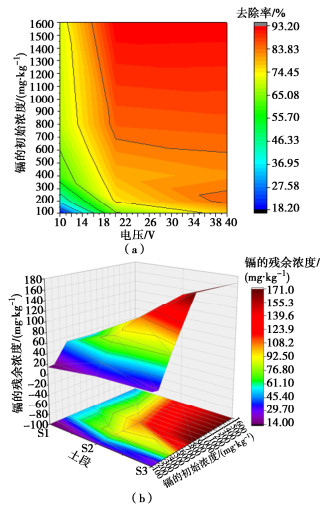
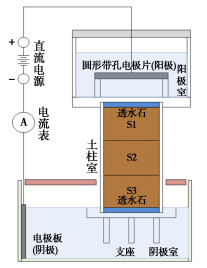
摘要: 使用自行设计电动修复装置,针对镉污染黏性土开展了室内土柱试验,分析了土柱中镉的去除效果、修复前后污染土的微观结构变化和镉的形态特征,探究了土壤中镉的去除机制。结果表明:镉初始浓度较小时,增大电压可以显著提高镉的去除率,电压的增大可加快土中不稳定形态镉的迁移。当镉初始浓度较大时,残余在土柱中的镉含量呈现出从阳极侧到阴极侧逐渐增大的现象。经过电动修复后,土颗粒从球形呈现的黏聚体结构变为了光滑、松散的结构。电压为40V时,约95%的弱酸提取态及可还原态镉从土壤中去除,修复后土柱中的残渣态等稳定形态的镉约为总镉的60%,有效降低了镉污染土的毒性。Abstract: A self-designed electrokinetic remediation device is used to carry out the soil column tests on cadmium- contaminated clayey soil. The removal mechanism of cadmium in soil is explored by analyzing the removal effects of cadmium in a soil column, the microstructural change of contaminated soil before and after remediation and the species analysis of cadmium. The results show that when the initial concentration of cadmium is relatively small, the removal rate of cadmium increases remarkably when increasing the voltage, since the unstable cadmium migrates faster at greater voltage. When the initial concentration of cadmium is relatively great, the residual content of cadmium exhibits a gradual increase trend from the anode to cathode. After the electrokinetic remediation, the appearance of soil particles changes from a spherical cohesive structure to a smooth and loose one. When the voltage is 40 V, about 95 % of the weak acid extractable and reducible cadmium is removed from the soil, and the residual cadmium in the soil column after remediation is about 60 % of the total cadmium, which effectively reduces the toxicity of the cadmium-contaminated soil.
-
Keywords:
- electrokinetic remediation /
- cadmium /
- contaminated clayey soil
-
-
-
[1] YAO W K, CAI Z P, SUN S Y, et al. Electrokinetic-enhanced remediation of actual arsenic-contaminated soils with approaching cathode and Fe0 permeable reactive barrier[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2020, 20(3): 1526-1533. doi: 10.1007/s11368-019-02459-4
[2] BARSOVA N, YAKIMENKO O, TOLPESHTA I, et al. Current state and dynamics of heavy metal soil pollution in Russian Federation: a review[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 249: 200-207. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.020
[3] ACAR Y B, GALE R J, ALSHAWABKEH A N, et al. Electrokinetic remediation: basics and technology status[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1995, 40(2): 117-137. doi: 10.1016/0304-3894(94)00066-P
[4] GOMES H I, DIAS-FERREIRA C, RIBEIRO A B. Electrokinetic remediation of organochlorines in soil: enhancement techniques and integration with other remediation technologies[J]. Chemosphere, 2012, 87(10): 1077-1090. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.02.037
[5] 付志平, 冼子良, 雷畅, 等. 三种连续提取法对矿区土壤和尾砂中Pb形态分析研究[J]. 广东化工, 2022, 49(6): 80-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDHG202206018.htm FU Zhiping, XIAN Ziliang, LEI Chang, et al. Speciation analysis of Pb in soils and tailings surrounding mine area by three sequential extraction procedures[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2022, 49(6): 80-83. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDHG202206018.htm
[6] 薛浩, 孟凡生, 王业耀, 等. 酸化-电动强化修复铬渣场地污染土壤[J]. 环境科学研究, 2015, 28(8): 1317-1323. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX201508021.htm XUE Hao, MENG Fansheng, WANG Yeyao, et al. Remediation of chromium residue-contaminated soil by preacidification electrokinetic remediation[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 28(8): 1317-1323. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX201508021.htm
[7] 李亚林, 刘蕾, 倪明, 等. 电动修复法对土壤中镉的去除及形态转化研究[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2016, 42(7): 76-79, 90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYAF201607023.htm LI Yalin, LIU Lei, NI Ming, et al. Study on cadmium removal and speciation transformation from soil by electrokinetic remediation[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2016, 42(7): 76-79, 90. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYAF201607023.htm
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 裘友强,张留俊,刘洋,刘军勇,尹利华. “双碳”背景下公路软土地基处理技术研究进展. 水利水电技术(中英文). 2025(01): 113-131 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: