Measurement and analysis of environmental vibration caused by maglev train
-
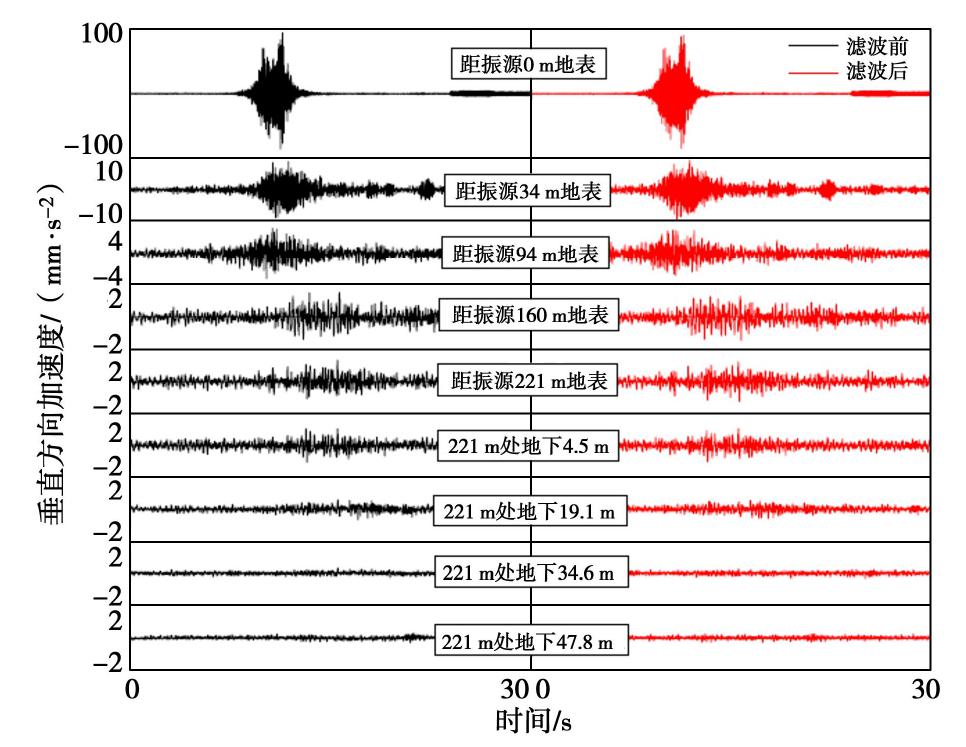
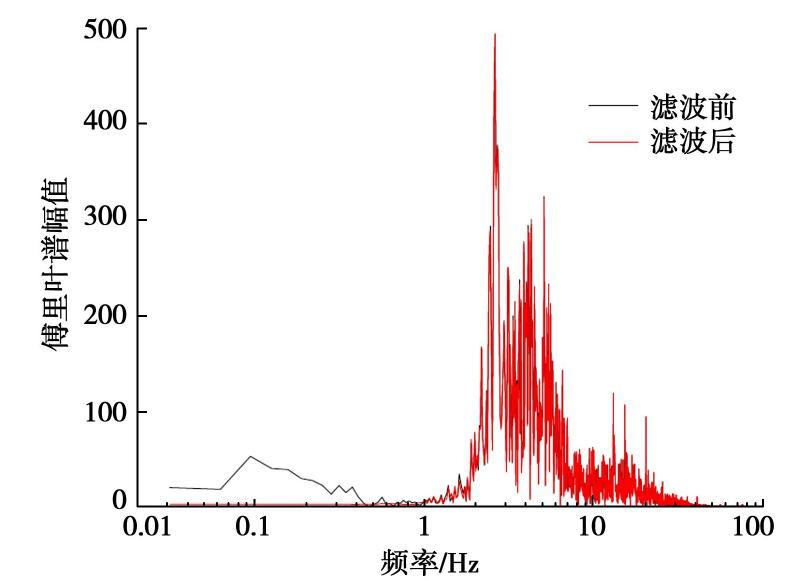
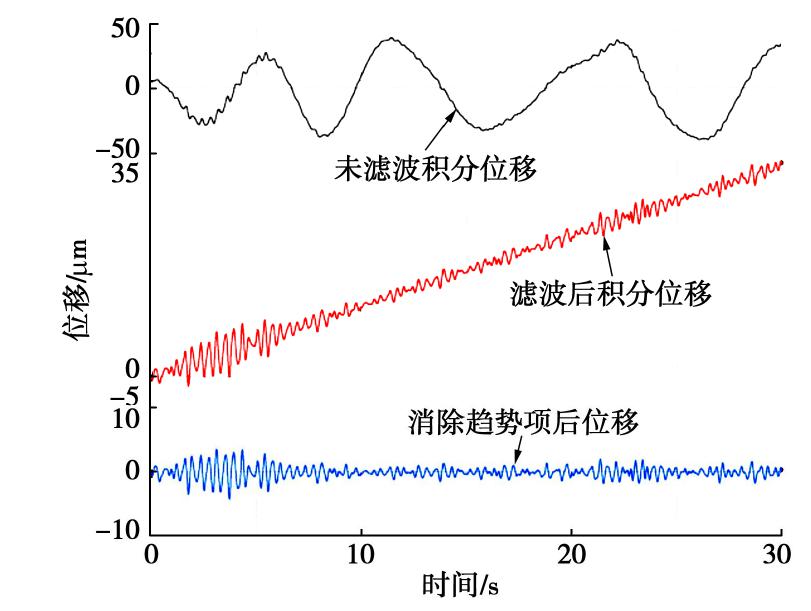
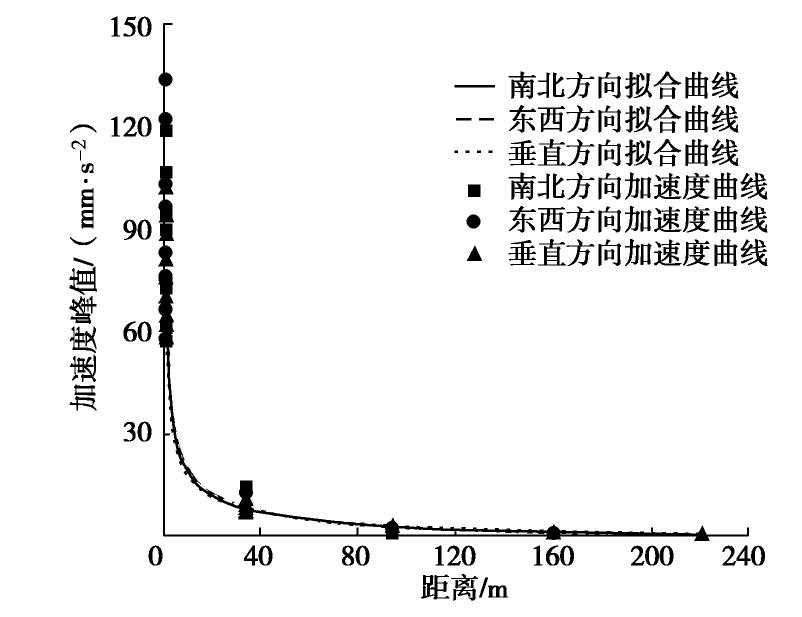
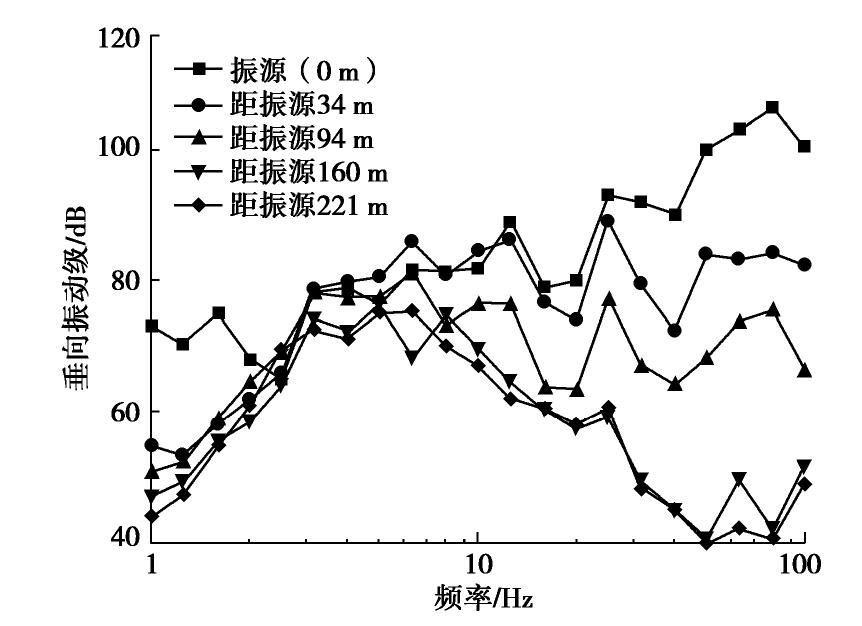
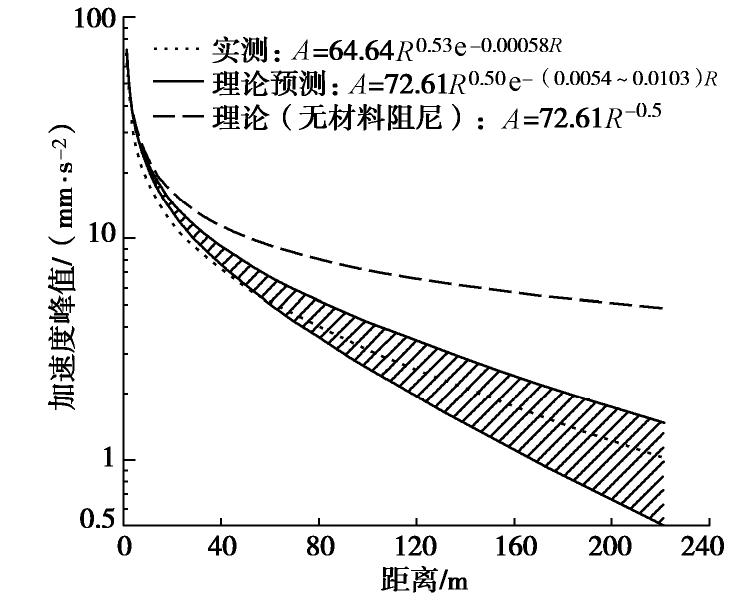
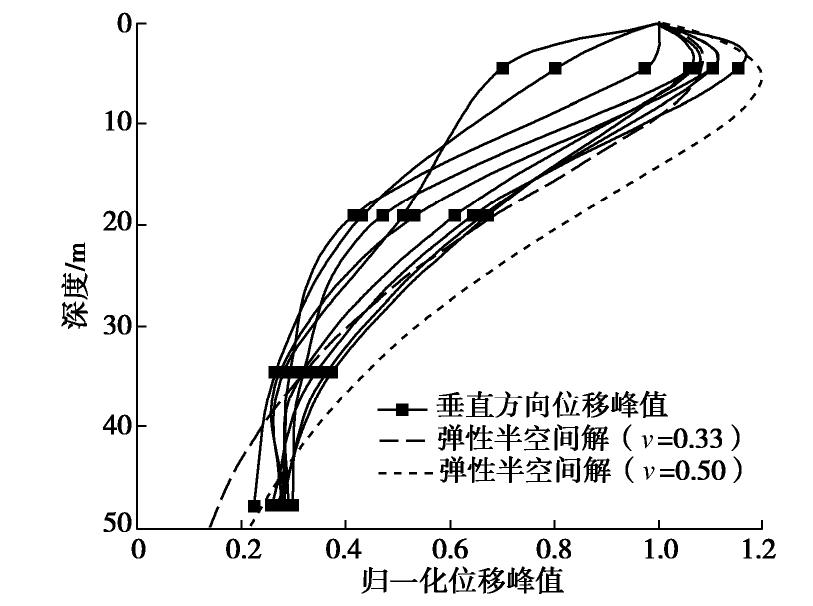
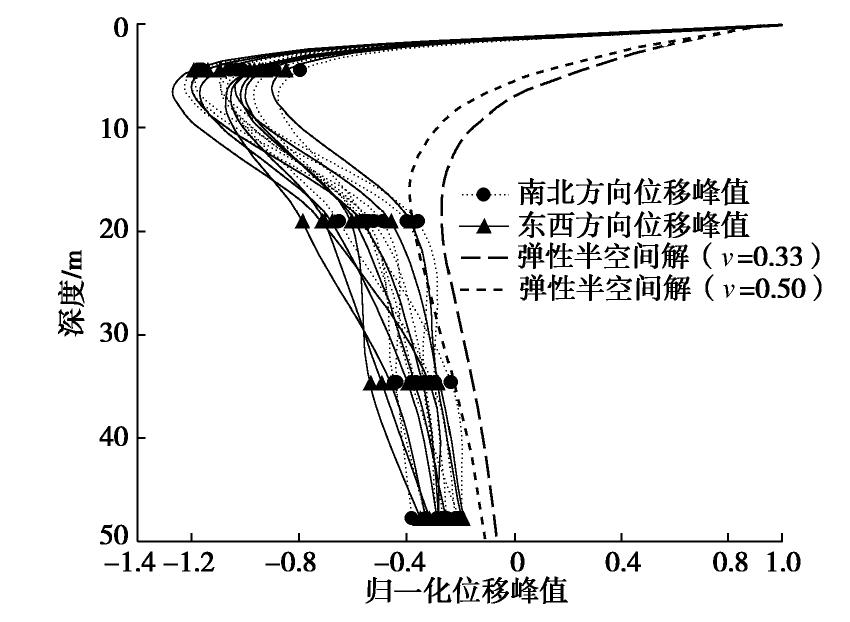
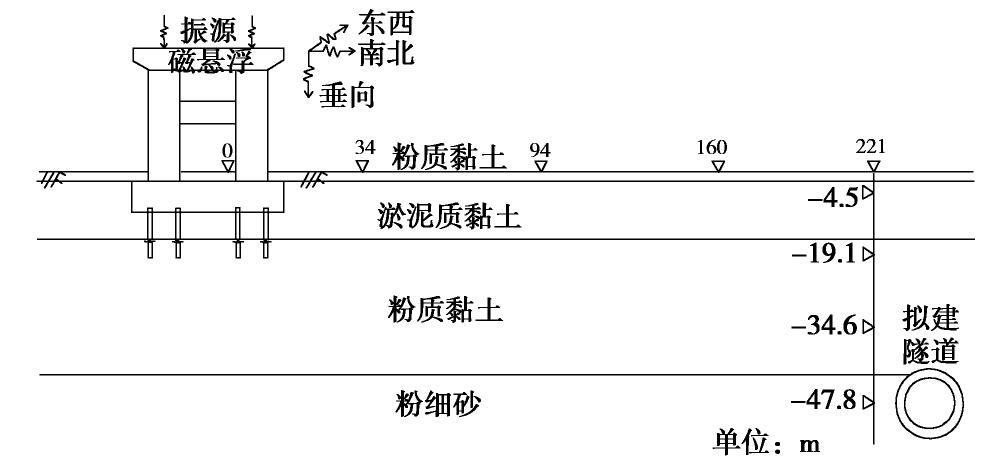
摘要: 对上海磁悬浮列车引起的场地环境微振动进行了现场实测,分析研究了磁悬浮列车运行引起的振动随距离和深度变化的规律。研究结果表明:实测磁悬浮列车引起的环境振动随距离的增加而减小,其远场土层优势频率为3~6 Hz。Bornitz的理论预测公式可较为准确的预测磁悬浮列车振动随距离的变化,但在近场区域会有2~8 mm/s2的高估,土体材料阻尼在环境振动衰减中会发挥一定的作用;磁悬浮列车引起的远场振动在地下5 m处存在放大区,而对于位移振幅随深度的变化,弹性半空间解析解会低估其振动量级。Abstract: Through the in-situ measurement of the environmental vibration caused by the maglev train in Shanghai, the decay of the vibration with distance and depth is analyzed. The results show that the vibration caused by maglev train decreases with distance, and the dominant frequency of far-field vibration is 3~6 Hz. The material damping of soil plays a certain role in the vibration decay and it cannot be ignored, especially in the far field. The Bornitz’s theoretical prediction formula can accurately predict the vibration with distance in general, although there is an overestimation of 2~8 mm/s2 in the near-field region. The vibration in far-field at the depth of 5 m is amplified compared to that of the ground. Regarding the vibration amplitude along the depth, the elastic analytical solution may underestimate the actual vibration.
-
Keywords:
- environmental vibration /
- maglev train /
- vibration decay /
- Rayleigh wave /
- material damping
-
-
表 1 不同振源位置及类型的辐射阻尼系数值
Table 1 Values of attenuation coefficient due to radiation damping for various combinations of source location and type
振源位置 振源类型 波的类型 n 地表 点振源 体波 2.0 地表 点振源 面波 0.5 地表 线振源 体波 1.0 地表 线振源 面波 0.0 地下 点振源 体波 1.0 地下 线振源 体波 0.5 -
[1] LAMB H. On the propagation of tremors over the surface of an elastic solid[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, 1904, A203: 1-42.
[2] DEGRANDE G. Wave propagation in the soil: theoretical background and application to traffic induced vibrations[C]//Structural Dynamics: EURODYN: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Structural Dynamics, 2002, Munich, Germany: 5-27.
[3] MA Q, ZHOU F. Ground vibration generated by an underground moving load[J]. Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, 2018, 55(4): 258-264. doi: 10.1007/s11204-018-9534-0
[4] 蒋通, 张昕. 高架轨道交通引起环境振动实测与数值模拟[J]. 同济大学学报, 2004, 32(5): 565-569. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2004.05.002 JIANG Tong, ZHANG Xin. Measurement and numerical simulation of environmental vibration caused by elevated rail transit[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 2004, 32(5): 565-569. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2004.05.002
[5] XIA H, ZHANG N, CAO Y M. Experimental study of train-induced vibration of environment and buildings[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2005, 280: 1017-1029. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2004.01.006
[6] REN X W, WU J F, TANG Y Q, et al. Propagation and attenuation characteristics of the vibration in soft soil foundations induced by high-speed trains[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2019, 117: 374-383. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.11.004
[7] XIA H, CAO Y M, DE Roeck G. Theoretical modeling and characteristic analysis of moving-train induced ground vibrations[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2010, 329(7): 819-832. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2009.10.007
[8] YANG Y B. Ground vibration induced by high-speed trains over viaducts[C]//ISEV2003. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2003: 147-157.
[9] 陈锋, 黄茂松, 竹宫宏和. 公路高架桥交通引起的地面振动:分析和验证[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2008, 30(1): 86-92. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2008.01.013 CHEN Feng, HUANG Mao-song, TAKEMIYA Hirokazu. Ground vibration caused by traffic of highway viaduct: analysis and verification[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2008, 30(1): 86-92. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2008.01.013
[10] 宋丽, 李中亮, 薛莲, 等. 上海光源实验大厅地基振动规律及相干性分析[J]. 噪声与振动控制, 2016, 36(5): 108-111. SONG Li, LI Zhong-liang, XUE Lian, et al. Analysis of ground vibration law and coherence of the experimental hall of Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2016, 36(5): 108-111. (in Chinese)
[11] 黄茂松, 任青, 周仁义, 等. 层状地基中瑞利波随深度的衰减特性[J]. 岩土力学, 2009, 30(1): 113-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.01.018 HUANG Mao-song, REN Qing, ZHOU Ren-yi, et al. Attenuation characters of Rayleigh wave in layered soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(1): 113-122. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.01.018
[12] KIM D S, LEE J S. Source and attenuation characteristics of various ground vibrations[J]. Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering and Soil Dynamics III. ASCE, Geotechnical Special Publication, 1998, 75(2): 1507-1517.
[13] ATHANASOPOULOS G A, PELEKIS P C. Effect of soil stiffness in the attenuation of Rayleigh-wave motions from field measurements[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2000, 19: 277-288. doi: 10.1016/S0267-7261(00)00009-9
[14] YANG X J. Evaluation of man-made ground vibrations[C]//Proceedings: Third International Conference on Recent Advances in Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering and Soil Dynamics, 1995, St. Louis.
[15] WOODS R D. Screening of surface waves in soil[J]. J Soil Mech Found Div ASCE, 1968, 4: 951-979.
[16] LYSMER J, WAAS G. Shear waves in plane infinite structures[J]. J Eng Mech Div ASCE, 1972, 98(EMI): 85-105.



 下载:
下载: